MISSOURI: To outsiders, the Assad regime in Syria usually appears almost as opaque as North Korea. When Hafez Assad, who ruled the country with an iron fist from 1970 until 2000, passed away, many wondered how his son Bashar would fare as leader.
More than a few questioned whether the mild-mannered, London-trained ophthalmologist Bashar would manage to maintain control of the country.
Even years after his ascension, observers still questioned whether he was the one really running the country, or if some top Baathist generals around him were calling the shots.
No one knew for sure because Bashar’s Syria simply is not the kind of place that opens itself up to outside scrutiny.
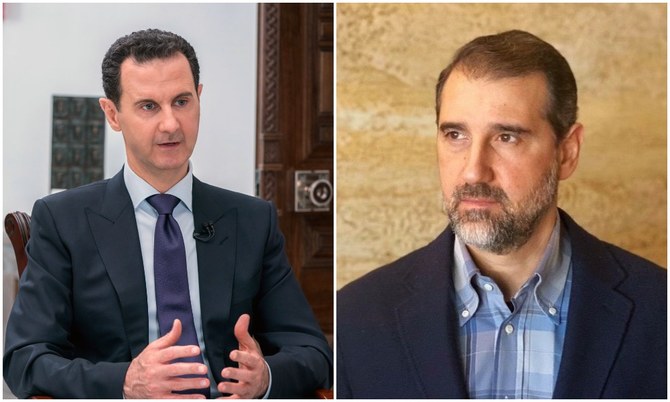
Imagine the surprise then when beginning in April, an apparent row between top members of the ruling family erupted straight into public view.
On one side of the dispute we have Bashar’s cousin Rami Makhlouf, whose father Mohammed was the brother of Anisa Makhlouf, who became Anisa Assad when she married Hafez.
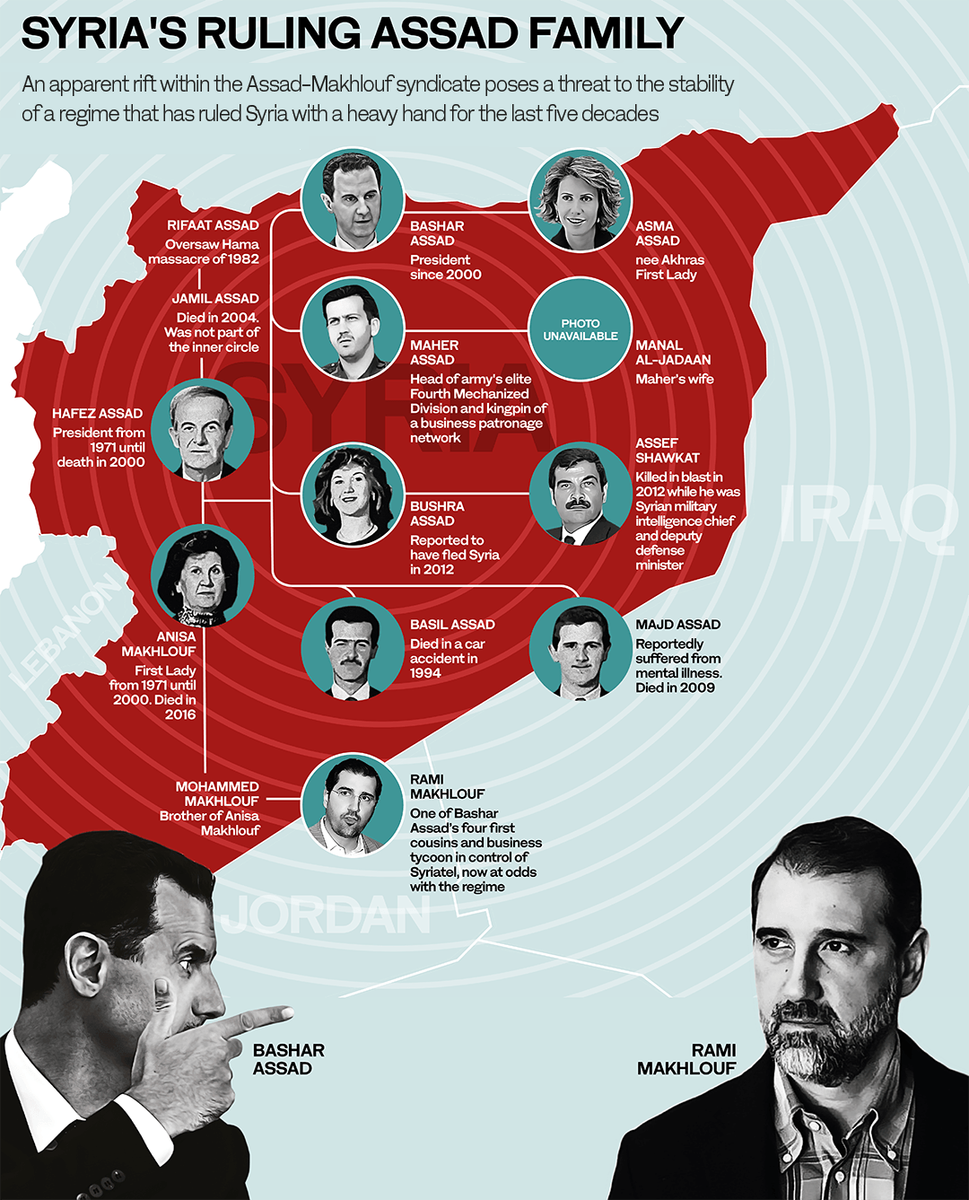
Often described as “the richest man in Syria,” Rami’s father after 1970 enjoyed Anisa’s support in taking control of most of the country’s economy.
