LONDON: “A force capable of overthrowing the regime is lurking in the heart of Iranian cities. From all indications, the ruling theocracy is at the point of being overthrown,” the leader of the global Iranian resistance declared to an audience of thousands tuning in to the online Free Iran Global Summit on July 17.
Five years ago, this declaration might have sounded like empty rhetoric from a fringe group. Now, two years after Tehran’s failed attempt at bombing the National Council of Resistance of Iran’s (NCRI) annual rally in Paris, the words of Maryam Rajavi, a former militant commander and now the NCRI’s president-elect, look much less like an empty threat and much more like a promise.
The NCRI is an umbrella group encompassing a broad spectrum of groups opposed to the Iranian regime, and is often described as the country’s government in waiting.
With its charismatic leader at the helm and thousands of Iranian, Western and Arab supporters behind its cause, the NCRI is increasingly being recognized as the legitimate and progressive alternative to the supreme leader and the cohort currently in power.
The NCRI, also known as the Mojahedin-e Khalq (MEK) in Persian, has three aims for Iran: The demise of the clerical regime, universal suffrage and people’s sovereignty, and social freedom and justice.
Its swelling legitimacy, and the credible alternative it presents for Iran’s future, have not gone unnoticed among political and security establishments in the West.
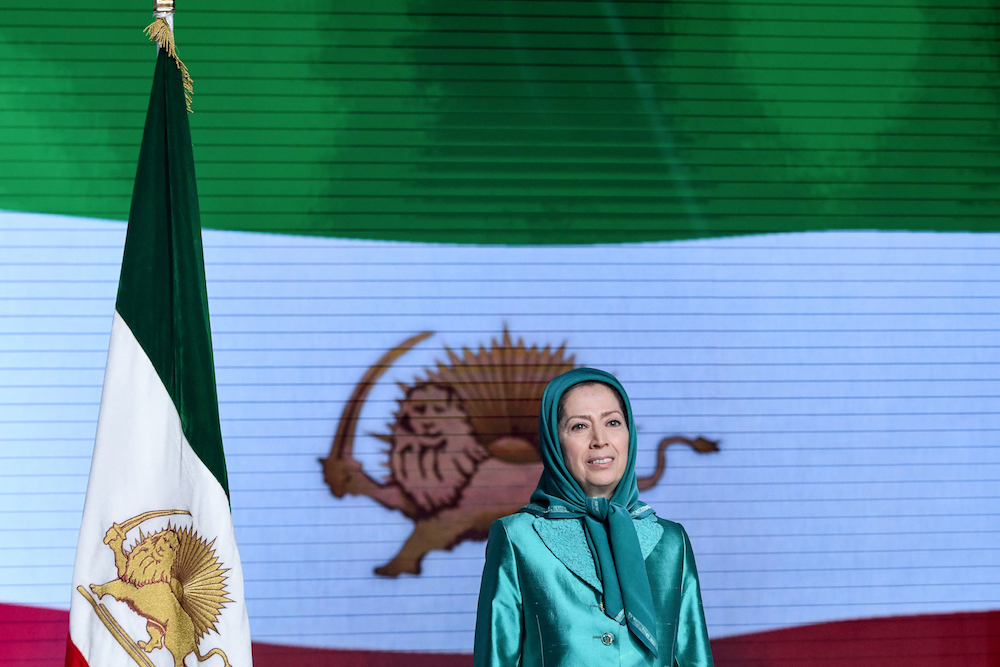

