JUBA, SOUTH SUDAN: As Sudan’s conflict heads toward its fifth month, a dire humanitarian crisis looms with thousands of people, many of them residents of the capital Khartoum, facing the prospect of death by starvation and malnutrition.
The tragic passing of Khaled Senhouri, a well-known violinist, who recently succumbed to hunger in Omdurman, highlighted the predicament of civilians for whom lack of food and water can be just as deadly as bullets.
With intermittent electricity, dwindling food supplies, and limited access to essential resources, Sudanese in Khartoum and other violence-torn towns and cities are locked in a desperate fight for survival.
In a heart-wrenching online post shortly before his death, Senhouri described the reality of life under siege. Unable to leave home to procure food because of the fighting, his was a despair now shared by countless others.

“Obtaining even meager supplies is a challenge, compounded by the constant threat of bullets and the scarcity of cash, electricity, water, and gas,” Yasir Hassan, a 45-year-old Khartoum resident, told Arab News.
Since the outbreak of violence in Khartoum on April 15 between the Sudanese Armed Forces and the paramilitary group Rapid Support Forces, the nation’s food imports and domestic agriculture have faced severe disruptions, leaving supermarket shelves bare.
Most markets, shops, and petrol stations are closed, and even basic commodities like cooking gas are scarce and exorbitantly priced on the black market.
In the face of such scarcity, the price of essential items has skyrocketed, with the cost of lamb reaching a staggering $91 per kilogram. Poultry meat is almost nonexistent, while fruit and vegetables are disappearing from the market.
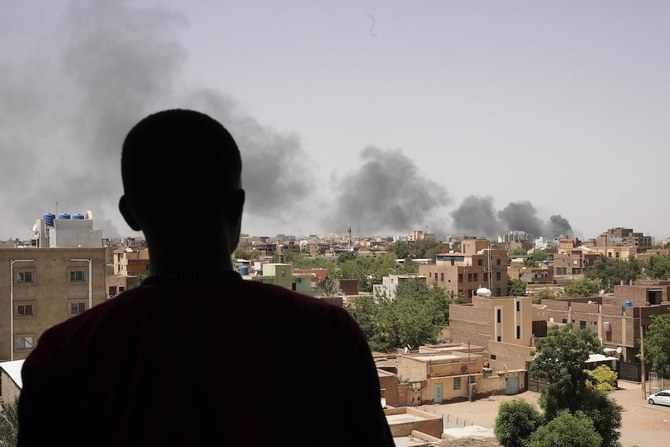

Clashes since April 15 have disrupted supply chains and caused food shortages in Sudan. (AP)
Tomatoes, cucumbers, and other fresh ingredients now cost a fortune, leaving families with no choice but to endure hunger and malnutrition.
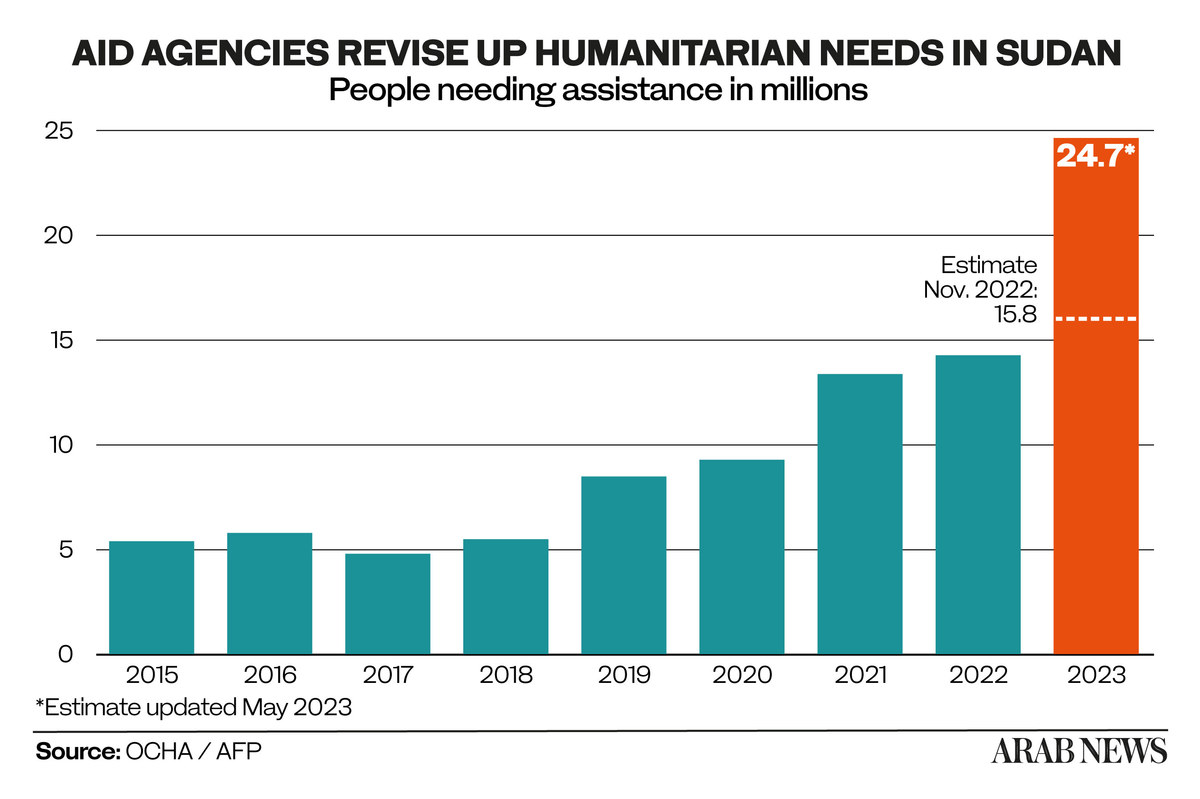
The UN says 25 million people – more than half Sudan’s population – need food and 13.6 million children are in desperate need of humanitarian aid.
More than 19 million people, which accounts for 40 percent of the population, are already experiencing hunger. The World Food Programme says it has reached more than 1.4 million people with emergency food aid as needs intensify.
Fighting in the capital – three cities built around the confluence of the White and Blue Niles, Khartoum, Omdurman and Bahri – has heavily affected areas housing important state or military installations.