Rami took over from his father, still enjoying his grandmother’s support until her illness in 2012 and eventual death in 2016.
On April 30, Rami posted the first of a series of videos on Facebook decrying the regime’s actions against him and his financial empire.
Staring into the camera, he asked: “Can you believe it? Security services have stormed the offices of Rami Makhlouf, their biggest funder and supporter, most faithful servant, and most prominent patron throughout the whole of the war … The pressure being put on us is intolerable, and inhumane.”
The regime, which means Bashar and possibly his wife Asma, is demanding that Syriatel, Rami’s giant telecommunications company, pay some $185 million in back taxes.
At first Rami appeared to refuse, appealing to his cousin in the videos. But with many of his top employees being rounded up and arrested over the last week, and the company facing the threat of seizure by the regime, now Rami claims to be willing to pay up.
He still resists pressure being put on him to resign, however, stating in his Facebook videos that this is a red line and that anyone who thinks he would resign “does not know me.”
Defiance is not the sort of thing people in Syria exhibit without dire punishments, of course.
Some think Rami is therefore engaged in some elaborate show in cahoots with Bashar, otherwise the former would never dare speak like this in public.
The show would be intended to demonstrate to Russia that rooting out corruption and raising money to pay back debts to Moscow are difficult, but that Bashar is working on it.
Would Russia, with its considerable intelligence assets in Syria, be fooled by such a display? Probably not.
Ordinary Syrians would likewise probably not accept such a show as evidence of an anti-corruption campaign.
Rami is also no ordinary Syrian. Over the years, he and his father took control of huge parts of Syria’s economy (up to 60 percent, according to the highest estimates), built their neo-patrimonial charities and even fielded their own Alawite Al-Bustan militia to fight in the civil war after 2011.
The militia alone had tens of millions of dollars in funding, and its fighters earned up to twice the pay of equivalent army personnel.
If anyone in Syria can publicly question the regime, it is Rami. Until recently he was the regime, occupying a place only below Bashar, his wife Asma, and his siblings Maher and Bushra.
The more likely story now unfolding in public in Syria involves intra-family jealousies and competition over a drastically shrinking economic pie.
Rami may indeed have proven resistant to demands that he contribute more to alleviating the regime’s economic woes, but the decision to move against his assets forcefully comes within a larger context.
While Bashar’s mother Anisa was alive and well, she would not have permitted any such actions against her other grandson.
From the time of her husband’s death in 2000 to her illness in 2012, accounts suggest that Anisa continued to favor Rami and kept Bashar’s Sunni wife Asma and her family from amassing too much power.
Asma’s family hails from the wealthy Sunni merchant classes of Aleppo and Homs, whose leading figures competed with the Makhlouf clan for business in Syria. Asma’s own charities also competed for prominence and influence with those of Rami.
As Anisa faded from the political scene, Asma’s influence began to rise. Hacked emails in 2012 showed Asma claiming that she was the “real dictator” in Syria.
Already in December 2019, just as increasing portions of Rami’s assets were being frozen under various pretexts by the Syrian state, the Daily Beast reported that “those of Asma’s paternal uncle, Tarif al-Akhras, were being thawed.”

Customers queue outside Syriatel, owned by businessman Rami Makhlouf, in the Syrian capital Damascus on May 11, 2020. (AFP)
The Daily Beast report added: “By September, Asma and a cadre of loyal officials who previously worked in her network of NGOs launched a hostile takeover of the Bustan Cooperative, a charitable organization run by Makhlouf through which the salaries of SSNP (the Syrian Social Nationalist Party) and other militiamen loyal to Rami had been paid.”
At the same time, Bashar’s younger brother Maher also appeared to view the Makhloufs with increasing suspicion, seeing them as competitors in Syria.
In August 2019, the regime disbanded Rami’s well-funded Al-Bustan militia. The SSNP, which functioned as a sort of fake opposition party in Syria, also saw the privileges of its members reduced at this time, presumably because of the Makhloufs’ association and prominent role within the party.
In December 2019 and March 2020, the regime seized assets from Rami’s petroleum companies — which he had been using to trade oil from the Kurdish- and American-controlled parts of the country — to pay off Syrian state budget deficits.
Those who had been before the war are concerned about the country and sacrificed with everything they have.
Rami Makhlouf, President Assad’s cousin and head of mobile operator Syriatel
The Makhlouf and Assad families have thus begun fighting over a revenue pie that has shrunk drastically since the outbreak of the civil war in 2011.
Understanding what has been happening between the two families offers us a glimpse into understanding the outbreak of the civil war in the first place.
Syria under the Assads was never ruled by terror alone. Generous public safety nets, free schooling, free health care, other services and various subsidies of an “Arab socialist state” likewise kept the population in line after Hafez took power in 1970.
Beginning in the mid-1980s but really gaining pace after Hafez’s death, however, increasing privatization of the economy and the selling off of state assets to politically connected individuals like Rami changed the Syrian social contract.
As the likes of Rami enriched themselves, average Syrians fell deeper into poverty. Especially after the end of Syria’s lucrative occupation of Lebanon in 2005, the economic crisis of 2008 and a series of droughts beginning in 2009, the plight of average Syrians became intolerable.
The uprising that began in 2011 thus represented average Syrians’ attempt to renegotiate their defunct social contract. The Assad regime responded to people’s demands with force.
The resulting economic collapse from the civil war now sees Bashar and his wife Asma likewise turning on cousin Rami for a greater share of Syria’s few remaining economic resources.
--------------------------------
David Romano is Thomas G. Strong Professor of Middle East Politics at Missouri State University



























