KYIV, Ukraine: He and his parents were among the last in their village to take a Russian passport, but the pressure was becoming unbearable.
By his third beating at the hands of the Russian soldiers occupying Ukraine’s Kherson region, Vyacheslav Ryabkov caved. The soldiers broke two of his ribs, but his face was not bruised for his unsmiling passport photo, taken in September 2023.
It wasn’t enough.
In December, they caught the welder on his way home from work. Then one slammed his rifle butt down on Ryabkov’s face, smashing the bridge of his nose.
“Why don’t you fight for us? You already have a Russian passport,” they demanded. The beating continued as the 42-year-old fell unconscious.
“Let’s finish this off,” one soldier said. A friend ran for Ryabkov’s mother.
Russia has successfully imposed its passports on nearly the entire population of occupied Ukraine by making it impossible to survive without them, coercing hundreds of thousands of people into citizenship ahead of elections Vladimir Putin has made certain he will win, an Associated Press investigation has found. But accepting a passport means that men living in occupied territory can be drafted to fight against the same Ukrainian army that is trying to free them.
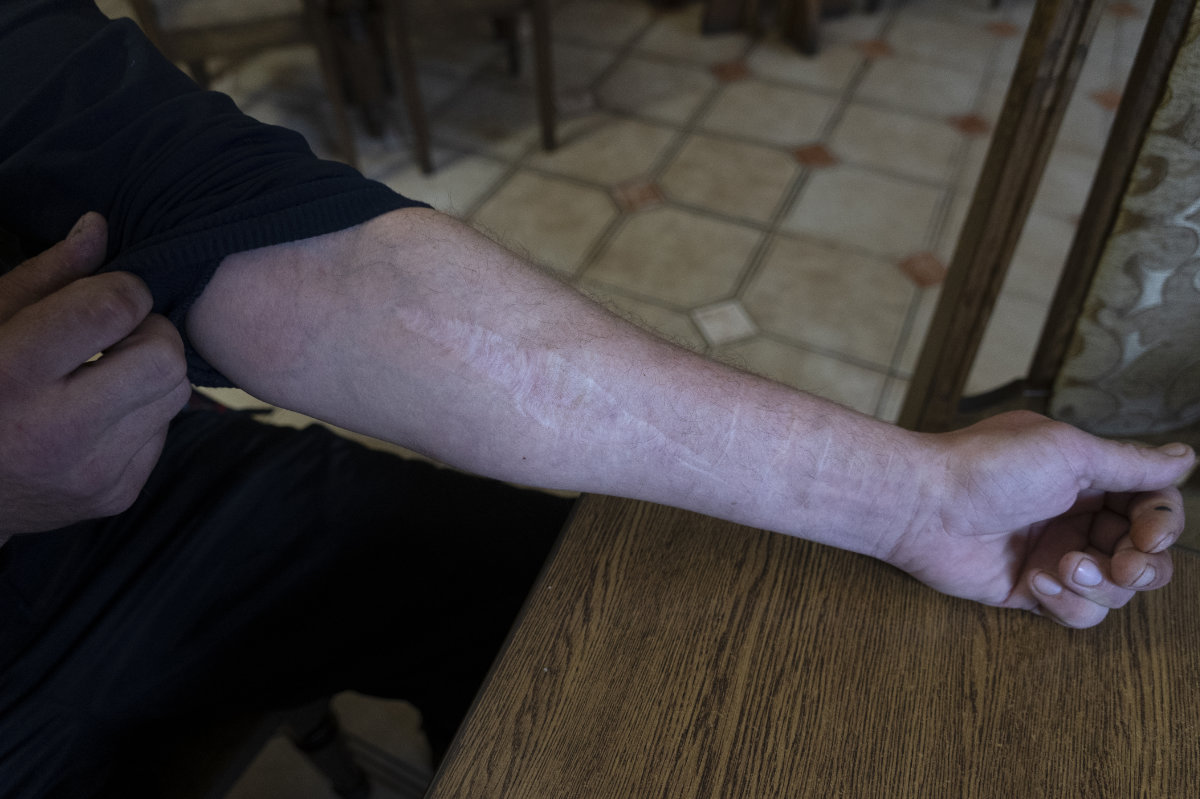
Vyacheslav Ryabkov of Ukraine's Kherson region shows the scars on his arms caused by Russian soldiers who cut him with a knife to coerce into accepting Russian domination. (AP)
A Russian passport is needed to prove property ownership and keep access to health care and retirement income. Refusal can result in losing custody of children, jail – or worse. A new Russian law stipulates that anyone in the occupied territories who does not have a Russian passport by July 1 is subject to imprisonment as a “foreign citizen.”
