LONDON: Syrian refugees in Lebanon are in an impossible fix, unable to safely return home while also facing mounting hostility from host communities and local authorities, especially following the death of a Lebanese Forces party official, allegedly at the hands of Syrian criminals.
Pascal Suleiman, the Byblos District coordinator of the Christian-based party, was reportedly kidnapped and later killed in a Syrian area near the Lebanese border. Seven Syrian nationals were arrested on suspicion of killing Suleiman in what was dubbed a botched carjacking.
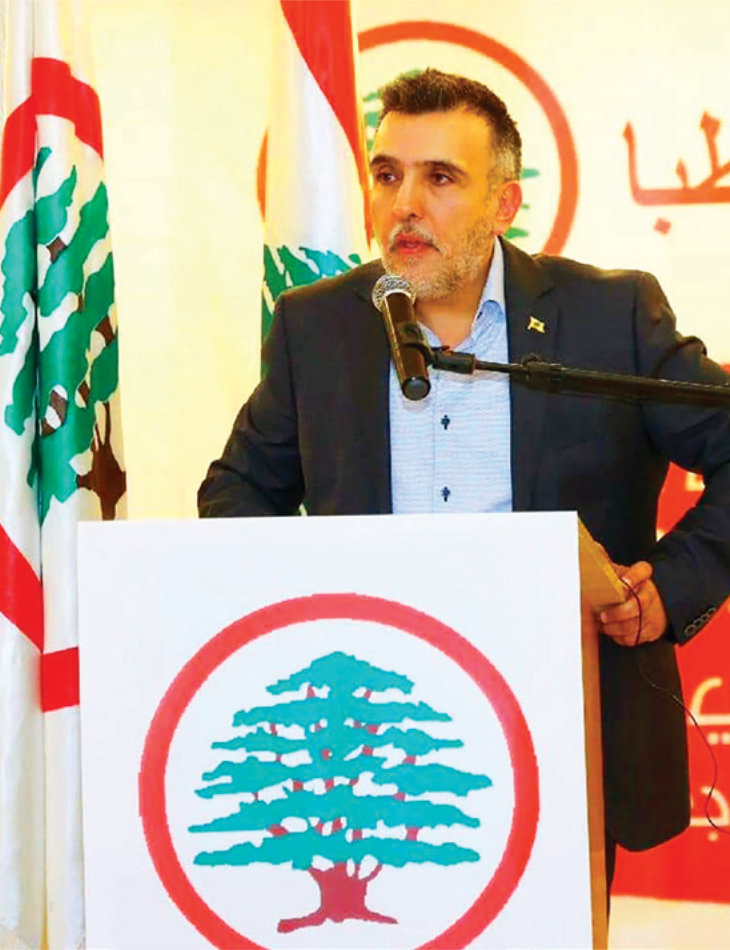

The killing of Pascal Suleiman, the Byblos District coordinator of the Christian-based Lebanese Forces party, is being blamed on Syrians but party leaders are not convinced. (AFP/File Photo)
The Lebanese Forces and its allies were not fully convinced that Syrians were behind the killing, which took place in an area controlled by its Hezbollah rivals, suggesting that Lebanese authorities were using the Syrians as a convenient patsy.
Although the scapegoating of Syrians in Lebanon has been commonplace since the Syrian civil war began in 2011, dispersing millions of refugees throughout the region, the murder of Suleiman has triggered a fresh wave of violence and vitriol against displaced households.
INNUMBERS
90% Syrian households in Lebanon living in extreme poverty.
52% Live in dangerous, sub-standard or overcrowded shelters. 80% Lack legal residency, leaving them vulnerable to exploitation.
100k Resettled from Lebanon to third countries since 2011.
Haneen, a Syrian university student whose name has been changed for her safety, described recently witnessing a group of Lebanese men assaulting and hurling abuse at a man they labeled “Souri” (Syrian).
“The slaps were so loud, I felt as if they were falling on my face,” she told Arab News.
Videos have emerged on social media in recent days showing Lebanese Forces supporters venting their fury on random Syrians in the street — many of them refugees. Angry mobs also vandalized cars with Syrian license plates and looted Syrian-owned businesses.

People march in Lebanon's northern port city of Tripoli on April 28, 2023, to protest against the forcible deportation of Syrian refugees. (AFP/File)
Other videos showed Lebanese men on motorcycles roaming the streets in various parts of the country, including Keserwan and Burj Hamoud, where they ordered Syrian occupants to leave their homes and businesses within 48 hours.
Intercommunal tensions in Lebanon have been stoked further by the rhetoric of Lebanese politicians, who frequently blame the country’s many ills on the presence of more than 1.5 million Syrian refugees.
