CAIRO: Hospitals across Sudan have been bombed, looted and occupied by armed factions since fighting broke out more than two months ago between the Sudanese military and the Rapid Support Forces (RSF), a paramilitary group. As a result, millions of civilians are being denied vital healthcare.
Medical supplies rapidly dwindled after the conflict began on April 15, with shipments of medicines and other medical supplies stolen or undelivered. Meanwhile, scores of health professionals have been killed, wounded or forced to leave the country.
Dr. Adel Mohsen Badawi Abdelkadir Khalil, 65, is among the many medics who chose to flee with their families, abandoning the private clinic in the capital Khartoum he had managed for more than 15 years.
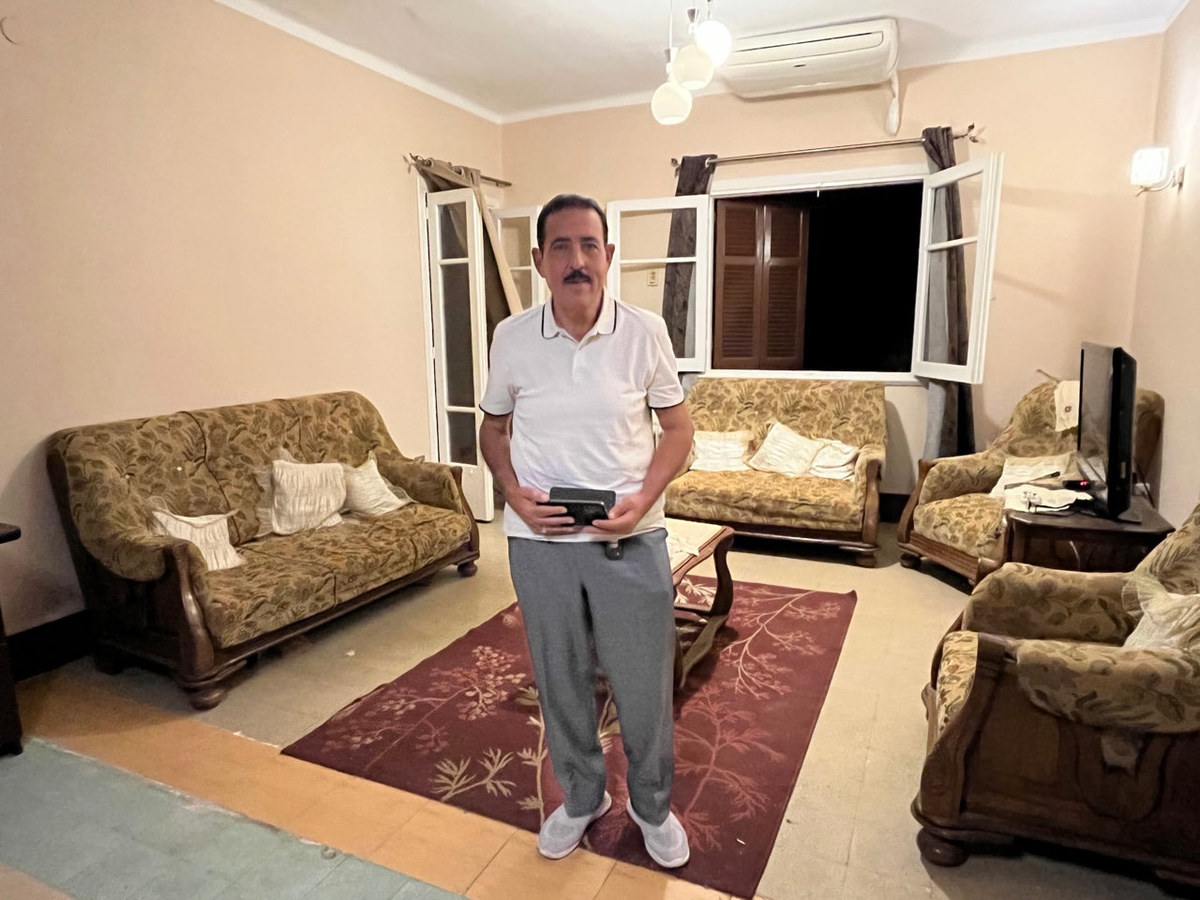

Dr. Adel Mohsen Badawi Abdelkadir Khalil at his new refuge in Cairo. (AN photo)
On April 21, fearing he would be conscripted by the RSF to treat the paramilitary group’s wounded, he made the painful decision to join the flood of refugees making the perilous journey north to the border with Egypt.