But Russia also offers incentives: a stipend to leave the occupied territory and move to Russia, humanitarian aid, pensions for retirees, and money for parents of newborns – with Russian birth certificates.
Every passport and birth certificate issued makes it harder for Ukraine to reclaim its lost land and children, and each new citizen allows Russia to claim a right – however falsely – to defend its own people against a hostile neighbor.
The AP investigation found that the Russian government has seized at least 1,785 homes and businesses in the Donetsk and Zaporizhzhia regions alone. Ukraine’s Crimean leadership in exile reported on Feb. 25 that of 694 soldiers reported dead in recent fighting for Russia, 525 were likely Ukrainian citizens who had taken Russian passports since the annexation.
AP spoke about the system to impose Russian citizenship in occupied territories to more than a dozen people from the regions, along with the activists helping them to escape and government officials trying to cope with what has become a bureaucratic and psychological nightmare for many.
Ukraine’s human rights ombudsman, Dmytro Lubinets, said “almost 100 percent … of the whole population who still live on temporarily occupied territories of Ukraine” now have Russian passports.
Under international law dating to 1907, it is forbidden to force people “to swear allegiance to the hostile Power.” But when Ukrainians apply for a Russian passport, they must submit biometric data and cell phone information and swear an oath of loyalty.
“People in occupied territories, these are the first soldiers to fight against Ukraine,” said Kateryna Rashevska, a lawyer who helped Ukraine bring a war crimes case against Putin before the International Criminal Court. “For them, it’s logical not to waste Russian people, just to use Ukrainians.”
Changing the law
The combination of force and enticement when it comes to Russian passports dates to the annexation of Crimea in 2014. Russian citizenship was automatically given to permanent residents of Crimea and anyone who refused lost rights to jobs, health care and property.
Nine months into the Russian occupation of the peninsula, 1.5 million Russian passports had been issued there, according to statistics issued by the Russian government in 2015. But Ukrainians say it was still possible to function without one for years afterward.
Beginning in May 2022, Russia passed a series of laws to make it easier to obtain passports for Ukrainians, mostly by lifting the usual residency and income requirements. In April 2023 came the punishment: Anyone in the occupied territories who did not accept Russian citizenship would be considered stateless and required to register with Russia’s Internal Affairs Ministry.

Russian officials threatened to withhold access to medical care for those without a Russian passport, and said one was needed to prove property ownership. Hundreds of properties deemed “abandoned” were seized by the Russian government.
“You can see it in the passport stamps: If someone got their passport in August 2022 or earlier, they are most certainly pro-Russian. If a passport was issued after that time – it was most certainly forced,” said Oleksandr Rozum, a lawyer who left the occupied city of Berdyansk and now handles the bureaucratic gray zone for Ukrainians under occupation who ask for his help, including property records, birth and death certificates and divorces.
The situation is different depending on the whims of the Russian officials in charge of a particular area, according to interviews with Ukrainians and a look at the Telegram social media accounts set up by occupation officials.
In an interview posted recently, Yevgeny Balitsky, the Moscow-installed governor in Zaporizhzhia, said anyone who opposed the occupation was subject to expulsion. “We understood that these people could not be won over and that they would have to be dealt with even more harshly in the future,” he said. Balitsky then alluded to making “some extremely harsh decisions that I will not talk about.”
Even children are forced to take Russian passports.
A decree signed Jan. 4 by Putin allows for the fast-tracking of citizenship for Ukrainian orphans and those “without parental care,” who include children whose parents were detained in the occupied territories. Almost 20,000 Ukrainian children have disappeared into Russia or Russian-held territories, according to the Ukrainian government, where they can be given passports and be adopted as Russian citizens.