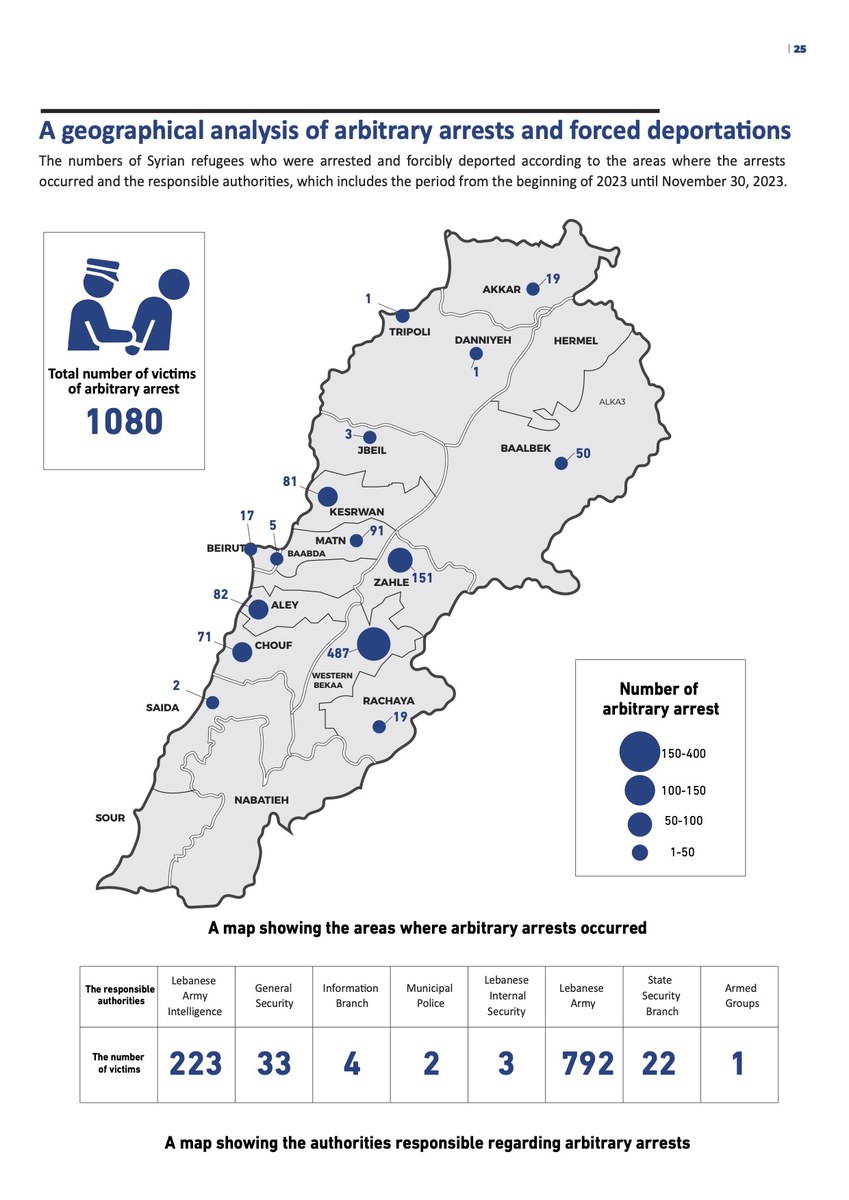
Infographic courtesy of Access Center For Human Rights (ACHR)
Between April and May 2023, the Lebanese army arbitrarily arrested and deported thousands of Syrians, according to Human Rights Watch.
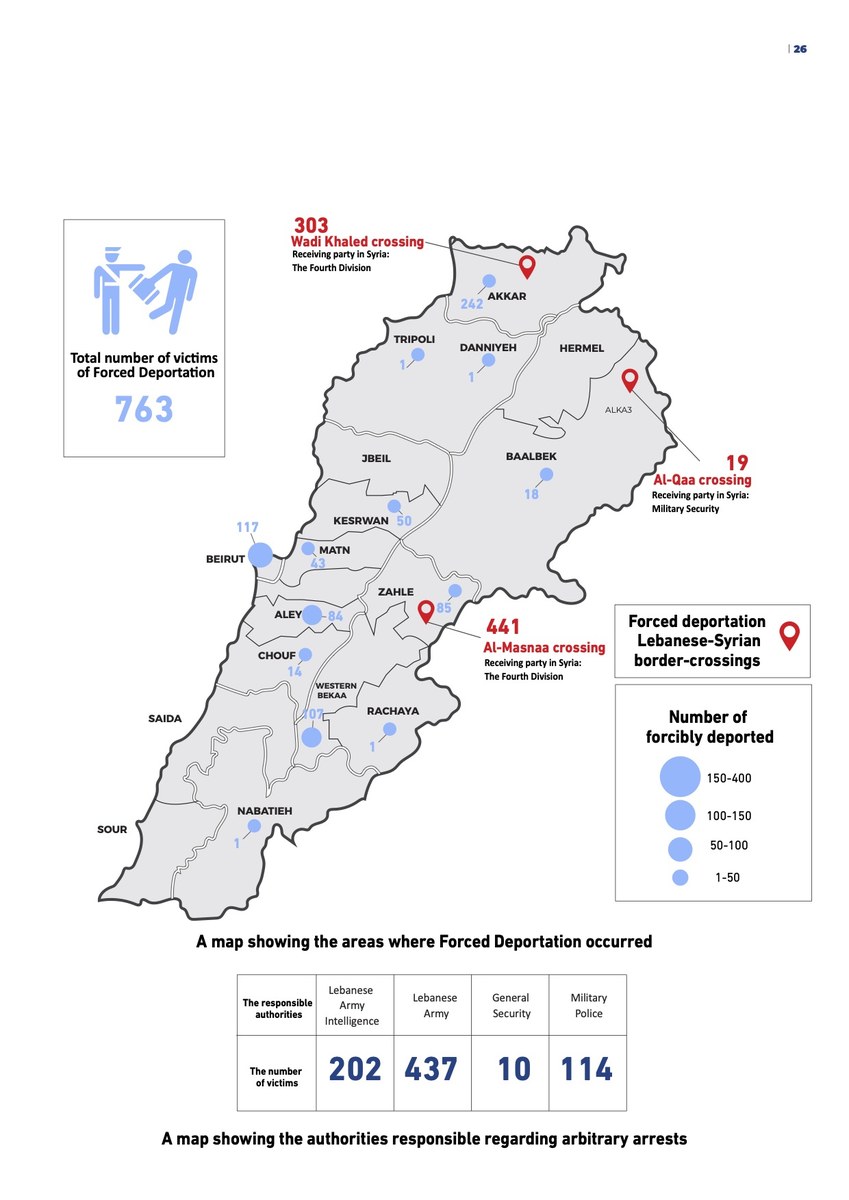
Infographic courtesy of Access Center For Human Rights (ACHR)
In a recent press conference, Bassam Mawlawi, the acting interior minister, said the country “will become stricter in granting residency permits and dealing with (Syrians) residing in Lebanon illegally.”
He claimed that “many crimes are being committed by Syrians” and stressed that the “Syrian presence in Lebanon can no longer be tolerated and is unacceptable.”
In October last year, he even sought to portray Syrian refugees as a danger to the country’s “existence” and “a threat to Lebanon’s demographics and identity.”