“I was inside my clinic preparing my tickets to go to Cairo when I saw attacks outside. People were yelling and weeping,” Mohsen told Arab News from an apartment in the Egyptian capital he shares with other displaced Sudanese families.
“I immediately locked all my doors and turned off the lights and hid there. If the RSF know you’re a doctor, they will take you to tend to their army.”
Mohsen said that when he and his family caught the bus to Egypt, he was careful not to tell officials or fellow passengers he was a health professional, instead concealing his 30 years of medical experience for his own safety.
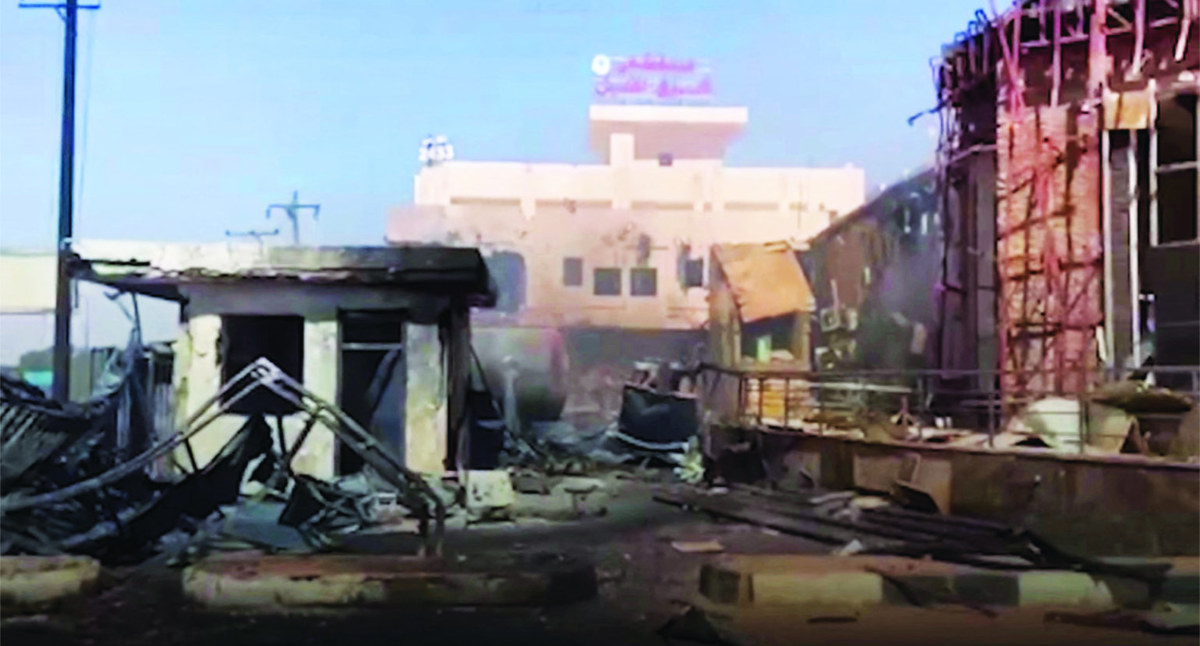

A video screengrab from social media shows the East Nile Hospital in Khartoum, one of many medical facilities damaged in the fighting since April 15. (Reuters)
The public-health sector has long been fragile in Sudan, where 65 percent of the population lives in poverty. With the departure of so many medical workers, aid agencies have warned that the nation is facing a major health emergency. According to the International Committee of the Red Cross, only 20 percent of health facilities are still operational in Khartoum.
“We have been witnessing the near collapse of the health system in Sudan,” Alyona Synenko, the Africa region spokesperson for the organization, told Arab News.
Those unable or unwilling to flee Khartoum have been forced to hunker down in their homes with little or no access to clean water or electricity. According to several Sudanese Arab News spoke to in Cairo, many of those who remained behind face the threat of dehydration and starvation, such is the scale of the need for aid in Khartoum and nearby cities.
The collapse of basic utilities and other public infrastructure is having an especially serious effect on hospitals by undermining their hygiene protocols, rendering vital medical equipment inoperative, and depriving chronically sick people of potentially life-sustaining treatment.
“Besides the departure of some of the medical personnel and the shortages of medical supplies, hospitals are suffering from a lack of food, clean water and electricity,” said Synenko.

