LONDON: The Arab world is mourning the death of Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II of Great Britain, an unwavering friend of the region and its people throughout the seven decades of her reign.
Only three months ago, Her Majesty celebrated her platinum jubilee, marking the 70th anniversary of her accession to the throne.
In June, Saudi Arabia’s King Salman and Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman wished her “sincere felicitations and best health and happiness,” as they joined other heads of state from across the region in sending messages of congratulations on the occasion of her jubilee.
Now, they have the sad task of sending their sincerest condolences to the British royal family and the people of the UK.
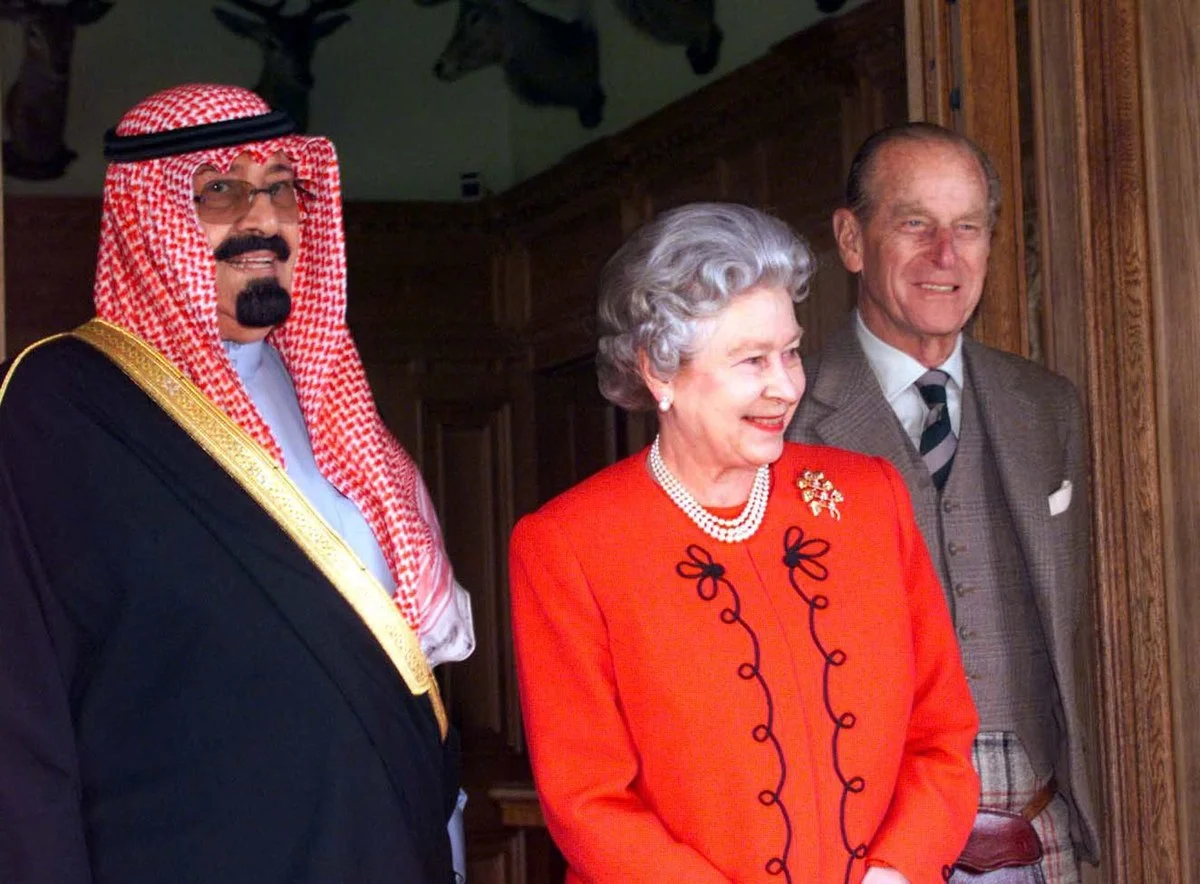

King Abdullah with the Queen and The Duke of Edinburgh durng the visit of the Saudi king. (AFP/File Photo)
For many of the ruling families throughout the Middle East, the death of the Queen marks not only the passing of a fellow monarch but also a friend, and a sad end to a history of friendship that dates back to the earliest days of her reign.
