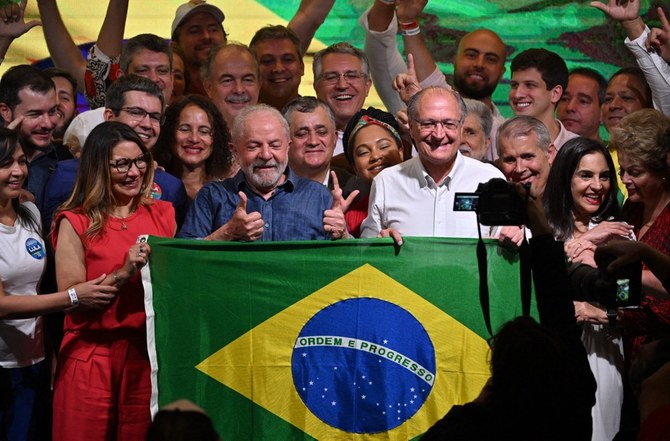
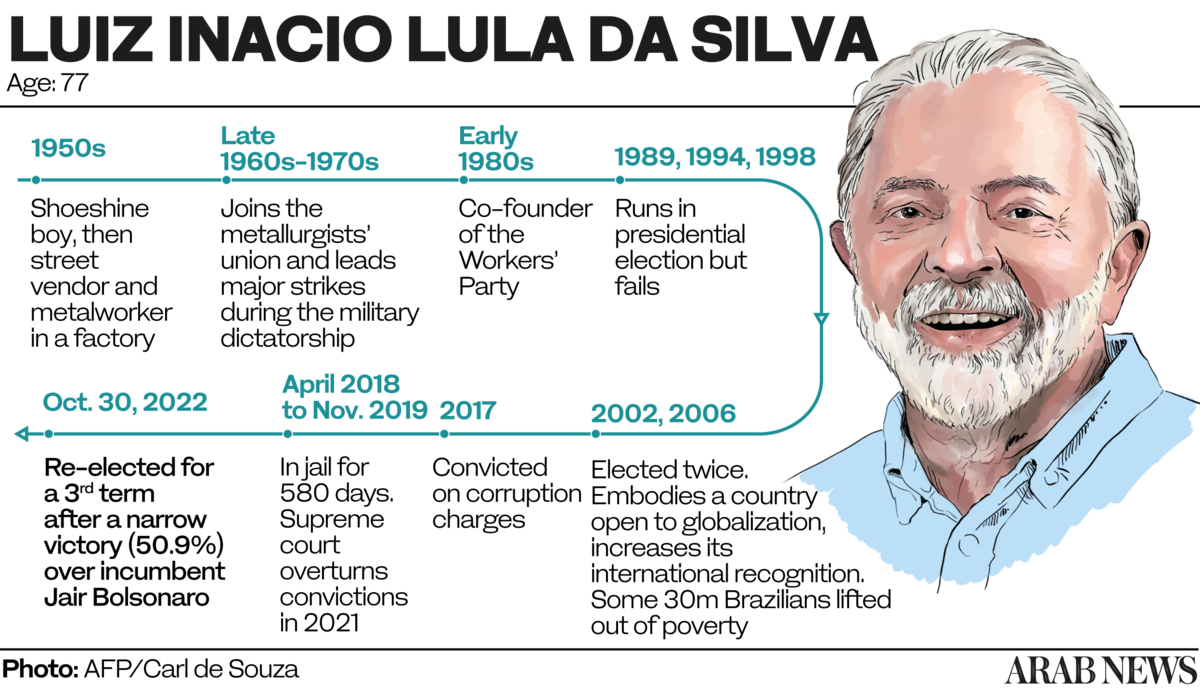
SAO PAULO: On Oct. 30, Brazilians elected former President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva after a highly polarized campaign against incumbent Jair Bolsonaro.