Hundreds of medical centers had closed in Khartoum since war erupted between Sudan’s army and the paramilitary RSF group in in mid-April. (AFP)
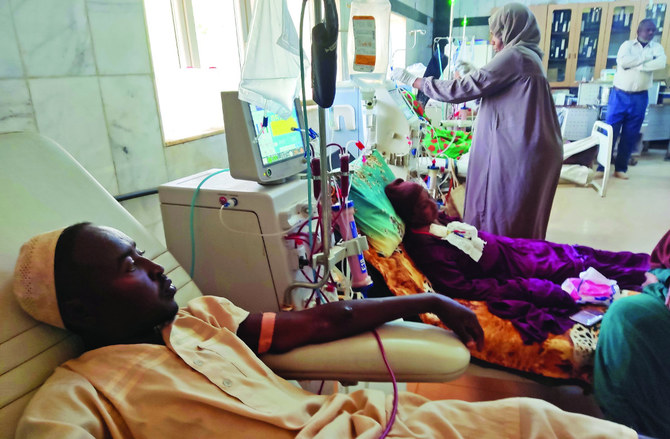
The fighting has, for example, left 12,000 dialysis patients at mortal risk as hospitals have run out of the medications they need and the fuel to power generators, according to the trade union that represents the country’s doctors. It has also impeded the delivery of humanitarian aid that 25 million people — more than half the population — now desperately need.
In addition, there are fears that the summer rainy season will bring with it seasonal epidemics such as malaria, which wreaks havoc in Sudan every year, and a shortage of drinking water could cause a cholera outbreak.
“Sudanese health workers and the volunteers of the Sudanese Red Crescent Society have been accomplishing the impossible, working in such extreme conditions,” said Synenko.
FASTFACTS
It is believed that fewer than 20 percent of health facilities in Khartoum are still operational.
As of late May, 14 medical professionals had been killed, 21 hospitals evacuated and 18 bombed, according to a doctors’ union.
“While we are working with the Ministry of Health to deliver urgent surgical supplies to hospitals, we are also calling on all actors to respect and protect medical facilities and personnel. This is not only an obligation under international humanitarian law, it is a moral imperative because numerous lives depend on their work.”
Dr. Atia Abdalla Atia, secretary-general of the Sudan Doctors trade union, told Arab News that he and his colleagues have documented the deaths of at least 14 medical professionals since the fighting began. The union has also confirmed the evacuation of 21 hospitals, the bombardment of 18, and one case of a doctor going missing, he added.
On Saturday, the trade union accused the RSF of raiding the Shuhada hospital, one of the few still operating in the violence-torn country, and killing a staff member. The RSF denied the accusation.
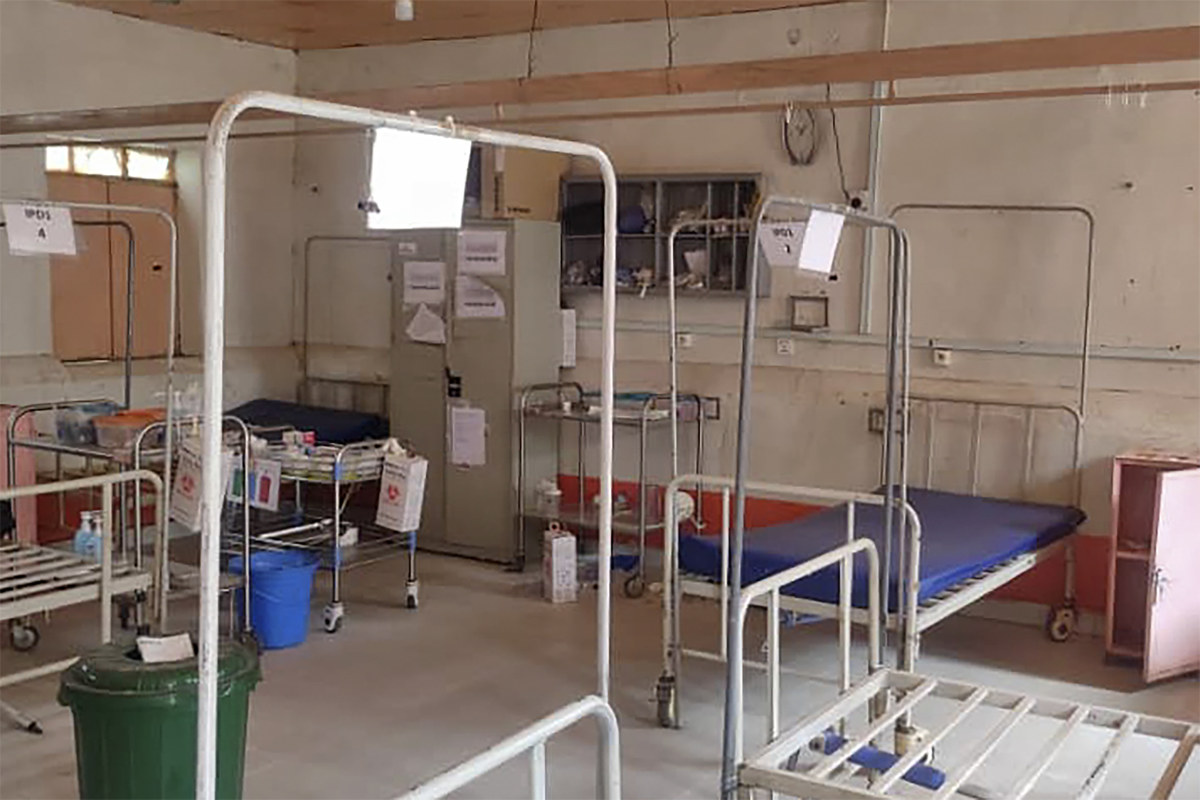

View of an abandoned hospital in El-Geneina, the capital of West Darfur, on May 1, 2023 as deadly fighting continued in Sudan between rival generals’ forces. (AFP)
The targeting of health facilities and medical personnel during a conflict is considered a war crime under international humanitarian law. The RSF has reportedly seized control of several hospitals to use as bases of operation.
During a meeting of the UN Security Council on May 22, Volker Perthes, the UN’s special representative for Sudan, highlighted reports of such activities and said the “use of health facilities as military positions is unacceptable.”
In a report published by medical journal The Lancet, aid agency Doctors Without Borders said that health professionals at facilities across Sudan have been repeatedly confronted by fighters who steal medicines, other health supplies and vehicles.
Jean-Nicolas Armstrong Dangelser, the agency’s emergency preparedness coordinator in Port Sudan, told the journal that although some instances of looting are financially motivated, others appear callously calculated to deliberately deprive patients of care.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