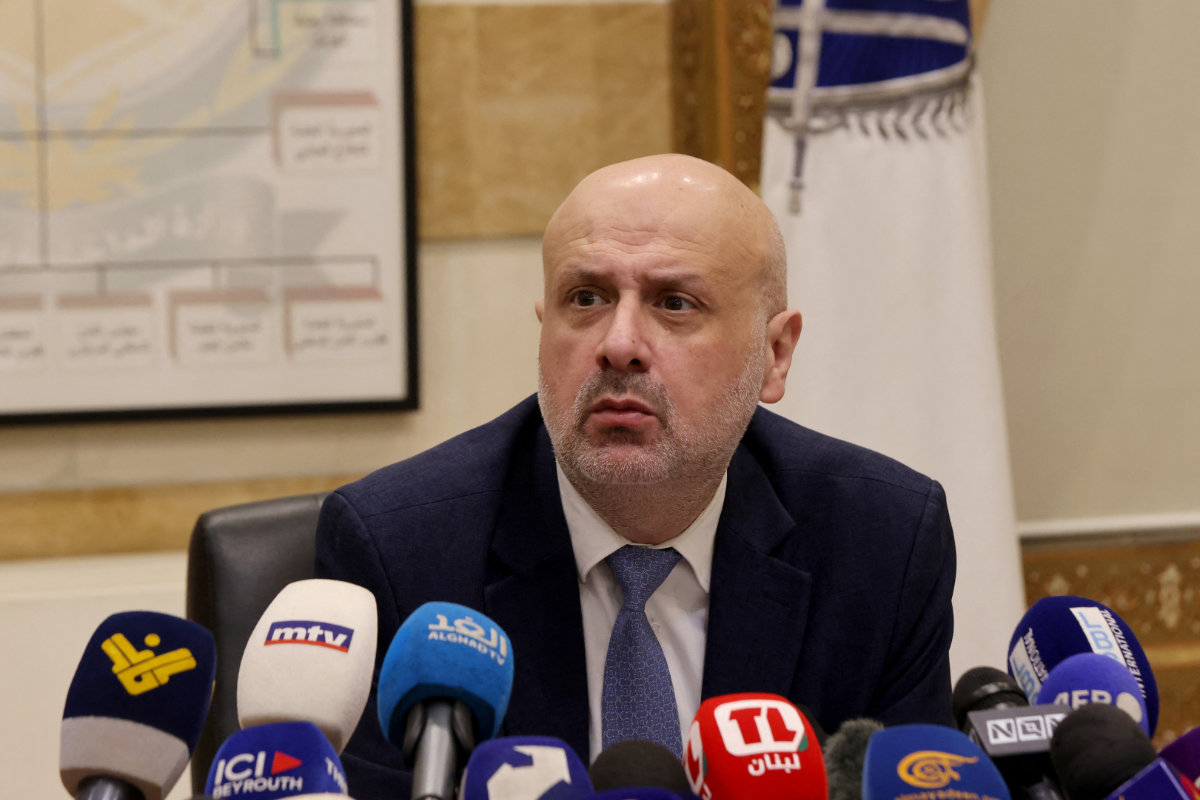

Lebanese Interior Minister Bassam al-Mawlawi speaks during a press conference on April 9, 2024, about the killing of local politician Pascal Suleiman on April 9, 2024. Lebanese officials blamed Syrian refugees, but leaders of the Lebanese Forces party were unconvinced. (AFP/File photo)
Echoing these sentiments was Abdallah Bou Habib, the acting foreign minister, who during a visit to the Greek capital Athens on April 8 described the number of Syrians in Lebanon as “a problem.”
Just days before Suleiman’s death, Amin Salam, Lebanon’s economy minister, said the caretaker government should declare a “state of emergency” regarding Syrian refugees.
Karam Shaar, a senior fellow at the Newlines Institute for Strategy and Policy, a nonpartisan Washington think tank, said Lebanese politicians were showing signs of “hysteria” over the Syrian presence in Lebanon.
ALSO READ: Lebanon PM warns Syrian refugees pose ‘danger to the nation’
While “part of that is understandable and fair,” Shaar told Arab News that “part of it is just Lebanese politicians scapegoating their failures and pinning them on Syrians.”
Omar Al-Ghazzi, an associate professor of media and communications at the London School of Economics, acknowledged that the influx had “made long-standing economic problems worse, whether in terms of infrastructure, public services and unemployment, particularly as Lebanese leaders stand accused of making financial profit from international aid.
“However, rather than blaming leaders and the political system for the collapsed economy in Lebanon, it became a convenient narrative to blame Syrians.”
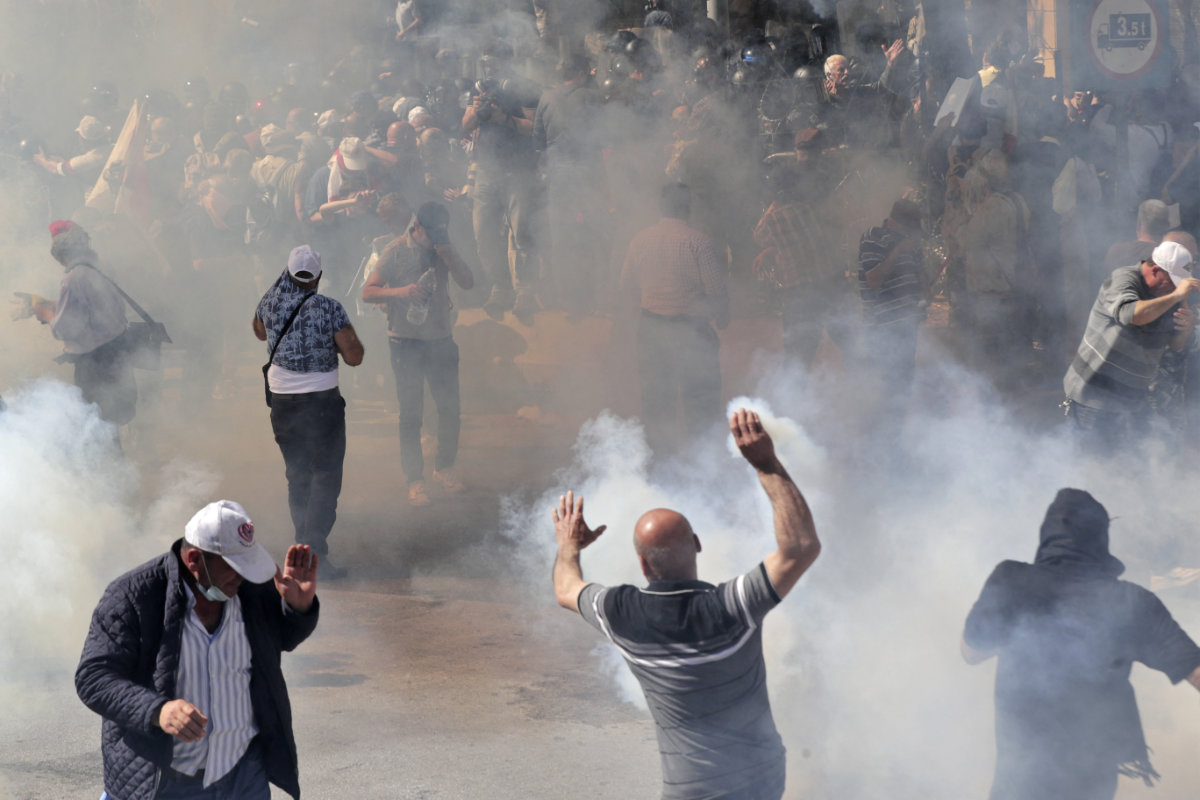

Lebanese demonstrators clash with security forces during a protest demanding better pay and living conditions in the capital Beirut on April 18, 2023 amid deteriorating living conditions, as the currency plummeted to new lows against the dollar. (AFP/File photo)
Furthermore, he told Arab News: “Sunni-Shiite tensions during the Syrian war, and Christian fears of Muslim dominance, have made any discussion of Syrian refugees take the form of a toxic and violent discourse — as if anti-Syrianness is the one thing that the divided Lebanese could agree on.”