That reign began on Feb. 6, 1952, the day her father, King George VI, died at Sandringham House in Norfolk while the 25-year-old Elizabeth and her husband, Philip, the Duke of Edinburgh, were in Kenya during a tour of Africa.
Having left England as a princess, the king’s daughter flew home in mourning as Queen Elizabeth II. Her coronation took place in Westminster Abbey on June 2 the following year, 1953.
Among the guests at the ceremony were members of four royal families from the Gulf: The rulers, or their representatives, of what were then the British protectorates of Bahrain, Kuwait and Qatar, and Prince Fahd bin Abdulaziz Al-Saud, representing the 78-year-old King Abdulaziz, Saudi Arabia’s founder and first king, who had only five months left to live.
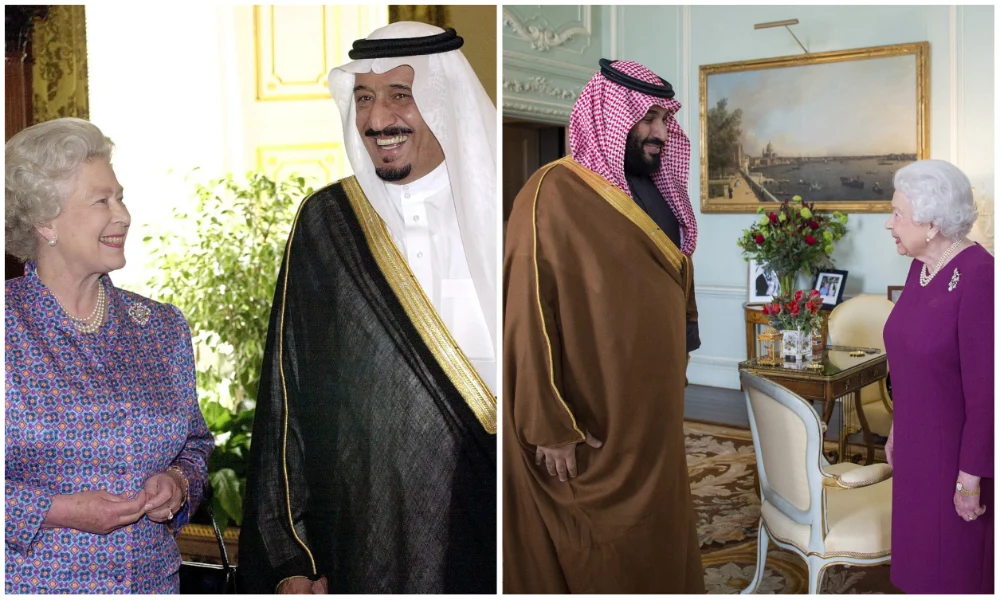

The Queen meeting with King Salman and Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman. (AFP/File Photos)
The bonds between the British and Saudi monarchies cannot be measured by the frequency of formal occasions alone, although an examination of the history of state visits hosted by Buckingham Palace reveals an illuminating distinction.
During the Queen's reign there were no fewer than four official visits to Britain by Saudi heads of state — a number equaled by only four other countries in the world, including the UK’s near-neighbors, France and Germany.
The first Saudi monarch to travel to London was King Faisal, who was greeted with all the pomp and ceremony of a full British state welcome at the start of his eight-day visit in May 1967.
Met by Her Majesty, other members of the British royal family and leading politicians, including Prime Minister Harold Wilson, the king rode to Buckingham Palace with the Queen and the Duke of Edinburgh in an open, horse-drawn state carriage that trundled through London streets lined with cheering crowds.
During a busy schedule, the king found time to visit and pray at London’s Islamic Cultural Centre. His son, Prince Bandar, who that year graduated from the Royal Air Force College Cranwell, in Lincolnshire, deputized for his father during a visit to inspect English Electric Lightning fighter jets being readied for shipment to Saudi Arabia.
The prince would later fly those Lightning fighter jets as a pilot in the Royal Saudi Air Force.
King Faisal’s successors followed in his footsteps with their own state visits to the UK: King Khalid in 1981, King Fahd in 1987 and King Abdullah in 2007.
Other monarchs from the region also paid formal visits to the Queen over the years. The first was King Faisal II, the last king of Iraq, who visited Britain in July 1956. Two years later, he and his wife and other members of the royal family were assassinated during the coup d’etat that established Iraq as a republic.
In 1966, Her Majesty hosted King Hussein of Jordan and his British-born wife, Toni Avril Gardiner, who upon her marriage changed her name to Princess Muna Al-Hussein.
