JUBA, South Sudan: The role of the Muslim Brotherhood in shaping Sudan’s continuing conflict is a cause for concern among experts, who warn that the group could influence the country’s military leaders and even determine the nation’s political direction.
As a transnational Islamist organization deeply rooted in Sudanese politics, the Muslim Brotherhood played a pivotal role in establishing the former Islamist government of Omar Bashir in 1989.

Sudan's strongman Omar al-Bashir (R) and breakaway Islamist Hassan al-Turabi met on March 14, 2014 for the first time in 14 years, as the government reached out to opponents after calls for reform. (AFP file photo)
Even after that government’s overthrow in 2019, the Brotherhood proved to be resilient and influential. Now, against the backdrop of the fighting between the Sudanese Armed Forces, or SAF, and the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces, or RSF, some fear that the group may attempt to make a comeback.
Over several decades, the Brotherhood was able to build support among various segments of Sudanese society through its advocacy of political Islam and social justice. During their rule, the Islamists implemented Sharia law — a move rejected by swathes of the population who adhered to Christianity and other local faiths, triggering a brutal civil war.
The fall of the Islamist government in 2019 marked an important turning point. However, concerns surrounding its lingering influence over Sudan’s military leadership have persisted.

Members of the Muslim Brotherhood rally in front of the Egyptian Embassy in Khartoum. (AFP File)
The Brotherhood’s influence has continued through para-police units affiliated with the former regime — units that have been accused of targeting women in response to their growing role in public life.
Differing visions of the role of Islam in Sudan’s democratic future have contributed to splits within the nation’s biggest political parties, providing the Brotherhood with new potential constituencies to exploit.
Following a 2021 agreement between Abdel Fattah Al-Burhan, head of the armed forces and the current de-facto ruler of Sudan, and Abdel-Aziz Al-Hilu, chair of the Sudan People’s Liberation Army, or SPLA-North, to separate religion and state, a schism emerged within the National Umma Party.
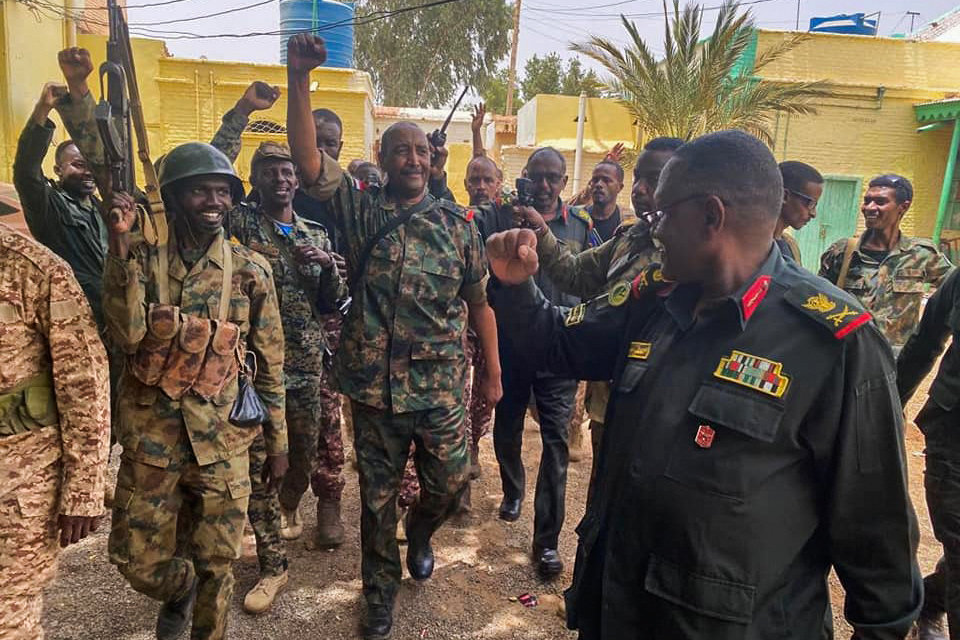

Sudanese army chief Fattah al-Burhan visiting the frontline in Khartoum amid fighting with paramilitary rivals in May. (AFP)
The party leadership suggested postponing the debate until the end of the transitional period, when a civilian-led government was expected to take over from Sudan’s military rulers. At the same time, however, the minister for religious affairs, Nasr Al-Din Mufreh, who was himself a National Umma Party member, began drafting legislation to ban religious-based political parties.