Anti-Syrian sentiments in Lebanon did not first emerge with the influx of refugees after 2011. They have far deeper historical roots.
“Since Lebanon’s independence, Lebanese political culture has sustained a sense of superiority over the country’s Arab neighbors, mainly Palestinians and Syrians, as well as a sense of being threatened by their presence and influence,” said Al-Ghazzi.
“Following the end of the Lebanese civil war, the hegemony of the Syrian regime in Lebanon exacerbated an anti-Syrianness that often took the shape of discrimination against Syrian laborers.”
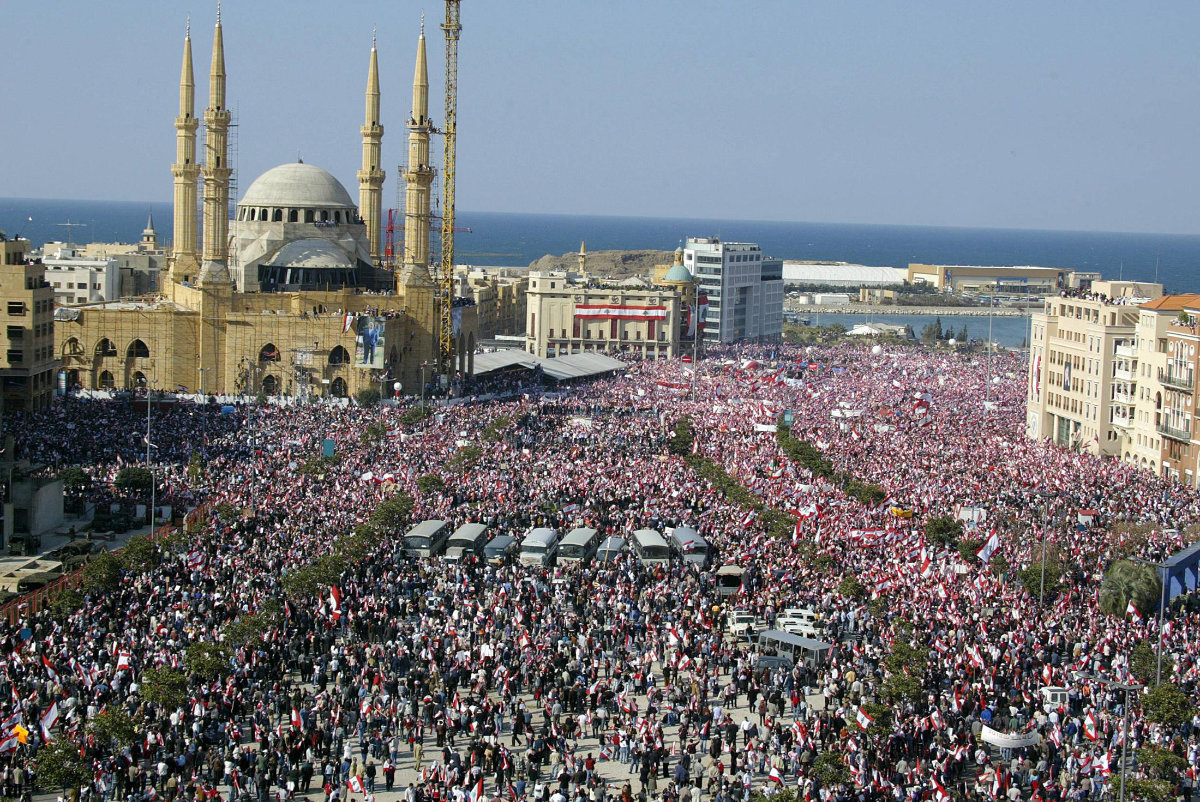

Tens of thousands of Lebanese citizens pack Martyrs Square in downtown Beirut on March 14, 2005, to press demands for justice for assassinated former prime minister Rafiq Hariri and for an end to Syrian military domination of Lebanon. (AFP/File photo)
However, Al-Ghazzi believes “this renewed racism cannot be separated from the rise of fascism and anti-immigrant sentiment in the West that gives legitimacy to nationalist chauvinism on a global scale.
“Sadly, it is marginalized and vulnerable Syrians who are paying the price of this politics. In Lebanon, they face daily acts of discrimination, humiliation and violence as they have to confront bleak prospects whether they stay in Lebanon, attempt illegal migration to Europe, or go to Syria.”
The arrival of Syrian refugees over the past decade has placed a burden on Lebanon’s already stretched services and infrastructure.
Lebanon hosts the greatest number of refugees per capita of any country in the world, according to Lisa Abou Khaled, spokesperson for the UN Refugee Agency, UNHCR, in Lebanon.
