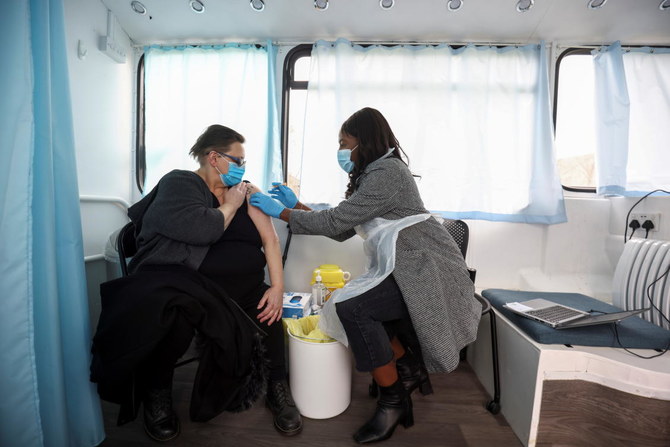
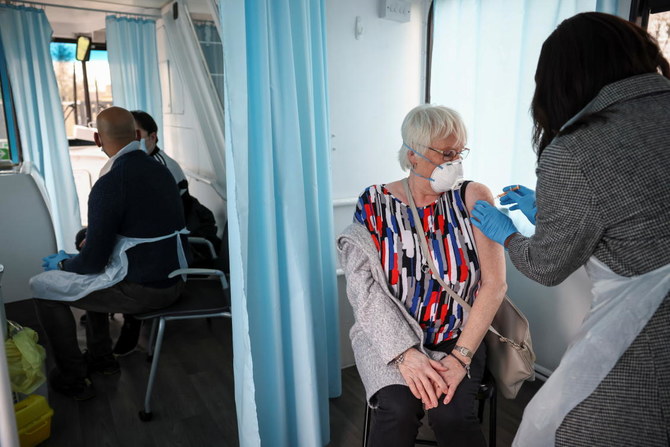
LONDON: The UK government said Sunday that it reached its goal of giving at least one COVID-19 vaccine shot to the most vulnerable people in the country, increasing pressure on ministers to clarify when they will ease a lockdown imposed in early January.
Some 15 million people, or 22% of the UK population, have received their first shot or were offered one. The figure includes most people in the government’s top four priority groups, including everyone over 75, frontline healthcare workers and nursing home staff.
“15,000,000! Amazing team,'' Nadhim Zahawi, the vaccines minister, said in a tweet that featured a red heart. “We will not rest till we offer the vaccine to the whole of phase1 the 1-9 categories of the most vulnerable & all over 50s by end April and then all adults.''
British Prime Minister Boris Johnson plans to unveil his roadmap for easing restrictions on Feb. 22 amid signs that infection rates, hospitalizations and deaths have fallen sharply since England’s third national lockdown began on Jan. 4.
Jockeying has already begun between those who want the measures lifted as soon as possible and those who fear moving too fast will lead to a resurgence of the virus.
Britain got a head start on its vaccination effort in December, when it became the first country to authorize widespread use of a COVID-19 shot. It ranks behind only Israel, 71%, the Seychelles, 53%, and the United Arab Emirates, 50% in the percentage of people who have received one dose, according to data compiled by Oxford University. The US is fifth at 15%.
At the same time, rules that have closed schools, restaurants and nonessential shops in the UK are starting to pay off. The number of new infections, hospital admissions and deaths recorded over the past seven days have all dropped by more than 20% from the previous week, according to government figures.
When Johnson announced the lockdown, he said the government would review the measures in mid-February based on their success in controlling the pandemic and progress in the vaccination effort. Johnson’s first priority is to reopen schools, and he has promised to give schools two weeks notice to give teachers time to prepare for the return of students.
The prime minister on Saturday applauded the vaccine rollout but urged people to be cautious.
“We have still got infections running very high throughout the country — levels which last year we would have thought were really very high indeed — (and) still, sadly, a great many deaths in our hospitals,” he said during a visit to a vaccine manufacturing facility in northeastern England. “Although the number is beginning to come down, and perhaps starting to come down quite fast, we need to look at the data very, very hard.”
Britain has reported over 117,000 virus-related deaths, the highest toll in Europe.
Mark Harper, a member of Parliament from the ruling Conservative Party, last week warned the government against “moving the goalposts” for deciding when to ease the lockdown.
Johnson should start by reopening schools, then gradually lift other restrictions as more people are vaccinated, said Harper, who leads a group of about 70 lawmakers who have lobbied for the government to consider the negative economic and social impacts of the restrictions, along with the health benefits.