In Khartoum, for example, medical warehouses were raided several days in a row. When staff were able to return, they found fridges unplugged and medicines spilled on the floor.
“The entire cold chain was ruined so the medicines are spoiled and can’t be used to treat anyone. We are shaken and appalled by these deplorable attacks,” said Armstrong Dangelser.
“We are experiencing a violation of humanitarian principles and the space for humanitarians to work is shrinking on a scale I’ve rarely seen before … People are in a desperate situation and the need for healthcare is critical, but these attacks make it so much harder for healthcare workers to help.”
Clashes between the military and the RSF intensified on Sunday as the fighting in Khartoum and the western regions entered its 12th week, according to a Reuters news agency report.

Air and artillery strikes as well as small-arms fire could be heard, particularly in the city of Omdurman, as well as in Khartoum, the report said.
More than 2,000 people have been killed since fighting broke out on April 15, according to the Armed Conflict Location and Event Data Project, which collects data on conflicts and other violence worldwide.
The UN estimates that upwards of 1.2 million people have been displaced, out of whom at least 425,000 have fled abroad.
Last week, military chief Gen. Abdel Fattah Al-Burhan called on young men to join the fight against the RSF and, on Sunday, the army posted photos it said were of new recruits.
Saudi Arabia took the lead in efforts to evacuate thousands of foreigners from Sudan in the early days of the conflict. The Kingdom’s diplomats have also been working with their US counterparts to help broker a lasting ceasefire in the country.
A five-day extension of the last truce expired last month with little sign of a let-up in the violence. That ceasefire did, however, allow surgical supplies donated by the International Committee of the Red Cross to be distributed to seven hospitals in Khartoum by the Ministry of Health, including anesthetics, antibiotics, dressings, sutures and infusions.
But according to Atia, the doctors who chose to remain in Sudan are generally working with only the most basic of medical equipment and supplies, which is putting patients at risk, and many of the remaining medical staff are desperate to leave.
“Everyone is asking where they can go to escape this,” he said.
In many areas, field hospitals staffed by volunteers have been set up in schools and other public buildings in an attempt to make up for the lack of operational state institutions, and help treat the chronically sick and, increasingly, those who succumb to the effects of dehydration and malnutrition.
“Everything has been left in the hands of civilians and the few doctors and hospitals that are left,” said Atia.
“We are trying to focus on the chronic diseases (and) also at home where people are dying due to lack of water, food and no access to drugs.”