Iran Maryam Rajavi speaks during a conference "120 Years of Struggle for Freedom Iran" at Ashraf-3 camp on July 13, 2019. (AFP/File Photo)
One long-time supporter of the NCRI, and a speaker at the 2020 Free Iran Global Summit, is Tom Ridge, who was the first ever US secretary of homeland security after the 9/11 attacks.
He is a former governor of Pennsylvania and an outspoken advocate for an Iran “free from tyranny.”
Ridge spoke with Arab News during the summit, and explained his long-running support for the NCRI — despite its designation by the US as a terrorist organization until 2012.
While secretary of homeland security, he had never seen any credible reports that justified the group’s terrorist designation, Ridge said.
“I began every day, for several years, in the Oval Office alongside President George Bush being presented with a threat report. I never ever saw a reference to the MEK in any plot that threatened Americans or American interests,” he added.
Having been removed from the US list of terrorist organizations in 2012, the NCRI is increasingly being recognized as the most important player in the landscape of resistance to Tehran’s clerical regime — both at home and abroad.
READ: Why Iran’s agents hound political refugees in distant Albania
“Within American political circles, these days there’s growing bipartisan recognition of the NCRI’s legitimacy,” Ridge said.
He argues that this consensus and recognition of the NCRI’s legitimacy are in the best interests of not just the Iranian people, but also of regional states and the US.
“Recognizing the existence of both an internal and external opposition group that rejects terrorism and embraces principles like gender equality and, most importantly, a non-nuclear Iran seems to be in everyone’s best interest in the globe, not to mention regional states such as Saudi Arabia,” he said.
Ridge spoke at the summit to highlight and denounce Iranian support for terrorism, and many other speakers did the same.
The issue of Iranian terrorism is central to the NCRI’s campaigning, and it is an issue the group is tragically familiar with.
FASTFACT
NCRI
Was founded by Massoud Rajavi and former Iranian President Abolhassan Banisadr in 1981 after their joint escape from the country.
In 2013, Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) forces and their Iraqi militia proxies attacked and killed over 50 NCRI members, and kidnapped more, from their base in Ashraf, Iraq.
This brazen attack was mortifying for the NCRI, but looking further back, the persecution that members of the Iranian opposition have experienced at the hands of the regime becomes even more egregious.
Up to 30,000 of the NCRI’s supporters and members were murdered by the regime in 1988, following a religious edict by hardline revolutionary Ruhollah Khomeini.

Iranian mourners attend the funeral of Morteza Ebrahimi, a commander of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps, who was killed in violent demonstrations in November 2019. (AFP/File Photo)
Amnesty International has referred to these murders as “ongoing crimes against humanity.” It continues to call for justice over the killings, and has implored the UN to set up an independent inquiry into the mass murders.
The most recent assault on the Iranian resistance — a bomb plot targeting its 2018 annual summit — was organized in part by an official Iranian diplomat, who just days ago began his trial in France for his role.
After 30 years of bombings, violence and targeted attacks, it is perhaps no surprise that the NCRI is so vehemently opposed to the regime’s use of terrorism as a tool of foreign policy.
These attacks, Ridge argues, are more than illegal and unjust. He believes that Tehran’s relentless assaults on the NCRI betray its fear of the movement’s popular appeal.

Leader of the People's Mujahedin of Iran Maryam Rajavi during an event. (Supplied)
“If an oppressive regime highlights an internal and external group as the enemy of the state, then there’s a pretty good justification to conclude that they’re fearful that their appeal is large,” he said.
NCRI members believe that Tehran is taking increasingly drastic measures against them because it knows that their appeal is increasing every year, and the West is starting to take notice of the credible, progressive alternative they present for Iran’s future.
Ali Safavi, a member of the NCRI’s foreign affairs committee, told Arab News that from the 2020 Free Iran Global Summit onward, its activities are only going to expand and intensify.
He said the group “aims to pave the way for more uprisings, like those witnessed in November 2019,” when huge anti-regime protests swept across virtually every Iranian city and town.

Former US Secretary of Homeland Security Tom Ridge speaks during a conference at Ashraf-3 camp on July 13, 2019. (AFP/File Photo)
Safavi added that the NCRI will “step up its campaign to hold the regime leaders accountable for their atrocities, first and foremost the 1988 massacre of 30,000 political prisoners,” and that it will continue to work on “breaking the climate of fear and repression” that Tehran has manufactured at home and pursues abroad through terrorism.
Rajavi, Safavi and their cohort in the NCRI were on the frontlines of the 1979 revolution, and it is looking increasingly likely that they will take leading roles in the next Iranian revolution.
This time, though, they say they will not allow their vision for Iran’s future to be distorted, as it was by Khomeini and his extremist ilk in 1979.
The next Iranian revolution will truly be of the people, and if the NCRI’s predictions are correct, it could be sooner than anyone expects.
----------------
Twitter: @CHamillStewart


