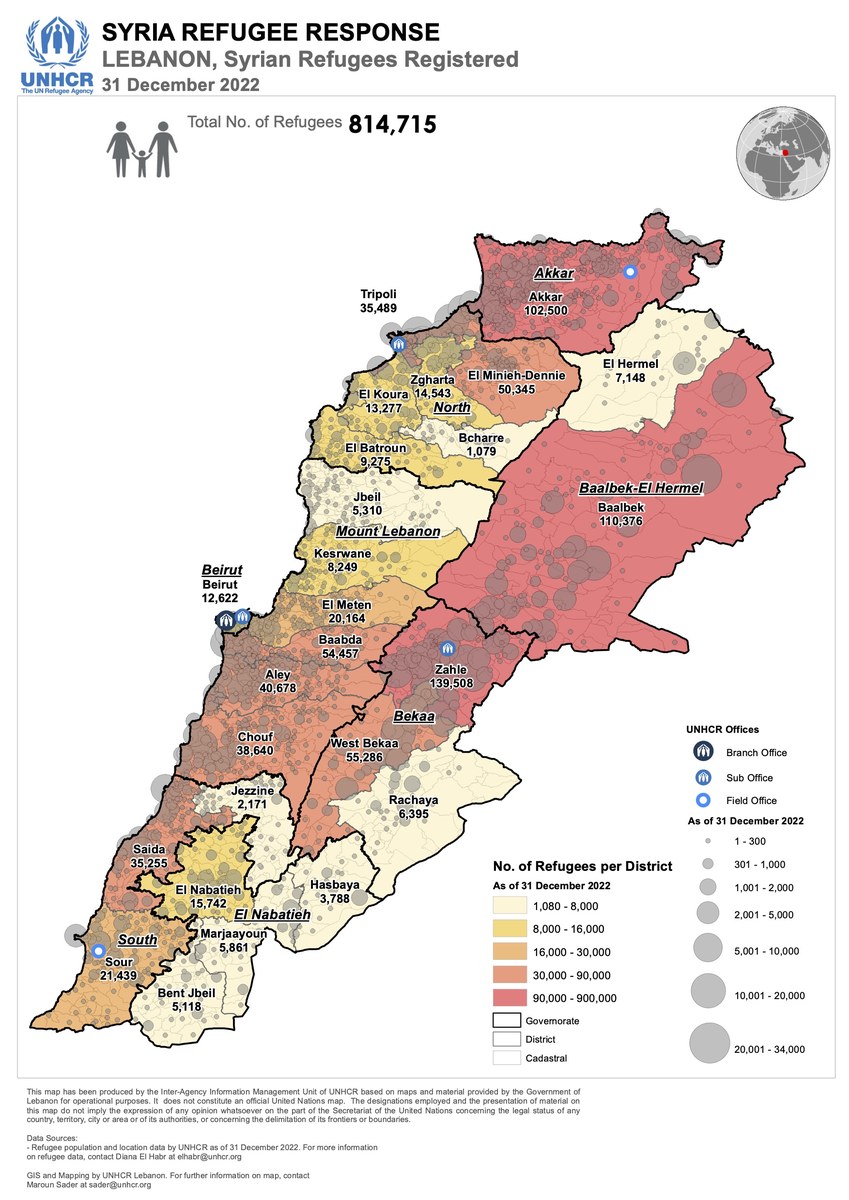
“UNHCR fully recognizes the impact this is having on the country, notably while it is facing the worst economic crisis in its modern history, pushing the most vulnerable to the brink,” she told Arab News.
Likewise, Shaar of the Newlines Institute said: “Lebanon’s economy is actually struggling, and yet the number of Syrians is on the rise — just from natural increases. So, the problem that Lebanon faces is real.”
He stressed the need for “a systemic solution to this crisis — a concerted effort to actually address it because otherwise, my main worry is that there will be more xenophobic rhetoric and attacks against Syrians.”
In the last five years, Lebanon’s currency has lost more than 98 percent of its value, according to the World Bank. The spillover from the ongoing war in Gaza has also dealt a major blow to the country’s stability.
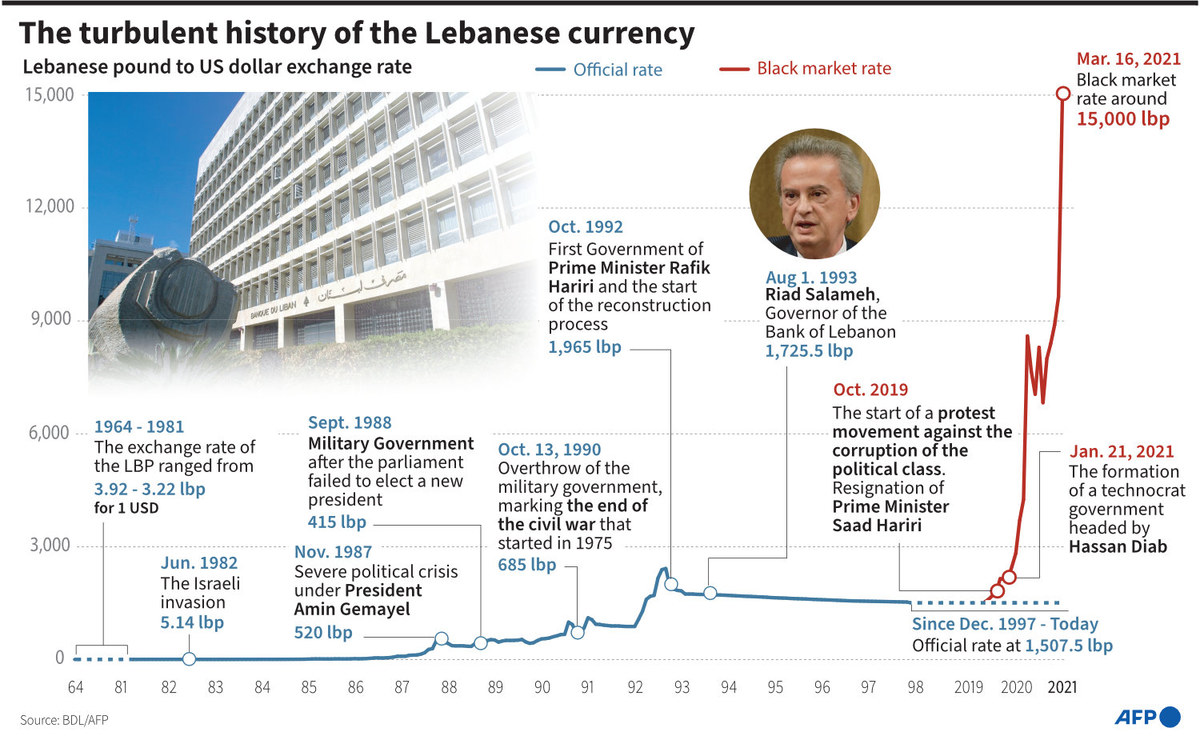
AFP infographic showing the extent of the depreciation of the Lebanese lira as of early 2021. A recent report of the World Bank says Lebanon’s currency has lost more than 98 percent of its value in the last five years.