“If you think about the restrictions that the government’s placed on everybody, they are the toughest set of restrictions that have ever been placed on the British people outside of the Second and First World Wars,” Harper told the BBC. “So it’s kind of just worth stepping back a bit and saying, ‘This isn’t normal, and it shouldn’t continue, frankly, for a moment longer than it’s absolutely necessary.’”
After meeting the target for reaching the most vulnerable people, UK authorities will progressively expand the vaccination drive to the next five priority groups until everyone over 50 and vulnerable younger people with health conditions that put them at higher risk from the virus have been offered the vaccine.
Public health officials say the top nine priority groups account for 99% of the deaths caused by COVID-19 so far.
While the vaccines currently authorized for use in the UK require two doses to ensure full protection against COVID-19, British authorities say one dose provides a significant level of protection.
Because of this, they have made it their priority to give the first dose to as many people as possible as quickly as possible. To do this, Britain has suggested that the second dose be administered after three months, instead of one month as recommended by the manufacturers.
Jeremy Farrar, director of the Wellcome Trust health think tank, said the number of COVID-19 infections in Britain is still too high to think about lifting the restrictions.
“We’ve made enormous progress … but the transmission is incredibly high still and we’ve got to get it lower,” he said.
There are other dangers on the horizon. UK government scientific advisers say the COVID-19 variant now predominant in the country may be up to 70% more deadly than previous variants, underscoring concerns about how mutations may change the characteristics of the disease.
The findings from the New and Emerging Respiratory Virus Threats Advisory Group, published Friday on the government’s website, confirm preliminary research released Jan. 21. The group, known as NERVTAG, includes experts from universities and public agencies across the UK
The new report is based on analysis of a dozen studies that found the so-called Kent variant, named after the county where it was first identified, was 30% to 70% more deadly than other variants. The studies compared hospitalization and death rates among people infected with the variant and those infected with other variants.
“Based on these analyses, it is likely that infection with (the Kent variant) is associated with an increased risk of hospitalization and death compared to infection with non-variant of cancer viruses,” the advisory group said. “It should be noted that the absolute risk of death per infection remains low.”
UK hits target: Gives at least 1 vaccine shot to 15 million
https://arab.news/6y7sy
UK hits target: Gives at least 1 vaccine shot to 15 million

- The UK will start administering vaccines from Monday to those aged between 65 and 69 and the clinically vulnerable to COVID-19
- Britain has registered nearly 117,000 deaths within 28 days of a positive COVID-19 test
Vehicle hits pedestrians near school in Beijing: Chinese police
“On June 26, 2025, at around 13:00, a traffic accident occurred near the intersection of Yucai Road and Dongmen Street in Miyun district,” local police wrote
BEIJING: A vehicle crashed into pedestrians in an “accident” near a school in Beijing on Thursday, Chinese police said, with footage shared online appearing to show young people lying injured in the street.
Videos geolocated by AFP to an intersection in Miyun district in the northeast of the capital showed a grey SUV wedged against a tree as several people and clothing were seen in the road.
In one clip a bloodied young person was seen being given first aid by somebody in white overalls.
“On June 26, 2025, at around 13:00, a traffic accident occurred near the intersection of Yucai Road and Dongmen Street in Miyun district,” local police wrote in an online statement.
A 35-year-old man surnamed Han “collided” with people “due to an improper operation,” it said, adding those injured were taken to hospital.
It did not give the number of injured.
“The accident is under further investigation,” the statement said.
China has seen a string of mass casualty incidents — from stabbings to car attacks — challenging its reputation for good public security.
Last year a man who plowed his car into a crowd of mostly school children in central China was handed a suspended death sentence with a two-year reprieve.
In November 2024 the attacker named as Huang Wen repeatedly rammed his car into a crowd outside a primary school in Hunan province.
When the vehicle malfunctioned and stopped, Huang got out and attacked bystanders with a weapon before being apprehended.
Thirty people, including 18 pupils, sustained minor injuries.
Some analysts have linked the incidents to growing anger and desperation at the country’s slowing economy and a sense that society is becoming more stratified.
In November last year, a man killed 35 people and wounded more than 40 when he rammed his car into a crowd in the southern city of Zhuhai, the country’s deadliest attack in a decade.
And in the same month, eight people were killed and 17 wounded in a knife attack at a vocational school in the eastern Chinese city of Yixing.
Lavrov says NATO spending increase won’t significantly affect Russia’s security

- NATO allies on Wednesday agreed to raise their collective spending goal to 5% of GDP over the next decade
MOSCOW: NATO’s decision to increase defense spending will not significantly affect Russia’s security, Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov said on Thursday.