Following these developments, Umma officials issued conflicting statements on the matter.
Al-Wathiq Al-Berair, secretary general of the National Umma Party, denied that his party was founded on a religious basis. However, another party official later stated it followed the principles of the 1881 Mahdist revolution, which had both religious and national aspects.
Over the years, many Islamists have shifted their approach, having decided to focus on supporting “sectarian” parties as a bulwark against the political left.
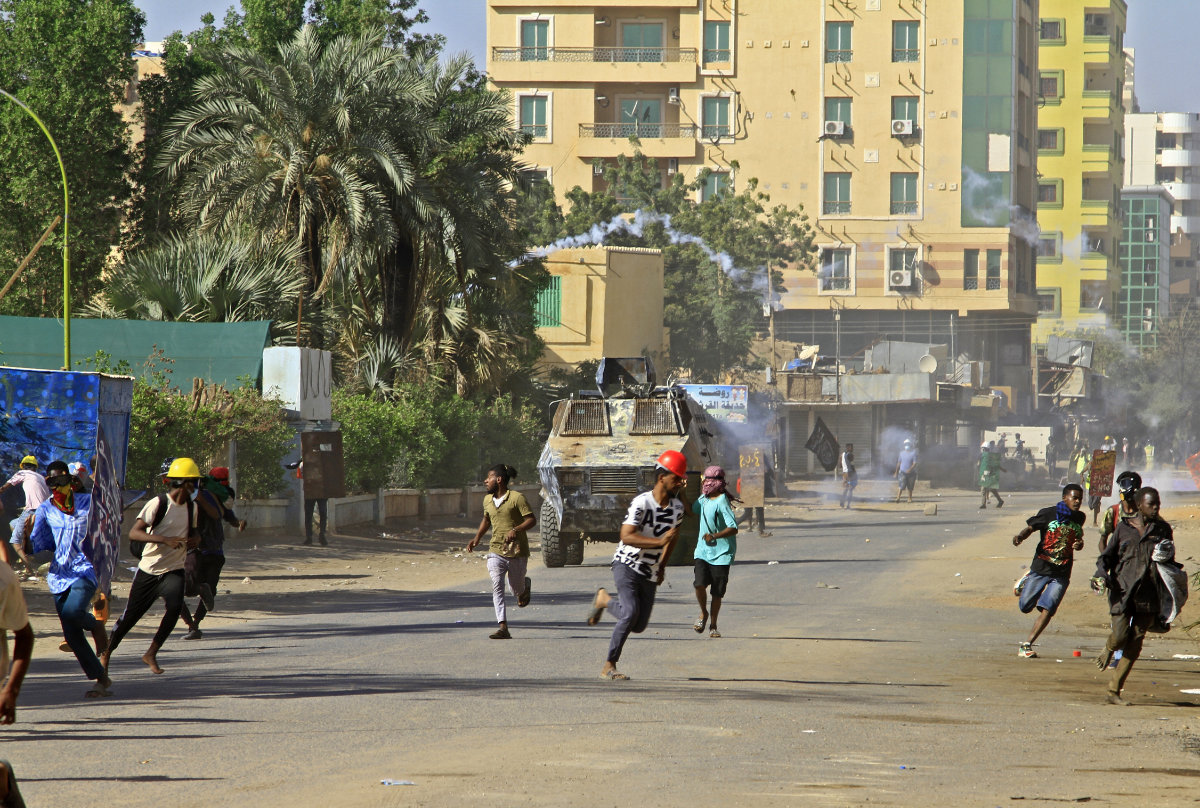
This photo taken on December 5, 2022, shows government security forces dispersing Sudanese activists demonstrating in Khartoum against a deal aimed at ending the crisis caused by the 2021 military coup. (AFP)
This new approach reflects an apparent recognition of their weakened position and failure to achieve their previous goals. The continuing demand among Islamists for early elections further emphasizes this shift in strategy.