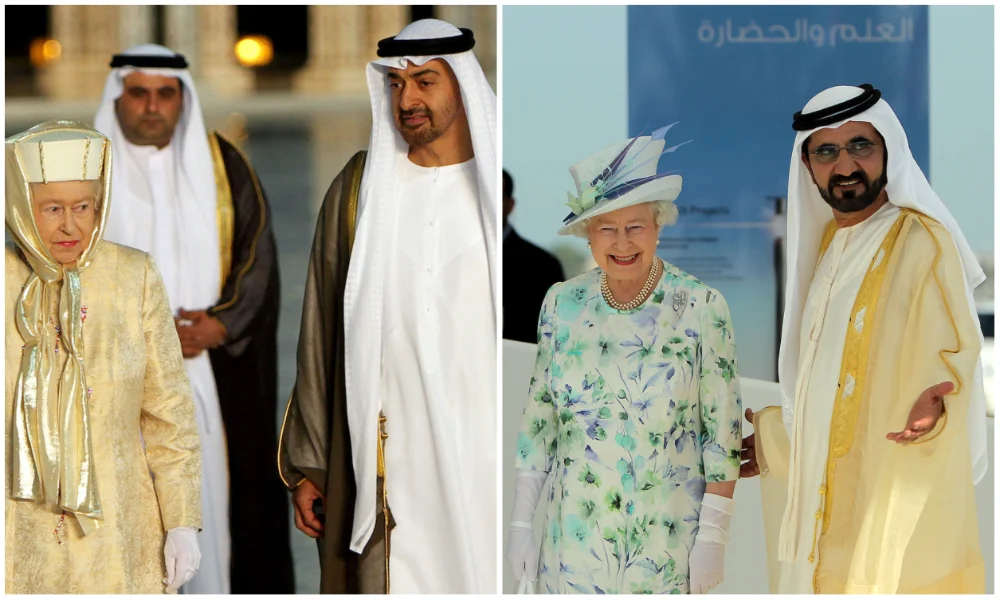

Britain's Queen Elizabeth II with then-Abu Dhabi Crown Prince Sheikh Mohammed bin Zayed Al-Nahyan, and meets with UAE vice president and Ruler of Dubai Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid Al-Maktoum. (AFP/File Photos)
Other state visits followed from the heads of state of Oman, Bahrain, Qatar, the UAE, Egypt and Kuwait.
The Queen, meanwhile, visited the Middle East on several occasions. In February 1979, she flew to the region on the supersonic jet Concorde and visited Riyadh and Dhahran during a Gulf tour that also took her to Kuwait, Bahrain, Qatar, the UAE and Oman.
In Saudi Arabia she was hosted by King Khalid and enjoyed a series of events including a desert picnic and a state dinner at Maathar Palace in Riyadh. In return, the Queen and Prince Philip hosted a dinner for the Saudi royal family on board Her Majesty’s Yacht Britannia.
Poignantly, Britannia would return to the Gulf only one more time, in January 1997 during its final tour before the yacht was decommissioned in December that year.
In 2010, the Queen returned to the region to meet Sheikh Khalifa, ruler of the UAE, and Sultan Qaboos of Oman.
However, the relationships between the British royal family and its counterparts in the Gulf have not been limited to great, formal occasions of state. Analysis of the regular Court Circular published by Buckingham Palace reveals that members of the royal family met Gulf monarchs or members of their families more than 200 times between 2011 and 2021 alone. Forty of these informal meetings were with members of the House of Saud.
