IRBIL, IRAQI KURDISTAN: It is seven years since their yellow flag first appeared in the campaign against Daesh, the extremist group which seized swathes of northern Iraq and eastern Syria. After Daesh captured large parts of northern Iraq, including Mosul, in 2014, the fighters of Al-Hashd Al-Shaabi, or Popular Mobilization Forces, won the admiration of many Iraqis for heeding Grand Ayatollah Ali Al-Sistani’s call to arms.
Since then, the umbrella organization of mainly Shiite militias has, however, adopted a more sinister cause. Last month, a convoy of Hashd fighters mounted a show of strength in Baghdad’s Green Zone, the center of Iraq’s political life, and forced the country’s elected leaders to release Qassim Musleh, a Hashd commander close to Iran who had been arrested in the western Anbar province.
Musleh has a reputation as a brutal operator. In late 2019, thousands of mainly young Iraqis took to the center of Baghdad to protest against systemic corruption and Iran’s influence over their country’s affairs.
After days of protests, snipers believed to be from Hashd units took to nearby rooftops and killed dozens of people. Musleh and his Iranian sponsors are thought to have been instrumental in ordering the killings. His recent arrest was in connection with the May 9 murder of Ihab Al-Wazni, a prominent activist in the southern shrine city of Karbala.
“Many Iraqi activists have been speaking out against Iran-backed militias’ ability to operate outside the boundaries of the law, and it makes sense that the militias would then seek to silence anyone working to constrain their positions of power,” Emily Hawthorne, a Middle East and North Africa analyst for Strator — a RANE Company, told Arab News.
Kyle Orton, an independent Middle East researcher, believes Iranian-controlled militias in Iraq were behind the worst atrocities against anti-corruption protesters. “The Hashd is fairly clearly more powerful than the Iraqi security forces, both in its ability to control the social and street-level space, and the political sphere, with its control of key ministries and its effective veto-wielding bloc in parliament,” he told Arab News.
The Hashd was first formed in June 2014 to defend Iraq against Daesh after that group conquered Mosul.
In 2018, about 30 militias under the Al-Hashd-Al-Shaabi umbrella were formally included in — and paid by — the Iraqi security forces. It has a significant presence in the Iraq parliament through the Fateh coalition, which has more than 40 seats in the 329-seat assembly.
On the ground, Hashd units have repeatedly targeted Ain Al-Asad airbase in Anbar and even Irbil International Airport in Iraqi Kurdistan, both of which host US troops and personnel. The US embassy in Baghdad’s Green Zone has also been repeatedly targeted.
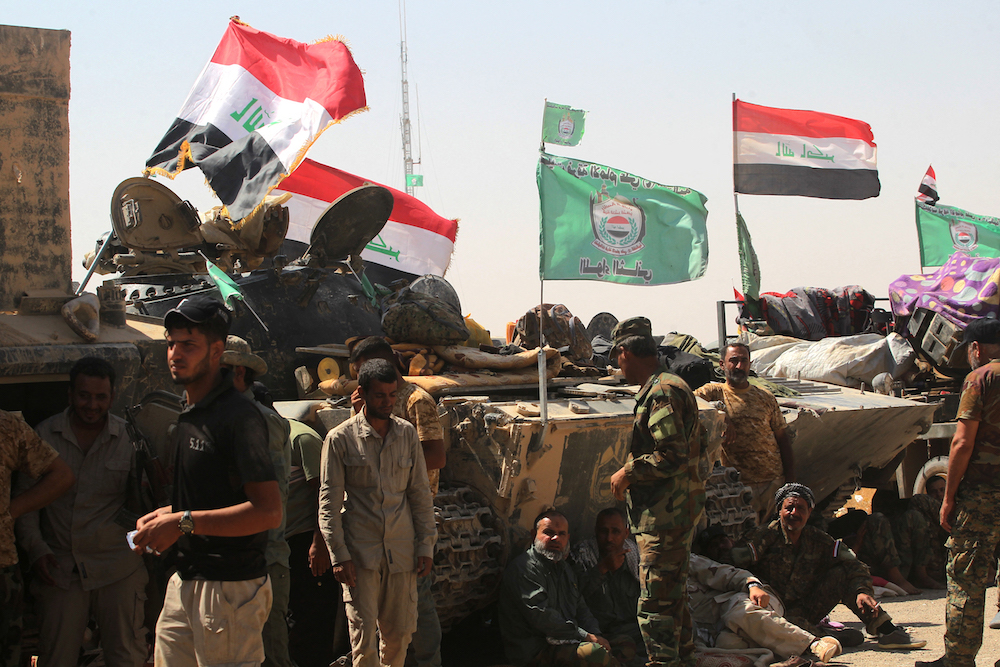

Al-Hashd Al-Shaabi fighters gather around the Tal Afar airport, west of Mosul, as they and Iraqi forces backed by local militia and a US-led coalition advanced in driving Daesh from the city in August 2017. (AFP/File)
While most of these attacks were with short-range rockets, the more recent ones have been carried out using explosive-laden attack drones, underscoring the evolving capabilities of such groups.