“It’s about eradication of identity,” said Rashevska, the lawyer involved in the war crimes case.
Natalia Zhyvohliad, a mother of nine from a suburb of Berdyansk, had a good idea of what was in store for her children if she stayed.
Zhyvohliad said about half her town of 3,500 people left soon after for Ukrainian-held lands, some voluntarily and some deported through the frontlines on a 40-kilometer (25-mile) walk. Others welcomed the occupation: Her goddaughter eagerly took Russian citizenship, as did some of her neighbors.
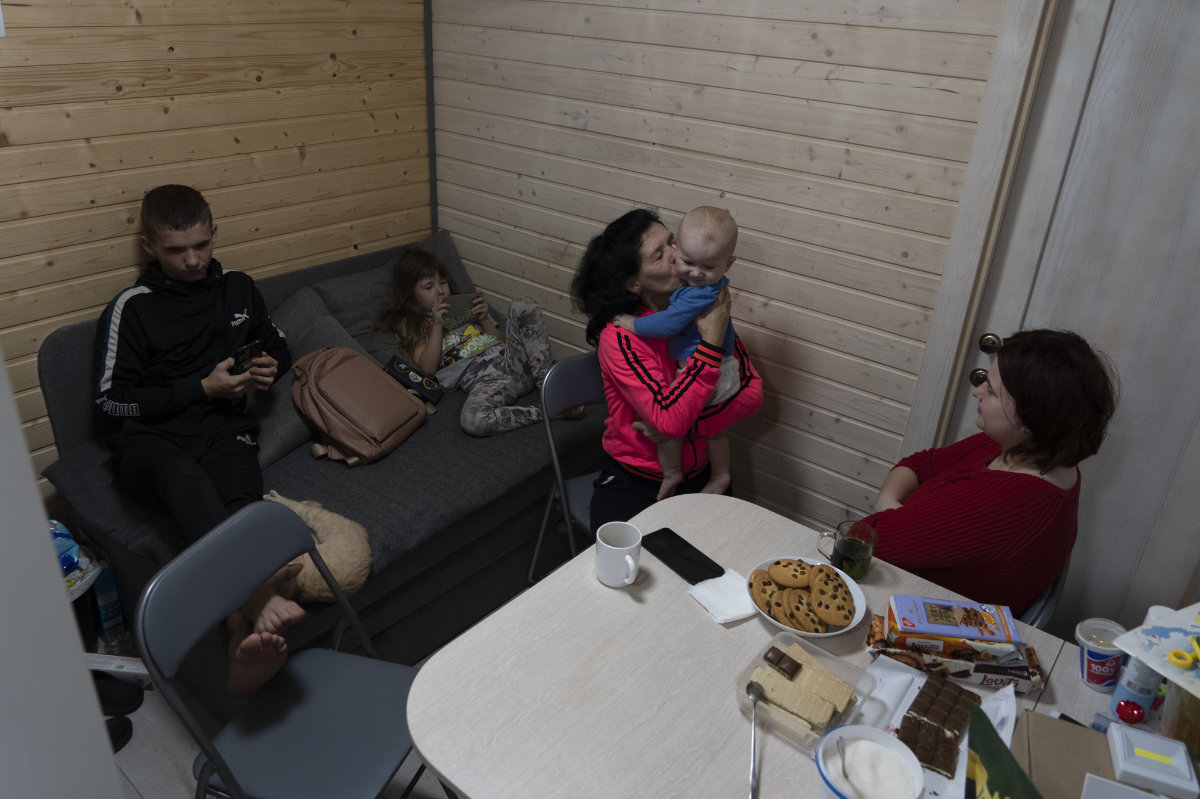

50-year-old Natalia Zhyvohliad, an internally displaced person from Nova Petrivka in the Zaporizhzhia region of Ukraine, with her children, daughter-in-law and grandson in their temporary modular house in Kolomyya, Ivano-Frankivsk region on Feb. 13, 2024. (AP)
But she said plenty of people were like her – those the Russians derisively call “waiters”: People waiting for a Ukrainian liberation. She kept her younger children, who range in age from 7 to 18, home from school and did her best to teach them in Ukrainian. But then someone snitched, and she was forced to send them to the Russian school.
