MAKKAH: On behalf of King Salman, Makkah Gov. Prince Khalid Al-Faisal on Wednesday handed over the Kaaba Kiswa (black cloth) to the senior caretaker of the Kaaba, Saleh bin Zain Al-Abidin Al-Shaibi.
The Kiswa will be replaced on the ninth day of the month of Dul Hijjah, following in the footsteps of the Prophet Muhammad and his companions.
It was reported that after the conquest of Makkah in the ninth Hijri year, the Prophet covered the Kaaba in Yemeni clothes as he performed his farewell pilgrimage.
The Kiswa is replaced once a year during Hajj after the pilgrims go to Mount Arafat, in preparation for receiving worshippers the next morning, which coincides with Eid Al-Adha.
Meanwhile, the General Presidency for the Affairs of the Two Holy Mosques has lifted the lower part of the Kiswa by about 3 meters and covered the raised area with white cotton fabric (approximately two meters in width from the four sides).
The move was designed as a precaution to maintain the cleanliness and safety of the Kiswa and prevent tampering with it.
The colors of the Kaaba’s coverings have seen regular changes through the ages.

The General Presidency for the Affairs of the Two Holy Mosques has lifted the lower part of the Kiswa by about 3 meters and covered the raised area with white cotton fabric (approximately two meters in width from the four sides). (SPA)
The Prophet Muhammad covered it with white-and-red striped Yemeni cloth, and Abu Bakr Al-Siddiq, Umar ibn Al-Khattab, and Uthman ibn Affan covered it with white. Ibn Al-Zubayr covered it with red brocade.
During the Abbasid era, it was draped once with white and once in red, while the Seljuk Sultan covered it with yellow brocade. The Abbasid Caliph Al-Nassir changed the Kiswa’s color to green and later to black brocade, and this has remained its color to the present day.
Dr. Fawaz Al-Dahas, director of the Center of Makkah History, told Arab News: “The Kaaba was covered once in white, once in red, and once in black, and the choice of color was based on the financial means in every era.”
Qubati fabric was brought from Egypt and was one of the best types of fabric used to cover the Kaaba. The Yemeni Kiswa was also a quality cloth and most famous at the time.
On why the colors changed over the ages, Al-Dahas said that white was the brightest color, but it was not durable. It often became torn, dirty, and impure as pilgrims touched it and because it was not practical or long-lasting it was replaced with black-and-white brocade and shimla, which was used for covering Arab tents.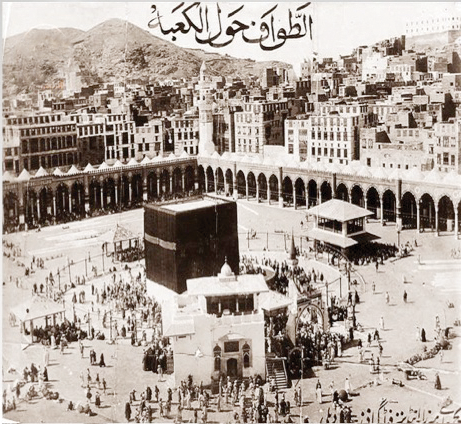
“The varying financial means controlled the type of fabric used for the Kaaba’s Kiswa,” Al-Dahas added.
He noted that the way humans perceived the Kiswa evolved after that, and it was replaced with a red brocade and qubati Egyptian cloth. Also, an antaa, which is a rug of leather, or a musouh, a collection of rough clothes, would be added to it.
“The Kiswa used to get changed from time to time whenever the fabric was available. This has been the case in the eras of the Rashidun Caliphate, the Umayyads, and the Abbasids,” he said.
Black was finally chosen at the end of the Abbasid era because it was durable and could withstand being touched by visitors, pilgrims, and people from different cultures from around the world.
With the continuation of the Umrah season, Al-Dahas said that the Kiswa was lifted to the middle of the Kaaba to preserve it and to prevent people from touching it.
History books speak of the first man to cover the Kaaba in pre-Islamic times, Tubbaa Al-Humairi, the king of Yemen. They mention that he covered the Kaaba in pre-Islamic times after he visited Makkah and entered it obediently.
Historians specialized in the Kaaba’s history mention in some accounts that Al-Humairi covered the Kaaba with a thick cloth called khasf and later with Maafir, which is originally named after an ancient city in Yemen where Maafir cloth was made. He then covered it with milaa, a soft, thin one-piece cloth known as rabitah. After that, he covered the Kaaba with wasael, a red-striped Yemeni cloth.