To make matters worse, funding for UN agencies to assist displaced communities is drying up fast amid the world’s multiple, overlapping humanitarian emergencies.
According to Abou Khaled, “in 2024, UNHCR and the World Food Programme are able to assist 88,000 fewer refugee families than in 2023 with cash and food assistance, reflecting a 32 percent decrease in the number of beneficiaries.”
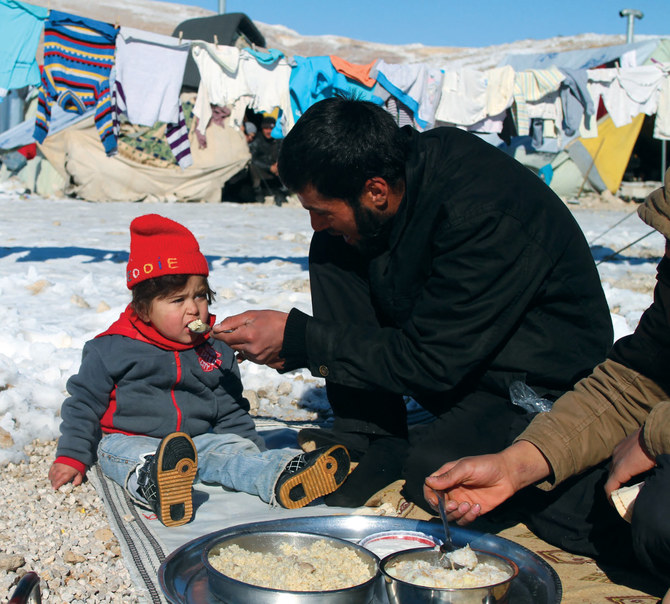
Syrian refugees in Lebanon are among the most vulnerable populations, with approximately 90 percent of households living in extreme poverty and 80 percent lacking legal residency.
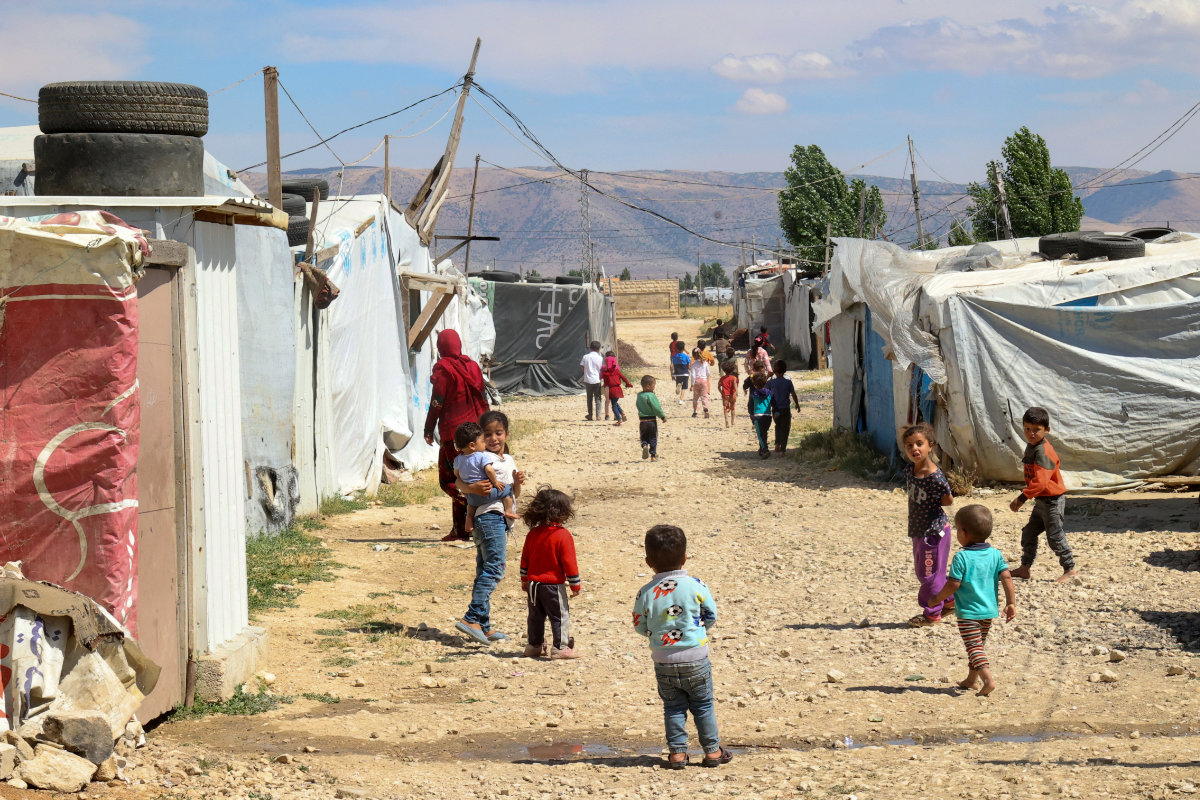

In this picture taken on June 13, 2023, Syrian children play between tents at a refugee camp in Saadnayel in eastern Lebanon's Bekaa Valley. (AFP)
Jasmin Lilian Diab, director of the Institute for Migration Studies at the Lebanese American University, said that “depriving Syrian refugees of proper documentation not only violates their fundamental human rights but also exacerbates their vulnerability.