NATO allies on Wednesday agreed to raise their collective spending goal to 5 percent of gross domestic product over the next decade, citing what they called the long-term threat posed by Russia and the need to strengthen civil and military resilience.
“As for the impact of this 5 percent goal on our security, I don’t think it will be significant,” Lavrov told a press conference.
“We know what goals we are pursuing, we don’t hide them, we openly announce them, they are absolutely legal from the point of view of any interpretation of the principles of the UN Charter and international law, and we know by what means we will always ensure these goals.”
NATO adopted the higher spending target in response to pressure from US President Donald Trump for European members to pull their weight, and also to European fears that Russia poses a growing threat to their security following the 2022 invasion of Ukraine.
Russia, which is spending more than 40 percent of this year’s budget on defense and security, denies any intention to attack a NATO state.
The Kremlin accused the alliance this week of portraying Russia as a “fiend of hell” in order to justify its “rampant militarization.”
Myanmar burns confiscated drugs worth around $300 million

- The destroyed drugs included opium, heroin, methamphetamine, marijuana, ketamine and the stimulant known as ice
- Myanmar has a long history of drug production linked to political and economic insecurity caused by decades of armed conflict
YANGON: Officials in Myanmar’s major cities destroyed about $300 million worth of confiscated illegal drugs Thursday.
The destroyed drugs included opium, heroin, methamphetamine, marijuana, ketamine and the stimulant known as ice, or crystal meth, Yangon Police Brig. Gen. Sein Lwin said in a speech at a drug-burning ceremony.
The drug burnings came nearly a month after UN experts warned of unprecedented levels of methamphetamine production and trafficking from Southeast Asia’s Golden Triangle region, where the borders of Myanmar, Laos and Thailand meet, and Myanmar’s eastern Shan State in particular.
The production of opium and heroin historically flourished there, largely because of the lawlessness in border areas where Myanmar’s central government has been able to exercise only minimum control over various ethnic minority militias, some of them partners in the drug trade.
The UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) said in a May report that the political crisis across the country after the military takeover in 2021 — which led to a civil war — has turbocharged growth of the methamphetamine trade.
In the country’s biggest city, Yangon, a massive pile of drugs worth more than $117 million went up in a blaze, Sein Lwin said.
Similar events to mark the International Day Against Drug Abuse and Illicit Trafficking also occurred in the country’s second-largest city of Mandalay, and in Taunggyi, the capital of eastern Myanmar’s Shan state, all areas close to where the drugs are produced.
A police official from the capital Naypyitaw told The Associated Press that the substances burned in three locations were worth $297.95 million. The official spoke on condition of anonymity because the information has not yet been publicly announced.
Myanmar has a long history of drug production linked to political and economic insecurity caused by decades of armed conflict. It has been a major source of illegal drugs destined for East and Southeast Asia, despite repeated efforts to crack down.
That has led the flow of drugs to surge “across not only East and Southeast Asia, but also increasingly into South Asia, in particular Northeast India,” the UN said last month. Drugs are increasingly trafficked from Myanmar to Cambodia, mostly through Laos, as well as through maritime routes linking Malaysia, Indonesia, and the Philippines, with Sabah in Malaysia serving as a key transit hub, it added.
The UN agency labeled Myanmar in 2023 as the world’s largest opium producer.
Indonesia launches first medical tourism special economic zone in Bali

- Sanur medical tourism zone will include international hospital, specialist clinics, research centers
- Initiative also aims to stem high number of Indonesians who annually seek health treatment overseas
JAKARTA: Indonesia has launched its first medical tourism special economic zone in Sanur, on the resort island of Bali, marking a major step in the country’s efforts to develop world-class healthcare services integrated with tourism.
In recent years Indonesia has been working to reform its healthcare sector to improve service standards and reduce the outflow of Indonesians seeking treatment overseas, including in Singapore, Malaysia and Thailand, who spend up to 150 trillion rupiahs ($9.2 billion) abroad annually.
The Sanur medical tourism zone will include a range of facilities, including an international hospital, specialist clinics, medical research centers and a garden with over 380 medicinal plant species.
“I think this is the first of its kind in our country — we envisioned creating a special economic zone offering world-class healthcare services,” President Prabowo Subianto, who inaugurated the project on Wednesday, said during his speech.
Indonesia, a country of more than 270 million people, has about seven doctors for every 10,000 people, according to World Health Organization data. This is below Thailand with nine doctors, the Philippines with eight doctors and Australia with 41 doctors per 10,000.