Al-Humairi’s successors used leather and qubati coverings with many others in the pre-Islamic era covering the Kaaba and considering it a religious duty and great honor.
Some accounts point out that the Kiswa at the time was layered on the Kaaba, and when it became heavy or worn out, it was removed or divided.
Historians confirm in an account that the Prophet was the first in Islam to cover the Kaaba with qubati, which is a thin white cloth made in Egypt and named after the Copts.
The accounts mention that in the conquest of Makkah, the Prophet kept the old Kiswa used in the era of the polytheists and did not replace it until a woman burned it while trying to scent it with incense. It was then covered with a Yemeni cloth.
Muslim kings and sultans then continued to undertake covering the Kaaba and caring for it.
During the Saudi era, the Kiswa has received great attention. The Islamic state that existed in Egypt at the time continued to send the Kiswa for centuries.
The Saudi founder King Abdul Aziz gave directions for the establishment of a private house for making the Kiswa in Ajyad neighborhood close to Makkah’s Grand Mosque, the first house dedicated to weaving the Kiswa in the Hijaz since the Kaaba was covered in the pre-Islamic era until the present era.
It was the factory where the first Kiswa in the Saudi era was manufactured in Makkah. Production was later moved to Umm Al-Joud. The new location was equipped with the latest advanced machines in the weaving industry at the time and continued to produce Kiswas that surpassed all previous ones.
A royal decree was issued by King Salman to change the name of the Kaaba Kiswa factory to the King Abdul Aziz Complex for the Kaaba’s Kiswa.
The desalination department is the first of the complex’s sections. It is responsible for the purity of water, which reflects on the quality and texture of silk, and the desalination of groundwater for washing and dyeing silk.
The dyeing process starts after the removal of the waxy layer coating the silk threads. The silk is then dyed in black and green using hot tubs and special chemicals mixed and weighted in specific rations to ensure the required degree of color stability.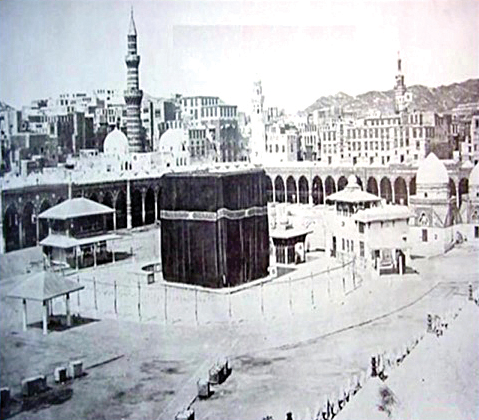
The cotton lining of the Kiswa is also washed and the silk is then dyed with black for the outer drape and with green for the inner one, as is the case for the covering of the Prophet’s chamber. Every Kiswa requires 670 kg of natural silk.
Various tests are carried out on silk and cotton threads to ensure their conformity to required standards in terms of the strength of silk threads and their resistance to erosion and climatic conditions. Tests on the silver-coated threads are also conducted to ensure their suitability and high quality.
With regard to machine textile manufacturing, the complex is equipped with advanced Jacquard machines, which create woven Qur’anic verses and produce black silk engraved with verses and prayers as well as plain silk made for printing verses and silver-thread and gold-plated embroidery. These machines use 9,986 threads per meter to weave the Kiswa in record time.
In the printing department, the process of placing the first drawing starts from printing the Qur’anic verses and Islamic motifs on the Kaaba’s belt. The section also prepares the manasij, two sides made of solid wood, and white raw fabric is pulled between them. The plain silk is then placed on top and the belt of the Kiswa is printed on it before the Kaaba’s door and the embroidery are added. Workers use silkscreen printing for the Qur’anic verses with white and yellow ink.
The belt department takes care of embroidering the gold, silver, and motifs. This process is carried out by placing cotton threads of different densities over the threads and the motifs printed on the black fabric. Technicians then begin making the necessary stitches of fillings and domes using silver wire coated with gold.
Sixteen pieces are produced for the Kaaba’s belt with Qur’anic verses written on them; six pieces of different sizes under the belt; four firm pieces for the Kaaba’s corners; 12 lamps below the belt; five pieces above the corner of the Black Stone, and the outside curtain of the Kaaba’s door.




