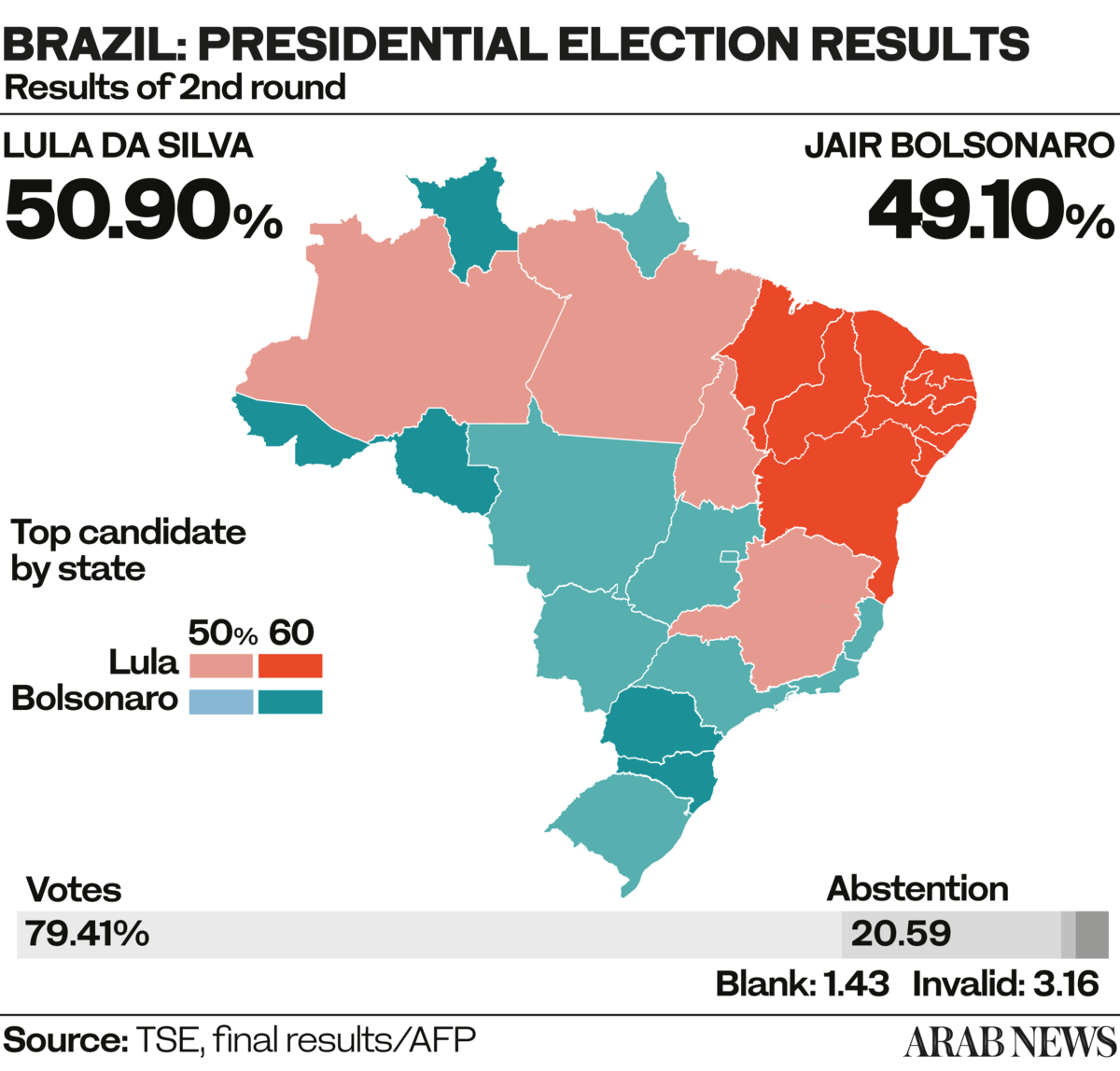
The divide in the South American country was reflected in the outcome: Lula received 50.9 percent of votes while Bolsonaro got 49.1 percent.
The large Brazilian-Arab community, estimated at more than 10 million people, was also divided.

Lula received 50.9 percent of votes. (AFP)
This could be seen, for example, in Foz do Iguacu, a city on the border with Paraguay and Argentina where thousands of Arab Brazilians live.
In August, part of the community organized a dinner with Lula, but as soon as the invitation was publicized on social media, Arab supporters of Bolsonaro began to protest. The dinner ended up being canceled.
That kind of controversy has been quite common in Brazil’s politically charged atmosphere over the past few months, and it has been no different with the Arab community, analysts say.
The first aspect to consider is that the community does not constitute an organized group of influence, said Tufy Kairuz, a researcher with a PhD in history from York University in Canada.
“Lebanese and Syrian immigrants began to arrive in Brazil at the end of the 19th century. Europeans in Brazil were usually Mediterranean, so Arabs were always considered to be white here. They adapted well,” Kairuz told Arab News, adding that as white, Christian people and members of an economic elite, Arab Brazilians tend to vote like the non-Arab Brazilian elite.
That is why many in the community voted for Bolsonaro, said Murched Omar Taha, president of the Institute for Arab Culture.
“Many Arab Brazilians are businessmen, and businessmen are among the segments who in general supported Bolsonaro,” Taha told Arab News.
At the same time, he said, among Brazilian Arabs there are many intellectuals, educators and artists — groups that tended to vote for Lula.
Mamede Jarouche, the son of Lebanese immigrants and a professor of Arab literature at the University of Sao Paulo, said a large part of the Arab community is completely integrated in Brazilian society, so Arab heritage does not play a role when it comes to voting.
“Descendants of the first waves of immigrants usually don’t feel much connected to their roots,” Jarouche told Arab News.