At all hours, she said, soldiers would pound on her door and ask why she didn’t have a passport yet. One friend gave in because she needed medicine for a chronic illness. Zhyvohliad held out through the summer, not quite believing the threats to deport her and send her brood to an orphanage in Russia or to dig trenches.
Then last fall, the school headmaster forced her 17-year-old and 18-year-old sons to register for the draft and ordered them to apply for passports in the meantime. Their alternative, the principal said, was to explain themselves to Russia’s internal security services.
By the end of 2023, at least 30,000 Crimean men had been conscripted to serve in the Russian military since the peninsula was annexed, according to a UN report. It was clear to Zhyvohliad what her boys risked.
With tears in her eyes and trembling legs, she went to the passport office.
“I kept a Ukrainian flag during the occupation,” she said. “How could I apply for this nasty thing?”
She hoped to use it just once — at the last Russian checkpoint before the crossing into Ukrainian-held territory.
When Zhyvohliad reached what is known as the filtration point at Novoazovsk, the Russians separated her and her two oldest boys from the rest of the children. They had to sign an agreement to pass a lie detector test. Then Zhyvohliad was pulled aside alone.
For 40 minutes, they went through her phone, took fingerprints and photos and questioned her, but they ultimately let her through. The children were waiting for her on the other side. She misses her home but doesn’t regret leaving.
“I waited until the last moment to be liberated,” she said. “But this thing with my kids possibly being drafted was the last straw.”
Weaponizing health care
Often the life-or-death decision is more immediate.
Russian occupation officials have said the day is coming soon when only those with Russian passports and the all-important national health insurance will be able to access care. For some, it’s already here.
The international organization Physicians for Human Rights documented at least 15 cases of people being denied vital medical care in occupied territories between February 2023 and August 2023 because they lacked a Russian passport. Some hospitals even featured a passport desk to speed the process for desperate patients. One hospital in Zaporizhzhia oblast was ordered to close because the medical staff refused to accept Russian citizenship.
Alexander Dudka, the Russian-appointed head of the village of Lazurne in the Kherson region, first threatened to withhold humanitarian aid from residents without Russian citizenship. In August, he added medicine to the list of things the “waiters” would no longer have access to.
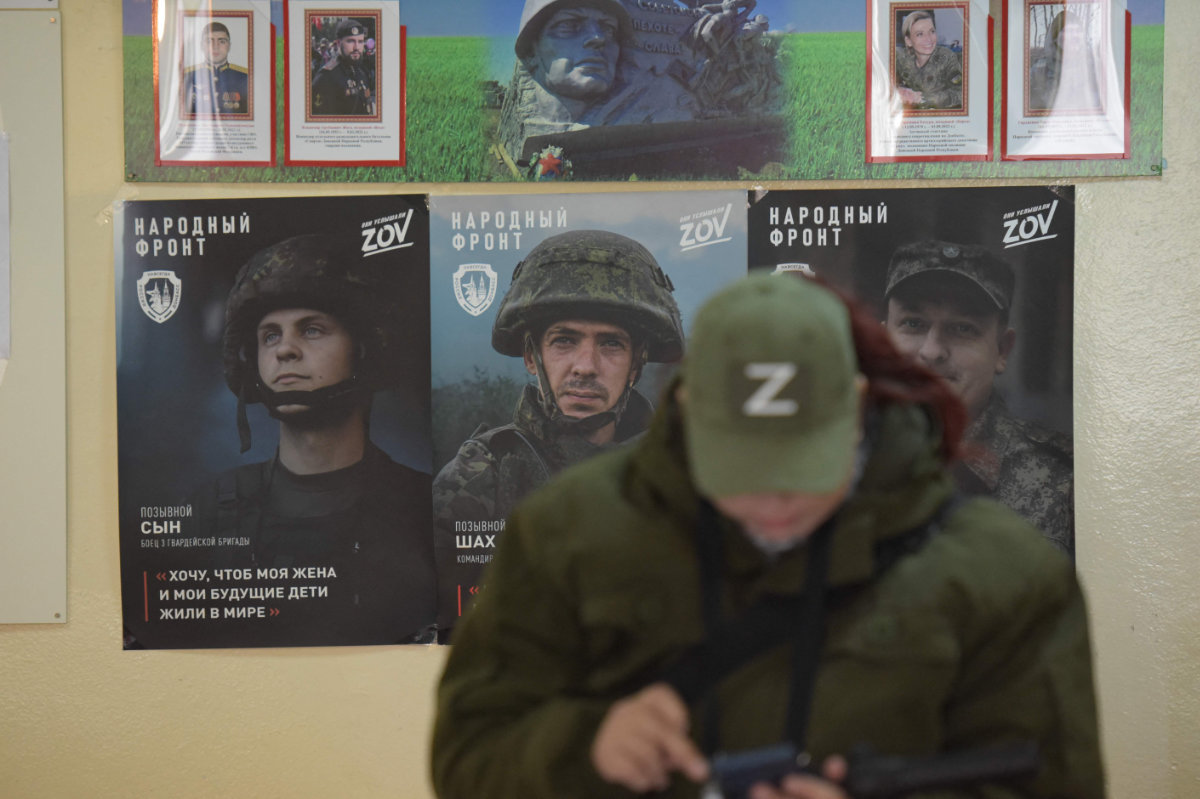

A woman is seen in front of posters and photographs of servicemen at a polling station during Russia's presidential election in Donetsk, Russian-controlled Ukraine, on March 16, 2024. (AFP)