To transform healthcare in the country, Indonesian lawmakers passed into law a health bill last year that allows foreign medical specialists to practice and be based in the country.
The Sanur medical tourism zone is also part of the government’s efforts “to provide the best healthcare services to all of its citizens,” Prabowo said.
“There are many Indonesian citizens who seek healthcare abroad, which affects our foreign exchange reserves. With this initiative, we can provide healthcare services that are on par with the best in the world.”
Indonesian officials hope the new special economic zone will not only boost the country’s health sector, but put Bali on the global map as a top destination for health and wellness tourism.
As the country’s top overall tourist destination, Bali welcomed 6.3 million international travelers in 2024.
The idea to develop a special zone dedicated to world-class healthcare does have the potential to effectively stem the number of Indonesians seeking medical services abroad, said Kharisma Utari, a researcher with Women’s World Banking.
“But I think we need to remember that quality healthcare cannot be solely developed from one hub. If this stands alone without improving the entire healthcare system nationally, there is a risk of this turning into a gimmick or a mere symbol,” Utari told Arab News on Thursday.
“Quality healthcare should be enjoyed evenly and inclusively across all regions, not just in one exclusive zone,” she added. “State budget should be directed to strengthen basic services that could reach all people.”
‘Thrown out like trash’ from Iran, Afghans return to land they hardly know

- More than 1.2 million Afghans deported from neighboring Iran since March 2024, IMO says
- Tehran had pledged mass deportations to counter growing local discontent over refugees
ISLAMABAD: Ghulam Ali begins his days in pain, his muscles aching from hauling grain on a rickety cart through the streets of Kabul, homesick for the country he called home for nearly four decades.
Ali is among more than 1.2 million Afghans deported from neighboring Iran since March 2024, according to the International Organization for Migration (IOM), after Tehran pledged mass deportations to counter mounting local discontent over refugees.
Thousands have also fled this month after Israeli and US airstrikes hit Iranian military targets.
For Ali, 51, whose family left Afghanistan during the Soviet invasion in the 1980s when he was just 10, Iran was home.
“I grew up there, worked there, buried my parents there,” he said during a midday break from work in Kabul, sipping green tea with a simple lunch of naan bread.
“But in the end, they threw us out like trash. I lost everything — my home, my little savings in cash, my dignity,” he told the Thomson Reuters Foundation by video link.

Like many others, he has returned to a homeland he barely knew and one that has changed drastically.
Outsiders in their own country, many men struggle to support their family while women face severe restrictions on their daily life under the ruling Taliban.
Since late 2023, an estimated 3 million Afghans have been forced out of Iran and Pakistan, where they had sought safety from decades of war and, since the Taliban’s return to Kabul in 2021, from extremist rule.
Unwelcome abroad, they have returned to a homeland facing economic collapse and international indifference.
UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres, in his latest report on Afghanistan, called on countries hosting Afghan refugees to protect those in need and abide by international obligations to ensure any returns to Afghanistan are voluntary.
“Returnees face immense challenges... in particular securing housing, employment and access to basic services,” he said.
Up to 10,000 Afghan women, men and children are taking the Islam Qala border crossing from Iran on a daily basis, according to the Taliban authorities. Inside Afghanistan, humanitarian aid agencies say conditions are dire, with inadequate shelter, food shortages and no road map for reintegration.
“They return to a homeland that is dramatically unprepared to receive them,” warned Arafat Jamal, the UNHCR representative in Afghanistan in a statement last month.
The Taliban’s deputy minister for border and refugees affairs, Abdul Zahir Rahmani, also told local media this week that Afghanistan had seen a sharp increase in refugee returns since this month’s 12-day air war in Iran.
Many said they had no say in the matter.
Ali said he was arrested at a construction site in Mashhad, Iran’s second-biggest city, lacking documentation during a crackdown on refugees by the Iranian police.
He and his wife, six children, two daughters-in-law and five grandchildren were deported in March.
“We were treated like criminals,” he said. “They didn’t care how law-abiding or in need we were. They just wanted all Afghans out.”
The extended family — 15 people aged 5 to 51 — is now packed into a two-room, mud-brick house on Kabul’s western fringes.
Ali said his Persian-accented Dari draws sneers from fellow laborers – another reminder he doesn’t fit in. But he brushes off their mockery, saying his focus is on feeding his family.
“We can barely afford to eat properly,” his wife Shahla said by video as she sat cross-legged on a worn rug.