“Without legal status, refugees face barriers accessing essential services such as healthcare, education, and employment, further marginalizing them within Lebanese society,” she told Arab News.
“This lack of documentation also increases the risk of exploitation, abuse, and detention, leaving refugees without legal recourse or protection. More recently, this has made them increasingly vulnerable to deportation amid ongoing raids and crackdowns.”
For Abou Khaled of UNHCR, housing is also a major concern. “More than half of the Syrian population (52 percent) live in dangerous, sub-standard or overcrowded shelters with the worst/most dangerous conditions reported in Mount Lebanon, (the) south and Beirut,” she said.
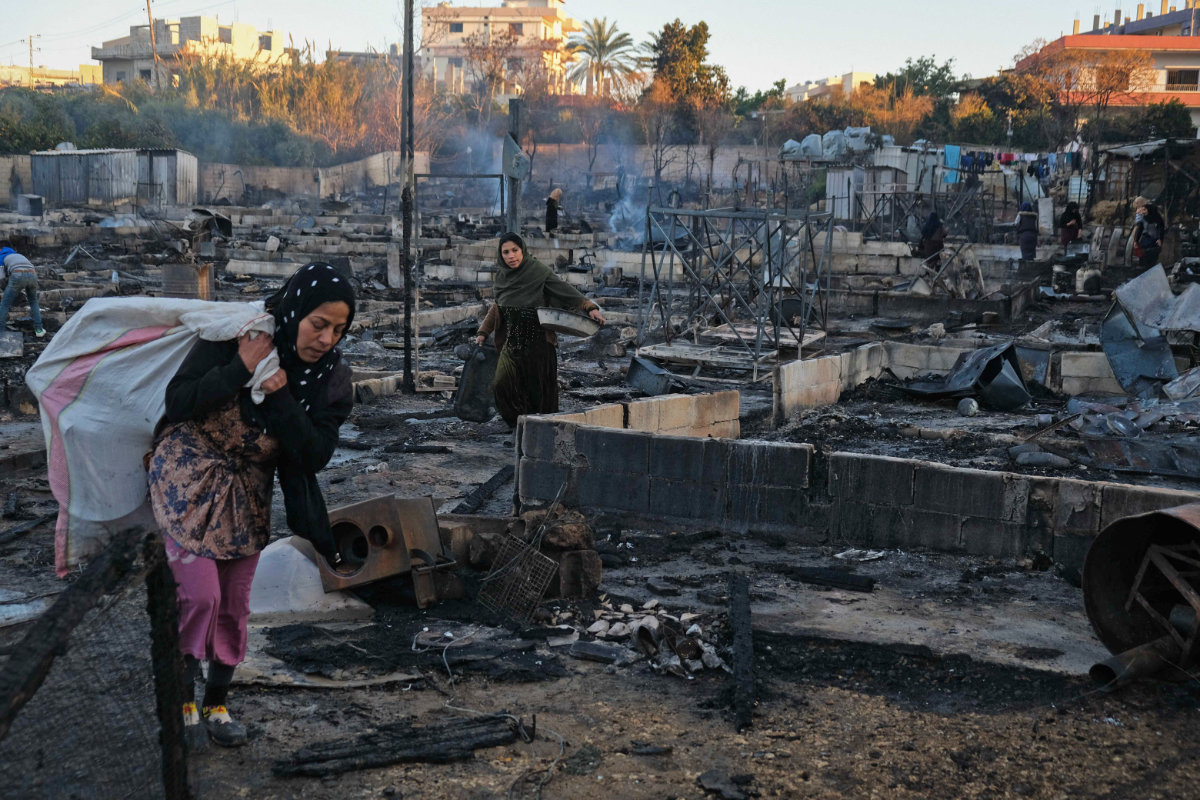

Syrian refugees salvage belongings from the wreckage of their shelters at a camp set on fire overnight in the northern Lebanese town of Bhanine on December 27, 2020, following a fight between members of the camp and a local Lebanese family. (AFP/File photo)
In March, a huge fire broke out in a Syrian refugee camp in Wadi Al-Arnab in the northeastern town of Arsal. The inferno, reportedly caused by an electrical fault, devoured more than 36 makeshift tents.
The fire was only the latest in a series of similar incidents to befall this vulnerable population. A similar blaze occurred in Hanine in Bint Jbeil District during a heatwave in July 2023, while another broke out in October 2022, reducing 93 tents to ashes.
Those living in rented accommodation are hardly better off. Average monthly rents in Lebanese pounds have “increased by 553 percent in 2023; from LBP 863,000 in 2022 to over 5.6 million LBP in 2023,” said Abou Khaled.
For Syrian refugees, unable to live under these circumstances but too frightened to return home, where they might face arrest, persecution, or conscription by the regime or one of the country’s armed factions, the most practical way out seems to be onward migration.