“When the coup happened in October 2021 and afterward, the Muslim Brotherhood kept quiet,” Peter Schuman, a former deputy joint special representative of the UN–African Union Mission in Darfur, told Arab News.
“There are, though, individuals who have pursued a certain interest, particularly Ali Ahmed Karti,” he added, referring to Sudan’s former foreign minister, who served in the post under Bashir from 2010 to 2015.
Against this backdrop, some Sudanese generals may view the Brotherhood as a potential ally in their pursuit of power and control. Indeed, the group’s political base and ability to mobilize support among Islamist groups in the region make it an attractive partner.

Analysts fear the Muslim Brotherhood’s exclusionary interpretation of Islam could jeopardize the inclusive governance necessary for sustainable democracy in Sudan. (AFP File Photo)
Speaking to Arab News, Cameron Hudson, an analyst and consultant on African peace and security, said that “the involvement of the Muslim Brotherhood could exacerbate existing divisions within the military, leading to factionalism and power struggles.”
Since the conflict in Sudan erupted on April 15, the RSF has adopted a vehemently anti-Islamist tone, accusing groups such as the Brotherhood of infiltrating the SAF as a vehicle to further their political agenda.
“We are fighting Islamists, not SAF. This is the political issue,” Youssef Ezzat, political adviser to the RSF, told Arab News, rejecting claims that the paramilitary group was responsible for starting the war.
“Islamists hijacked the SAF, and they want to control the country. This is the root cause for the war … Islamists promised Al-Burhan to be a full-power president without RSF.”
While the political reality is probably more complicated than how the RSF seeks to portray it, the Muslim Brotherhood’s influence does call into question the durability of Sudan’s secular foundations.
“There are concerns that the group’s support for political Islam could undermine the country’s secular state institutions and lead to a more conservative and restrictive society,” Brian Adeba, deputy director of policy at The Sentry, a Washington-based investigative non-profit organization, told Arab News.
The impact of the Brotherhood’s involvement in Sudan might very well be felt beyond the country’s borders. Khalid Mustafa Medani, author of “Black Markets and Militants,” draws attention to the group’s wider regional network.
“Its actions in Sudan could have ramifications for neighboring countries and regional stability,” he told Arab News. Sudan’s location and porous borders create an environment that terrorist organizations such as Daesh could exploit for their own gain.
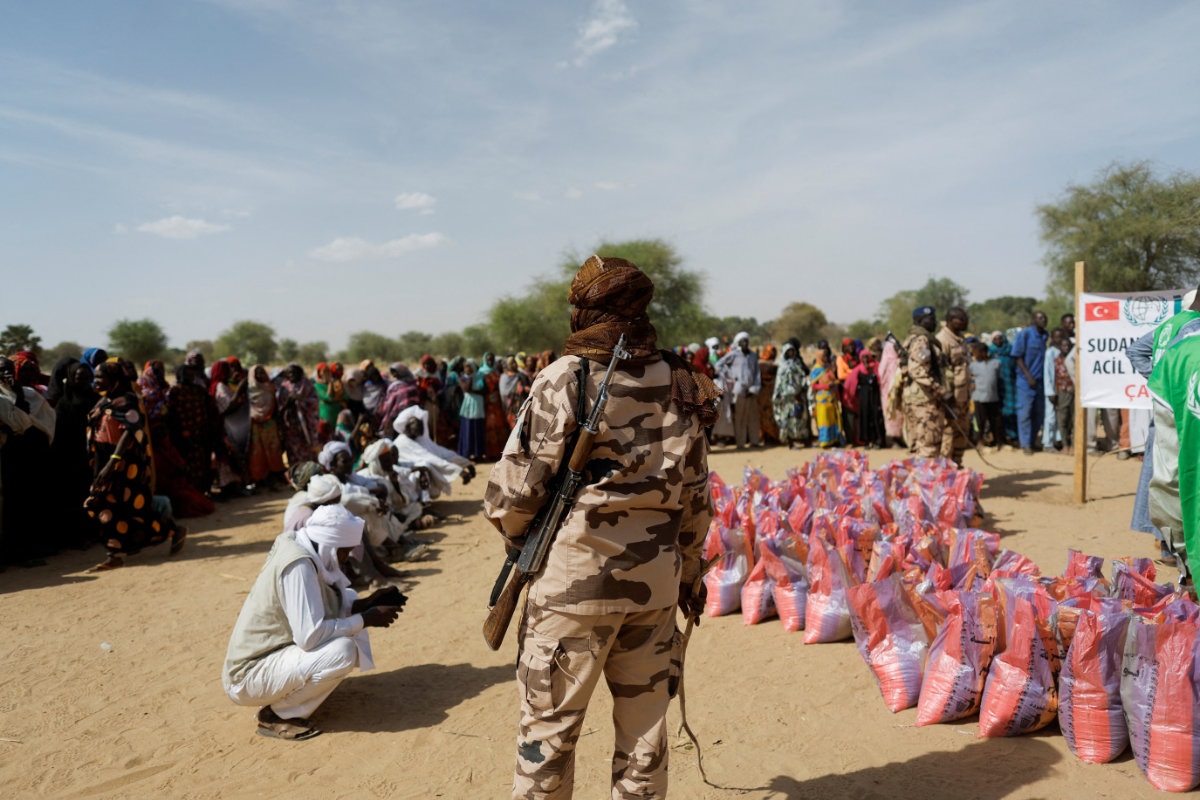

A soldier stands as Sudanese women who fled the violence in their country, wait to receive food supplies from a Turkish aid group IHH near the border between Sudan and Chad in Koufroun, Chad, on May 7, 2023. (REUTERS/File Photo)