Residents, he said in the video on the village Telegram channel, “must respect the country that ensures their safety and which is now helping them live.”
As of Jan. 1, anyone needing medical care in the occupied region must show proof they have mandatory national health insurance, which in turn is only available to Russian citizens.
Last year, “if you weren’t scared or if you weren’t coerced there were places where you could still get medical care,” said Uliana Poltavets, a PHR researcher. “Now it is impossible.”
Dina Urich, who arranges the escapes from occupied territory with the aid group Helping to Leave, said about 400 requests come in each month, but they only have the money and staff for 40 evacuations. Priority goes to those who need urgent medical care, she said. And Russian soldiers at the last checkpoints have started turning back people without the Russian passports.
“You have people constantly dying while waiting for evacuation due to a lack of health care,” she said. ““People will stay there, people will die, people will experience psychological and physical pressure, that is, some will simply die of torture and persecution, while others will live in constant fear.”
Importing loyalty
Along with turning Ukrainians into Russians throughout the occupied territories, the Russian government is bringing in its own people. It is offering rock bottom mortgage rates for anyone from Russia who wants to move there, replacing the Ukrainian doctors, nurses, teachers, police and municipal workers who are now gone.
Half of Zhyvohliad’s village left, either at the start of the war when things looked dark for the Kherson region or after being deported across the frontline by occupation officials. The school principal’s empty home was taken over by a Russian-appointed replacement.
Artillery and airstrikes damaged thousands of homes in the port city of Mariupol, which was besieged by Russian forces for months before falling under their control. Most of the residents fled into Ukrainian-held territory or deep inside Russia. Russians often take over the property.
Russia also offered “residential certificates” and a 100,000 ruble ($1,000) stipend to Ukrainians willing to accept citizenship and live in Russia. For many people tired of listening to the daily sounds of battle and afraid of what the future might bring, it looked like a good option.
This again follows Russia’s actions after the annexation of Crimea: By populating occupied regions with Russian residents, Russia increasingly cements its hold on territories it has seized by force in what many Ukrainians describe as ethnic cleansing.
The process is only accelerating. After capturing the town of Adviivka last month, Russia swooped in with the passports in a matter of days.