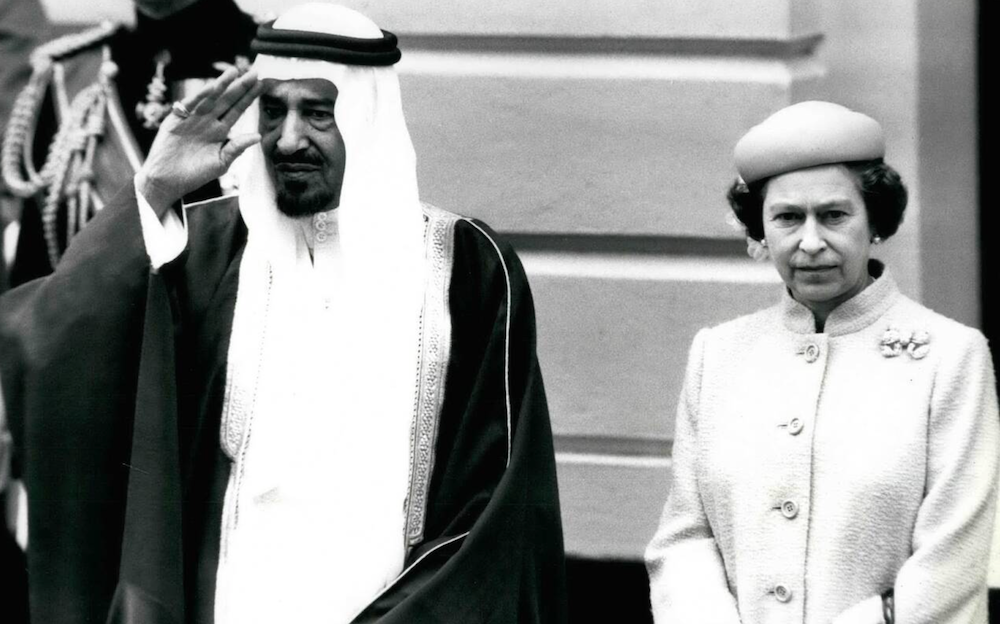

King Khalid of Saudia Arabia welcomed at Victoria Station by Queen Elizabeth in 1981. (Alamy)
The frequency of these meetings with heads of state from the Middle East, equivalent to almost one a fortnight, serve as evidence of the strong bonds of friendship that existed between Her Majesty and the region.
One such meeting took place in March 2018, when Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman had a private audience and lunch with the queen at Buckingham Palace. Later, he dined with the Prince of Wales and the Duke of Cambridge at Clarence House, during a visit to the UK that included meetings with the then British Prime Minister Theresa May and her foreign secretary, Boris Johnson.
Serious matters, such as trade and defense agreements, are often the topics of discussion during such meetings. But good-natured fun, rather than rigid formality, has been the hallmark of private gatherings between the royal families, as Sir Sherard Cowper-Coles, the British ambassador to Saudi Arabia from 2003 to 2006, would later recall.
In 2003, for example, Crown Prince Abdullah, Saudi Arabia’s future king, was a guest of the Queen at Balmoral Castle, her estate in Scotland. It was the prince’s first visit to Balmoral and, happily accepting an invitation for a tour of the large estate, he climbed into the passenger seat of a Land Rover, only to discover that his driver and guide was none other than the Queen herself.
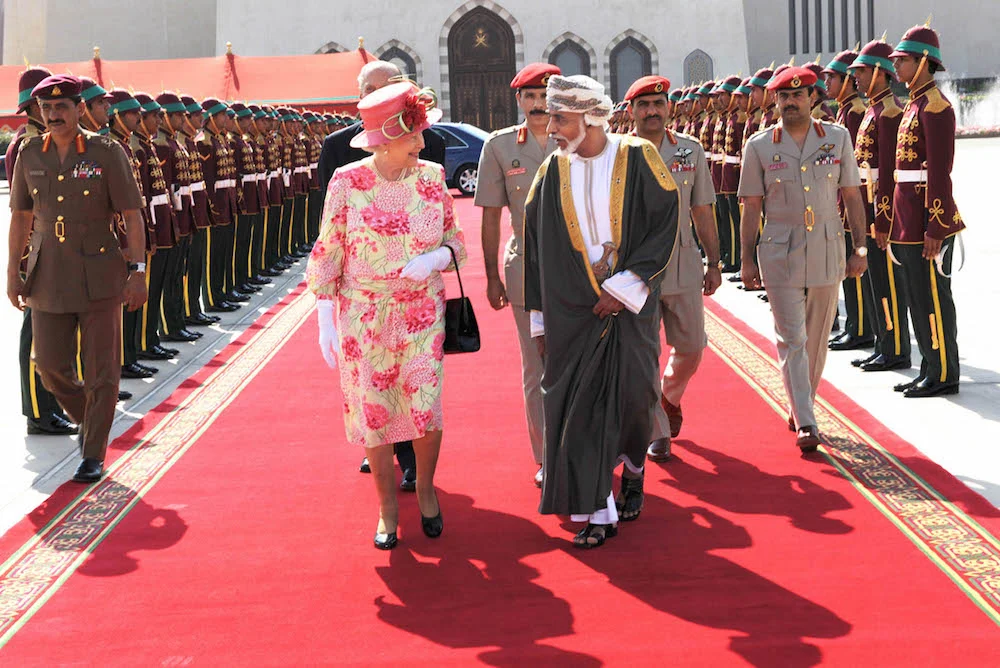

In 2010, the Queen returned to the region and met with Sultan Qaboos of Oman. (AFP)
Her Majesty, who served during the Second World War as an army driver, always drove herself at Balmoral, where the locals were used to seeing her out and about behind the wheel of one of her beloved Land Rovers. She was also known for having great fun, at the expense of her guests, as she hurtled along narrow country lanes and across the estate’s rugged terrain.