To safeguard Sudan’s democratic values and foster political pluralism, experts such as Sargis Sangari, CEO of the Near East Center for Strategic Engagement, argue that a future transitional government needs to confront the Brotherhood’s influence and counter its narrative, while underscoring the importance of alternative channels for political participation.
“The Muslim Brotherhood’s dominant presence has marginalized other ethnic groups and led to the persecution of religious minorities,” Sangari said.
For his part, Adeba highlights the Brotherhood’s extensive network and mobilization capabilities within the country, pointing out how it has successfully infiltrated political parties and civil society organizations, enabling it to influence Sudan’s political landscape.
Such successes have raised concerns among experts over the group’s ability to shape Sudanese political discourse and limit pluralism.
The experts say that the conflict has presented the Brotherhood with an opportunity to capitalize on the power vacuum created by the ousting of Bashir.
International affairs expert, Gordon Kachola, says that the group was able to take advantage of the transitional period, using its networks to fuel sectarian tensions and exacerbate the crisis. This has further complicated efforts to establish stability and consolidate power in Sudan.
Peter Schuman, an expert in regional security, believes the Brotherhood poses a challenge to Sudan’s long-term democratic aspirations. In his view, the group’s presence undermines the establishment of democratic institutions, thus hindering the country’s journey toward stability.
Schuman also believes the Brotherhood’s exclusionary interpretation of Islam could jeopardize the inclusive governance necessary for sustainable democracy in Sudan.
Hudson, the analyst and consultant, also has concerns about the Muslim Brotherhood’s role in Sudan’s transition, arguing that the group’s influence could impede the development of democratic institutions and stifle dissenting voices.

The resurgence of the Muslim Brotherhood in Sudan could impede the development of democratic institutions and stifle dissenting voices, warn experts. (AFP File Photo)
He believes that Sudan’s transitional government should address the Brotherhood’s influence to ensure the preservation of democratic values. As the international community, regional actors and Sudanese society at large have been demanding an end to the fighting, Hudson says that “negotiations without the participation and monitoring of civilians are hard to be understood.”
The Brotherhood’s control over various sectors, particularly agriculture, has also brought to the fore its impact on Sudan’s economy and society.
Medani says that the group’s control over the black market, in particular, has allowed it to sustain its power while contributing to the impoverishment of Sudanese society.
Sudan’s economic crisis, exacerbated by international sanctions and government policies, has fueled public discontent and protests, which Brotherhood-aligned politicians have in the past struggled to contain.
When Sudan eventually arrives at its post-conflict destination, the influence of the Brotherhood will remain a contentious issue. Balancing the desire for stability with the preservation of democratic values will be a delicate task.