“The motivations for these operations are a confluence of issues,” Joel Wing, author of the “Musings on Iraq” blog, told Arab News. “Both the Hashd brigades and Iran want the US military out of Iraq. It would be a great victory for them if that happened.”
For Iran, proxy attacks by Iraqi militias are a way for it “to pressure the US over its (Iran’s) nuclear program and sanctions.”
The array of units under the Hashd umbrella is bewildering. There are militias loyal to Al-Sistani, widely viewed as a figure of moderation and an opponent of overseas interference in Iraq. There are even tribal defense units, the so-called Sunni Hashd.
These groups exist to make the organization seem more diverse and legitimate, both domestically and internationally. “The reality is this is a ‘popular front’ tactic. All these groups are dependent and subordinate to Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC),” Orton said.
Behind an elaborate facade of names and acronyms, Iran is sponsoring an array of more effective paramilitary groups, according to the analysts. “The most powerful brigades within the Hashd are all pro-Iran,” Wing said, identifying them as the Badr Organization, Asaib Ahl Al-Haq and Kataib Hezbollah.
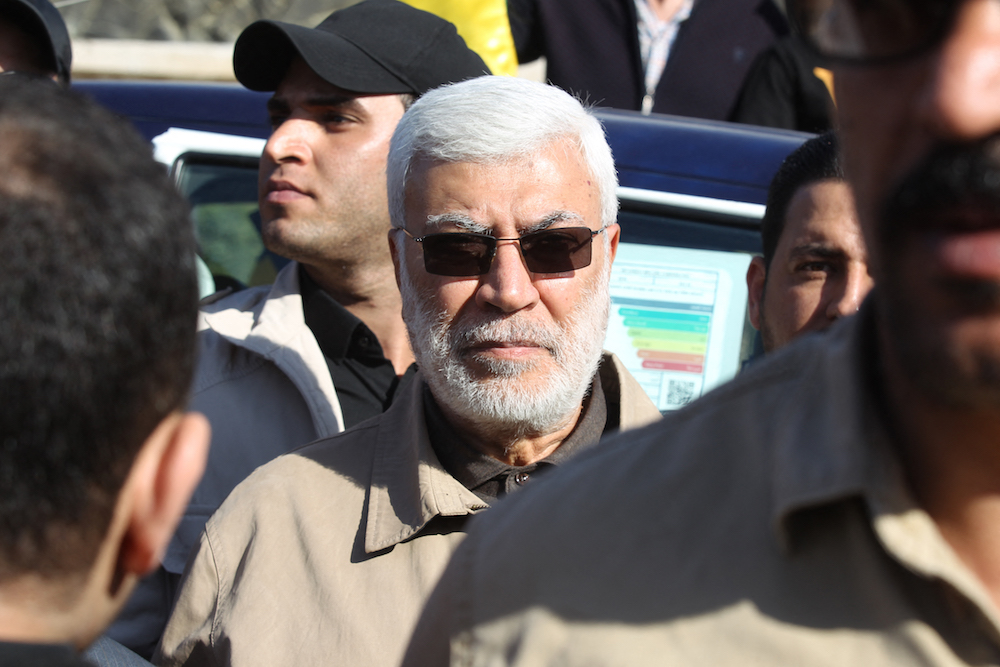

Abu Mahdi Al-Muhandis, head of the Kataib Hezbollah, was killed beside Iranian commander Qassem Soleimani at Baghdad’s international airport. (AFP/File)
Iranian policy in Iraq has, however, had its share of setbacks. In January 2020, the US killed Qassem Soleimani, the head of the Quds Force, the IRGC’s overseas arm, in a drone strike. Soleimani was the architect of Iranian policy in Iraq and elsewhere across the Middle East, from Lebanon to Syria and Yemen.