According to Sir Sherard’s account, Prince Abdullah took the impromptu roller coaster ride well — although at one point, “through his interpreter,” the crown prince felt obliged to “implore the Queen to slow down and concentrate on the road ahead.”
Aside from the commonality of their royal status, the Queen and the monarchs of the Gulf bonded over their mutual love of horses, a shared interest that dated back to at least 1937 when Elizabeth was an 11-year-old princess.
To mark the occasion of the coronation of her father that year, King Abdulaziz of Saudi Arabia, presented King George VI with an Arabian mare. A life-size bronze statue of the horse, Turfa, was unveiled in 2020 at the Arabian Horse Museum in Diriyah. At the time, Richard Oppenheim, then the UK’s deputy ambassador to the Kingdom, told how the two royal families have always shared this common interest.
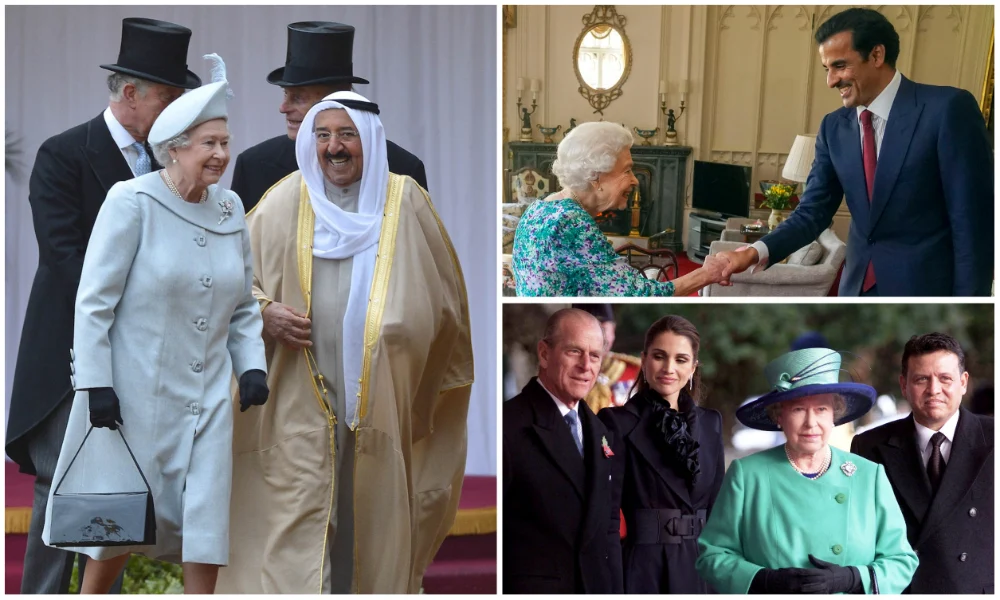

Clockwise from Left: Queen Elizabeth with Emir of Kuwait, Sheikh Sabah Al-Ahmad Al-Sabah; meeting Qatari Emir Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al-Thani; with the King Abdullah II and Queen Rania of Jordan. (AFP/File Photos)
“The Queen has many horses, and King Salman and the Saudi royal family also have a long-held love of horses,” he said.
The Queen also shared this appreciation of horses with Sheikh Mohammed Al-Maktoum, the ruler of Dubai and vice-president of the UAE, who owns the internationally renowned Godolphin horse-racing stables and stud in Newmarket, the home of British horse racing.
The two were often seen together at great events on the horse-racing calendar, such as the annual five-day Royal Ascot meeting, regarded as the jewel in the crown of the British social season. Team Godolphin has had several winners at Royal Ascot, and the Queen’s horses have won more than 70 races there since her coronation.