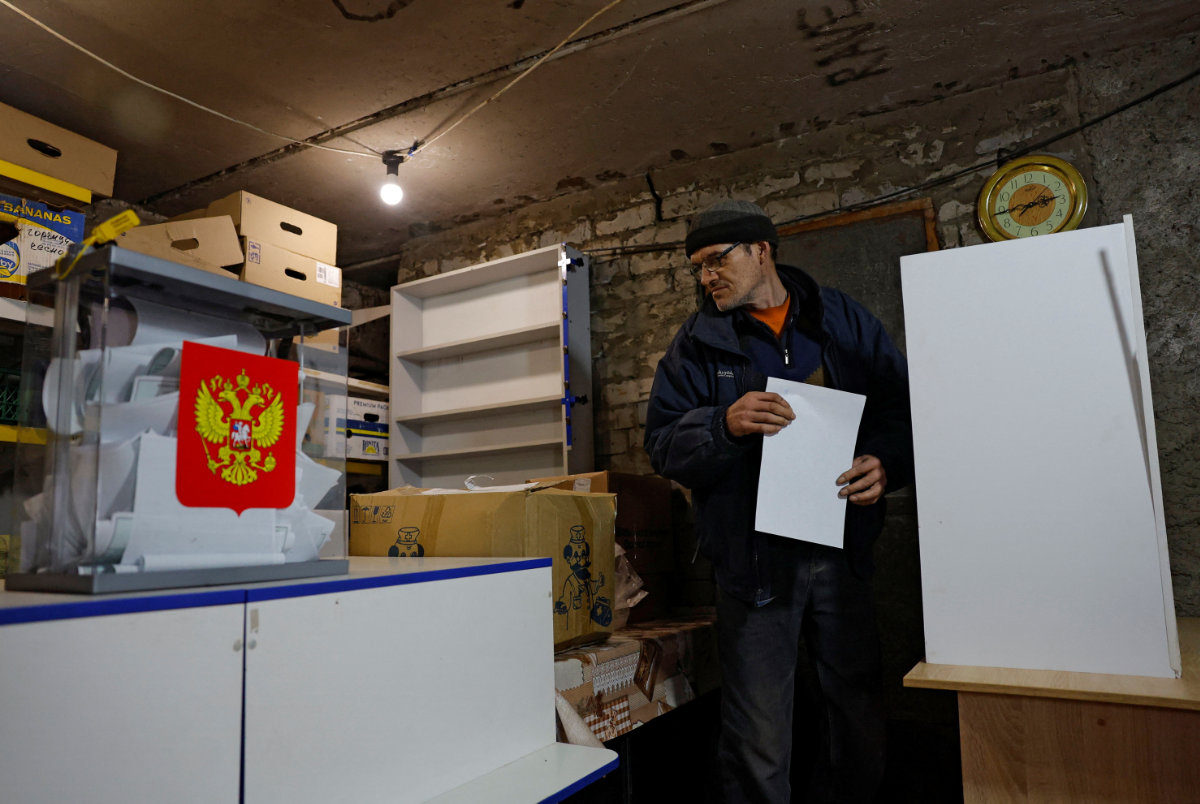

Local resident Sergey casts his vote into a mobile ballot box in the basement of a destroyed apartment building in the town of Avdiivka in Russian-controlled Donetsk Region, during Russia's presidential election on March 16, 2024. (REUTERS)
The neighboring Kherson town of Oleshky essentially emptied after the flooding caused by the explosion of the Kakhovka Dam. The housing stipend in Russia looked fabulous by comparison to the shelling and rising waters, said Rima Yaremenko.
She didn’t take it, instead making her way through Russia to Latvia and then to Poland. But she believes the Russians took the opportunity to drive the “waiters” from Oleshky.
“Maybe they wanted to empty the city,” she said. “They occupied it, maybe they thought it would be theirs forever.”
Ryabkov said he was offered the housing stipend when he filled out his passport paperwork but turned it down. He knows plenty of people who accepted though.
By the time the Russian soldiers caught Ryabkov in the street, in December, everyone in his village was either gone or had Russian citizenship. When his mother arrived, he was barely recognizable beneath all the blood and the Russian guns were trained on him. She flung herself over his body.
“Shoot him through me,” she dared them.
They couldn’t bring themselves to shoot an elderly woman, and she eventually dragged him home. They started preparations to leave the next day.
It took time, but they made it out using the Russian passports.
“When I saw our yellow and blue flag, I started to cry,” he said. “I wanted to burn the Russian passport, destroy it, trample it.”