Tellingly, Abu Mahdi Al-Muhandis, head of the Kataib Hezbollah, was killed beside Soleimani as they were being driven from Baghdad’s international airport.
In May, Reuters reported that Iran had changed its strategy vis-a-vis its militia proxies. Instead of relying on the larger established groups, Tehran has started to form small elite groups that are more loyal and better trained to do its bidding in the region.
“This shift in strategy grants both Iran and established groups like Kataib Hezbollah plausible deniability whenever a smaller, likely linked group conducts an attack. It is indicative of a desire to protect the political position in Baghdad that a well-known group like Kataib Hezbollah enjoys,” Hawthorne, the Stratfor analyst, told Arab News.
Both Wing and Orton believe that the shift to smaller units masks a commitment to continued domination via plausible deniability. “Today, it’s unclear whether Iran is attempting to regain control of these factions or simply backing all the new front groups that Hashd brigades have created, to deny responsibility for attacks upon US targets in Iraq,” Wing said.
Soleimani’s death may well have caused Iran’s different power centers to experiment with divergent interests and objectives. The power centers range from the Quds Force, which organizes and trains Tehran’s proxy militias across the Middle East, to the Iranian foreign ministry.
“It has been reported that they don’t all agree on how to use their Iraqi allies,” Wing told Arab News. “The Hashd brigades were also competing with each other for a period to try to show which one was the leader of the resistance within Iraq, and the attacks were part of that.”
Orton sees Iran as adopting the same model in Iraq as it did in Lebanon in the 1980s, when it split Hezbollah from Amal, previously the dominant Shiite militia in the country. “The use of ‘new’ pseudo-groups or fronts, where they exist — some are entirely imaginary, existing solely online to claim recent attacks — is just the latest iteration of this effort to embed the Islamic Revolution in local conditions.”
That effort appears to be back on track following Soleimani’s killing. Hashd seems to be succeeding in spreading its control over broad areas of the northern Middle East. Musleh, the man at the center of the latest clashes between the militia and central government in Baghdad, is head of the Hashd in Anbar, traditionally a Sunni stronghold.
Hashd fighters have taken part in battles in neighboring Syria to help Iran prop up the Assad regime in Damascus. Hashd groups also proved instrumental in Iran’s ability to move weapons overland across Iraq into Syria.
Groups such as Kataib Hezbollah control important border points with Syria in both Anbar and Nineveh in northern Iraq, in addition to their own smuggling routes. “They are able to move men and material back and forth at will,” Wing told Arab News, referring to the paramilitary forces.
That said, Iran has been forced to change tactics in response to risks from the Israeli Air Force. Instead of shipping missiles through Iraq to its militia proxies in Syria, it has begun delivering smaller pieces of equipment along with advisers. These are much less detectable.
Given all that it has invested in these networks, the analysts are skeptical that Iran will relinquish control over them, even if it means a comprehensive nuclear deal with the US and Western powers that includes extensive sanctions relief for its economy.
“Iran will never ‘cut off’ any of the Iraqi militias, Hezbollah or the Houthis, because it cannot; they are integral, organic parts of the revolution,” Orton told Arab News.
“Any proposal in the nuclear negotiations for Iran to in some way trade its ‘proxies’ is a non-starter as such.”
____________
• Twitter: @pauliddon

