“Rent is 4,000 afghanis ($56) a month — but even that is a burden. One of my sons is visually impaired; the other returns home every day empty-handed.”
For women and girls, their return can feel like a double displacement. They are subject to many of the Taliban’s most repressive laws, including restrictions on their movement without a “mahram,” or male companion, and curbs on education and employment.
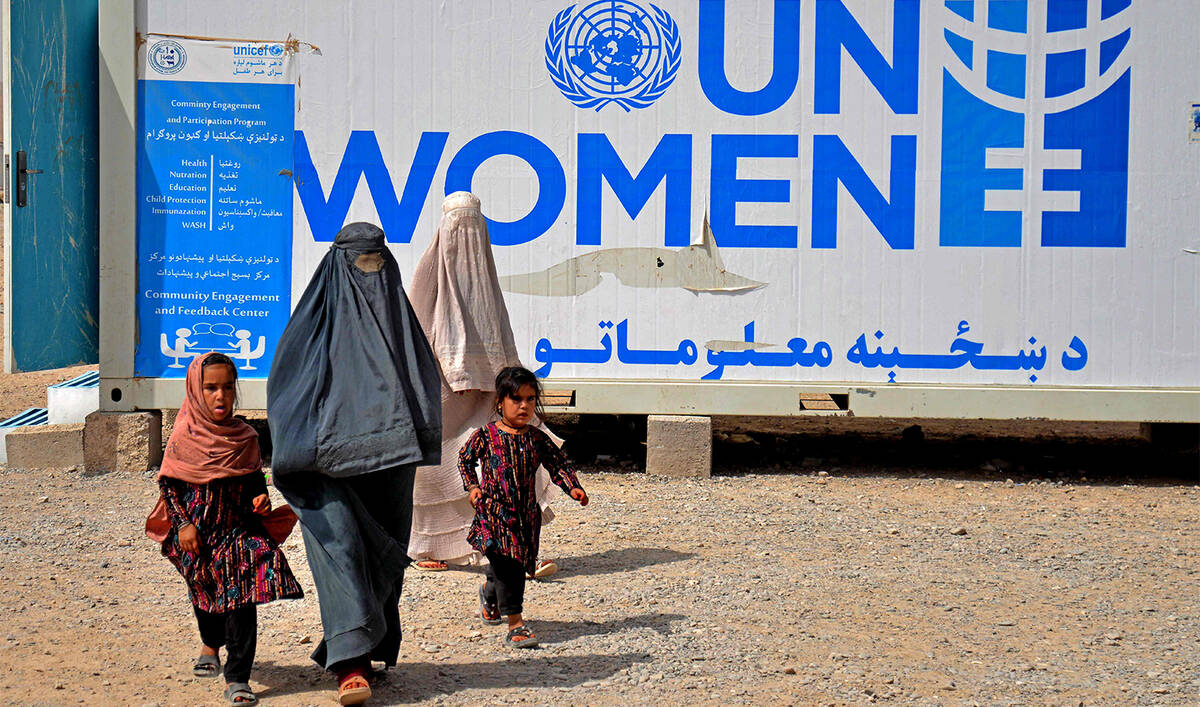

On Kabul’s western edge, 38-year-old Safiya and her three daughters spend their days in a rented house packing candies for shops, earning just 50 afghanis for a day’s work, below Afghanistan’s poverty level of $1 a day.
Safiya said they were deported from Iran in February.
“In Tehran, I stitched clothes. My girls worked at a sweet shop,” said Safiya, who declined to give her last name.
“Life was tough, but we had our freedom, as well as hope … Here, there’s no work, no school, no dignity. It’s like we’ve come home only to be exiled again.”
During their deportation, Safiya was separated from her youngest daughter for a week while the family was detained, a spat over documents that still gives the 16-year-old nightmares.
In Iran, said Safiya, “my daughters had inspiring dreams. Now they sit at home all day, waiting.”
Afghans are also being forcibly deported from next-door Pakistan – more than 800,000 people have been expelled since October 2023, according to Amnesty International.
Born in Pakistan to Afghan refugee parents, Nemat Ullah Rahimi had never lived in Afghanistan until last winter, when police barely gave him time to close his Peshawar grocery store before sending him over the Torkham border crossing.
“I wasn’t allowed to sell anything. My wife and kids — all born in Pakistan — had no legal documents there so we had to leave,” said the 34-year-old.
Rahimi now works long hours at a tire repair shop at a dusty intersection on the edge of Kabul as he tries to rebuild a life.
“I can’t say it’s easy. But I have no choice. We’re restarting from zero,” he said.