This year, 10 of the Queen’s horses ran at Ascot. However, suffering increasingly with mobility problems, she did not attend the event. It was the first time she had missed it in her 70-year reign.
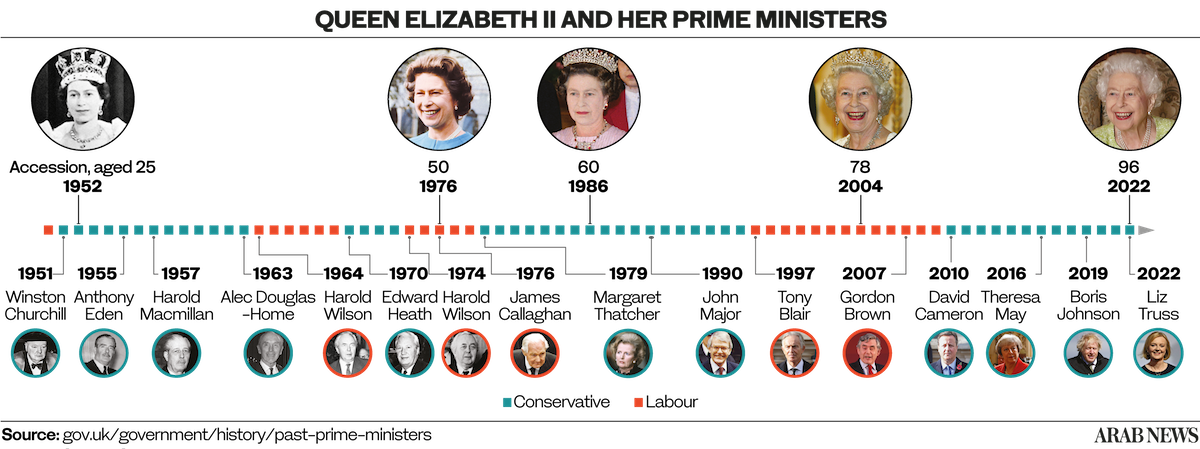
No fewer than 16 British prime ministers served under the Queen. When she ascended the throne in 1952, Winston Churchill, the revered wartime leader, was prime minister. His successor, Anthony Eden, appointed by the Queen in 1955, was the first of 15 who would receive her official blessing at Buckingham Palace.
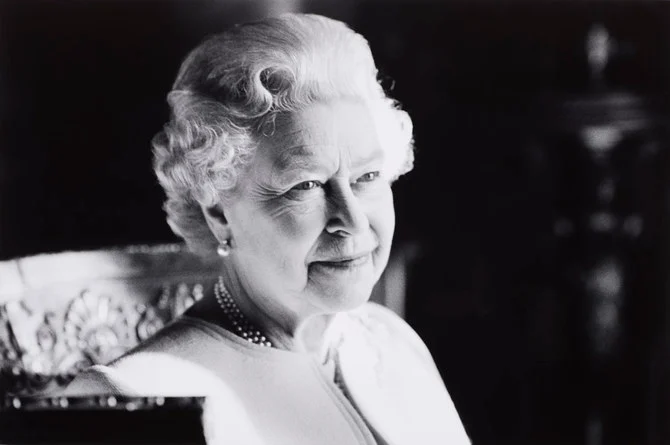

Queen Elizabeth - 1926-2022. (Supplied/Royal Family)
The Queen broke with this tradition only once, and only at the very end of her reign. Increasingly frail, she was advised by her doctors not to travel to London from her Scottish home, Balmoral, and so it was there, on Tuesday this week, that she met Liz Truss, the newly appointed leader of the Conservative party, and asked her to form a government.
It was to be the final formal duty of her long reign.
During the jubilee weekend in June, flags flew from homes and public buildings across the UK and the wider Commonwealth of 150 million people, thousands of street parties were held, beacons were lit across the country and British voices everywhere sang the national anthem.
Today, as the flags fly at half-mast and the royal baton is passed to the Queen’s eldest son, Charles, the British people, after 70 years of singing the words “God Save The Queen,” must now learn to once again sing “God Save The King.”
On her 21st birthday, in a speech broadcast on the radio from Cape Town while she was still Princess Elizabeth, the future Queen made a solemn pledge.
“I declare before you all,” she said, “that my whole life, whether it be long or short, shall be devoted to your service.”
Her life, thankfully, was long. Her devotion to her duty was complete.

