Bolsonaro received 49.1 percent of the vote. (AFP)
He added, however, that first- or second-generation Brazilian Arabs tend to follow Middle Eastern politics and feel closer to the Arab world.
“Most of the Muslim people who are concerned with the Palestinian cause oppose Bolsonaro,” he said.
Since the 2018 presidential campaign, Bolsonaro had pledged to move the Brazilian Embassy in Israel from Tel Aviv to Jerusalem.
He was greatly supported by the Brazilian-Israeli community, and the idea of the embassy move was discussed with it.
THE IRAN FACTOR
A March 11, 2021 report by the Arab News Research and Studies Unit examined Brazil’s role as an important strategic trade partner for Iran in Latin America.
The report’s author Hamdan Al-Shehri noted that relations between Iran and Brazil have passed through several distinct phases in recent decades, sometimes reflecting general shifts in the latter’s foreign policy, at other times resembling an ill-defined relationship based primarily on mutual trade interests.

A worker checks coffee beans on a cleaning machine at a processing plant in Brasilia. (AFP)
He said: “The dynamic of the relationship has also been influenced by the personalities of successive leaders of both states, their ideological leanings, and their perceptions of the West.”
As president, Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva “placed a high value on the relationship with Iran because he wanted to move the focus of his foreign policy away from the countries of North America and Europe and toward the developing nations of Latin America, Africa, and the Middle East.”
By contrast, Al-Shehri added: “The warmth went missing from the relationship after Dilma Rousseff became president of Brazil between 2011 and 2016.
Read the full report on Arab News Research & Studies by clicking here
“The election of Jair Bolsonaro in 2018 did little to improve ties. The right-wing president aligned himself closely with former US President Donald Trump, becoming one of the few world leaders to openly back the elimination on Jan. 3, 2020, of Qassem Soleimani, commander of Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps’ extraterritorial Quds Force.”
As opposed to its diplomatic accomplishments, Iran, currently being rocked by anti-government protests, has had limited success in winning over the publics of Latin America.
According to 2015 poll data from the Pew Research Center, involving 45,435 respondents across 40 countries, some 79 percent of Brazilians said they held a negative view of Iran, while just 11 percent looked upon the country favorably.
Al-Shehri said: “Relationships with Latin American nations remain primarily the Iranian regime’s way of countering the impact of international sanctions and diversifying its means of survival.
“Through these connections, Iran hopes to project the image of a global power, overcome diplomatic isolation, win support for its nuclear program, and potentially respond to US pressure from close proximity.”
He pointed out that the Brazil-Iran trade surplus in 2018 reached $2.2 billion in favor of the former.
“Regardless of who is in power, economic and commercial interests have and will remain a consistent driver of bilateral ties between the two countries, particularly in oil, gas, mineral exploration, and agriculture,” he added.
But “he had to give up on that idea after he suffered great pressure from Arab nations, which are important commercial partners for Brazil,” Taha said.
Brazil is the world’s largest exporter of halal meat and poultry. The agribusiness sector, which massively supported Bolsonaro, also pressured him not to move the embassy to Jerusalem, Taha added, “but if he had four more years, maybe he’d do it.”
Bolsonaro’s pro-Israel rhetoric, which displeased many Brazilian Arabs, was amplified by his evangelical allies.
His wife Michelle is a member of a Baptist church and is usually seen wearing the colors of the Israeli flag. On Oct. 30, she was photographed voting with a T-shirt with the Israeli flag.
“As a sheikh, I thought she lacked sensitivity and common sense. It was really a provocation,” Jihad Hammadeh told Arab News, adding that the photos immediately went viral.
“Many people who hadn’t decided yet ended up voting for Lula after that. Many felt it as an insult.”
Hammadeh said many Brazilian Arabs remember that Lula had close relations with Arab countries and played a central role in supporting the Palestinians. In 2010, shortly before leaving the presidency, he recognized Palestine as a sovereign state.
Domestically, Lula has also showed more openness toward Muslims than Bolsonaro has, said Hammadeh.
“When the president himself opens the doors for you and establishes a dialogue, you feel more comfortable,” he added.

Domestically, Lula has also showed more openness toward Muslims than Bolsonaro has, said Jihad Hammadeh. (AFP)
“In Bolsonaro’s administration, we didn’t have the same closeness with the president than we used to have with Lula.”
Kairuz, the researcher, predicts that in his second term, Lula will work to strengthen Brazil’s ties with Arab and Muslim nations. “Lula has a solid reputation in these countries,” he said.
“That’s why many of them, immediately after the election result was publicized on Oct. 30, sent messages to congratulate him.”
On Nov. 1, Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman sent a cable to Lula in which he “expressed sincere felicitations to the president-elect, wishing him every success and the government and friendly people of Brazil steady progress and prosperity.”