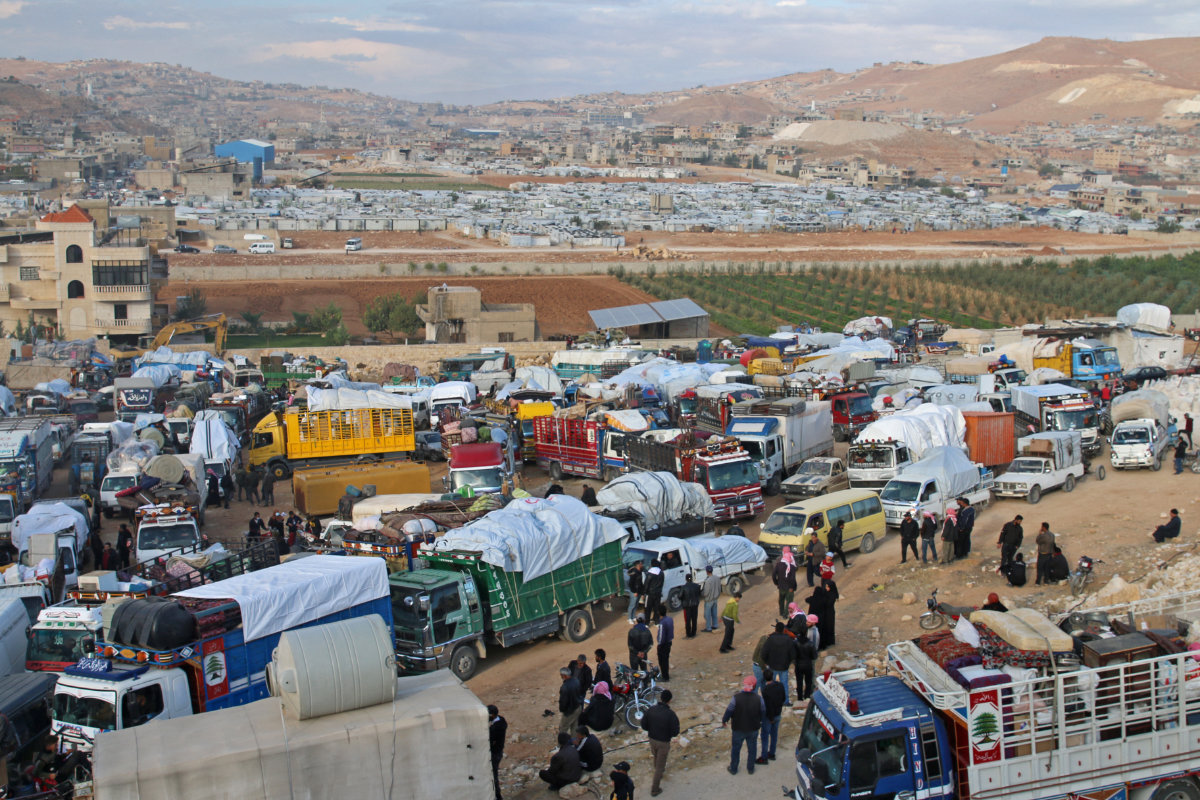

Displaced Syrians leave Lebanon towards Syrian territory through the Wadi Hamid crossing in Arsal on October 26, 2022. (AFP/File photo)
“UNHCR does not hinder the return of refugees to Syria,” said Abou Khaled. The UN agency “is also actively working to support durable solutions for Syrian refugees, including resettlement to third countries, and return to Syria.”
She added: “Resettlement allows responsibility sharing and show of solidarity with host countries like Lebanon, supporting large refugee populations.” This, however, “depends on quotas UNHCR receives by resettlement countries.
“Overall, since 2011 and up to the end of 2023, about 100,000 refugees have been resettled from Lebanon to third countries. In 2023, there was a 9.25-percent increase in resettlement departures when compared to 2022, and the highest number recorded since 2017.”
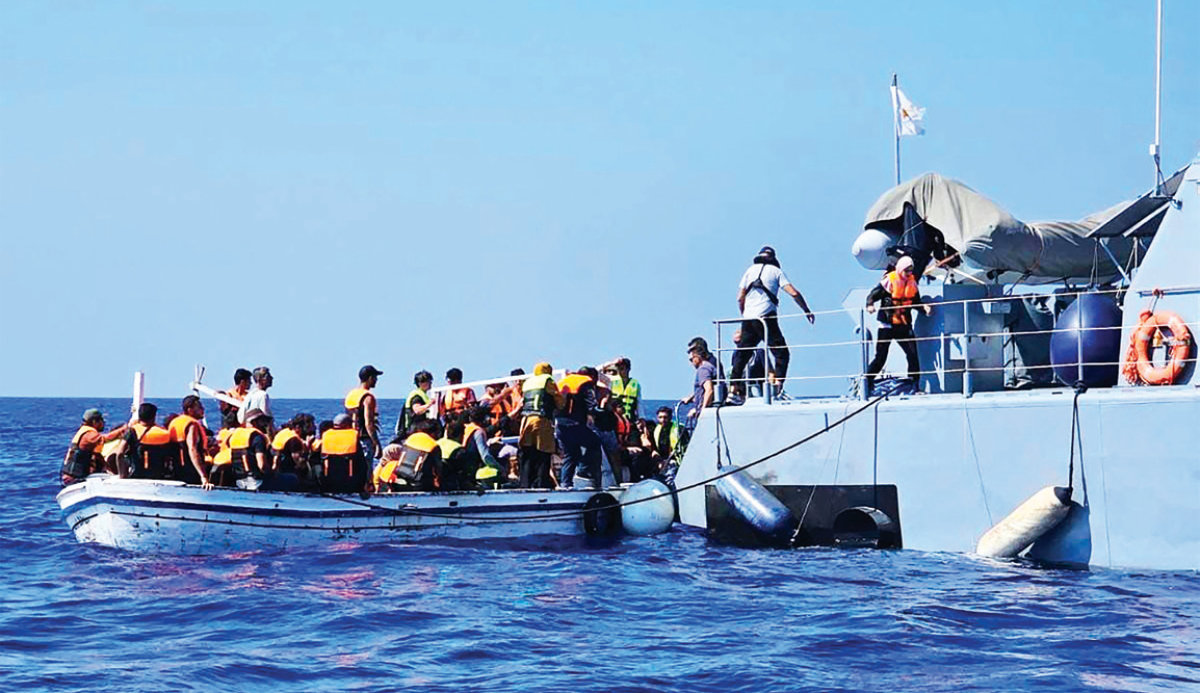
For many Syrians in Lebanon, onward migration through legal routes is out of reach. Hundreds have instead resorted to making the dangerous sea journey to the EU’s easternmost state, Cyprus, which is a mere 160 km from Lebanon.

Caption
Earlier this month, Cyprus expressed concern over the sudden surge in arrivals of Syrian refugees from Lebanon. With more than 600 Syrians crossing in small boats, the island’s reception capacity has reached breaking point, Reuters reported.
Shaar suspects “the number will only increase going forward as the situation becomes worse and worse” in Lebanon.
Diab of the Institute for Migration Studies at LAU said that “while sea journeys to Europe may seem like the only option for some Syrian refugees in Lebanon, safe alternatives do exist in theory — albeit a much slower process that many refugees cannot afford to wait for.”








