The Darfur region, already ravaged by brutal conflict in the early 2000s, has seen some of the worst of the violence. Fighting there has recently concentrated around Nyala, after clashes in El-Geneina where the UN had reported atrocities.
A series of ceasefires brokered by Saudi Arabia and the US in indirect negotiations in the early stages of the conflict have gone ignored or not fully respected by the dueling factions.
As a result, many Sudanese workers have gone unpaid for four consecutive months. The collapse of the banking system and the lack of cash liquidity due to the conflict have left families burdened with debts and unable to meet their basic needs.
The health sector is also grappling with immense challenges. Attacks on health workers have put the few remaining hospitals in Khartoum at risk. The scarcity of medicines and difficulty in accessing treatment have further aggravated the crisis.
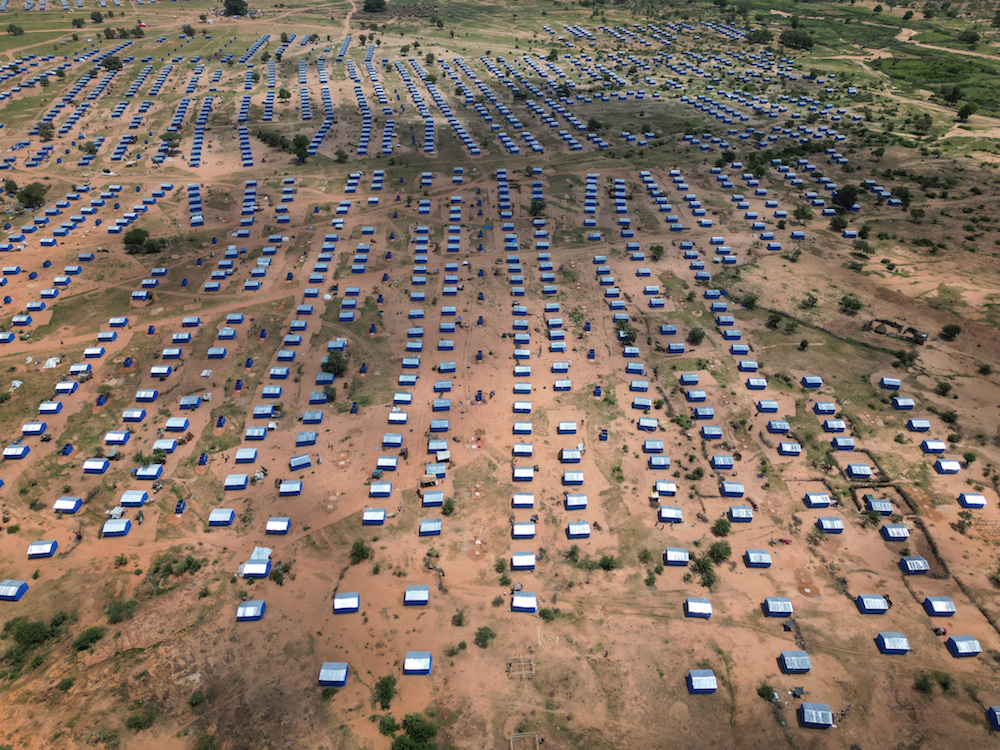

An aerial view of refugee camp of Sudanese people, who fled the conflict in Geneina in Sudan's Darfur region, in Ourang on the outskirts of Adre, Chad July 25, 2023. (Reuters)
The International Rescue Committee warns that the country is hurtling toward a man-made food crisis, which could grow worse in the coming year if global food price inflation continues on its current trajectory.
Farmers in several states across Sudan say the conflict is disrupting the production of staple crops like sorghum and millet, which aid agencies say could drive the nation deeper into hunger and poverty.
Even though many agricultural areas in Sudan are relatively calm and not directly affected by the fighting, delays have been caused by factors such as a lack of credit.
Banks have been looted in Khartoum and supply chains have faced disruption, impacting the availability of crucial agricultural resources like fertilizers, seeds, and fuel. Several warehouses storing these inputs have also been plundered.

Big commercial farmers, who are responsible for a significant portion of the sorghum production, are particularly affected as they struggle to access fuel, fertilizers, and other resources necessary for timely planting.
The fertile land between the White Nile and Blue Nile rivers is now home to several hundred thousands of the 2.6 million people displaced by the conflict. Desperate people and criminal opportunists are exploiting the security vacuum to steal from stores and empty homes.
Given that around 65 percent of the population is engaged in the agricultural sector, disruptions in farming activities have wide-ranging implications for Sudan’s economy and the well-being of its people.
This crisis has led to a significant reduction in crop yields and a scarcity of essential food supplies across the country. The cumulative effects of these disruptions are likely to result in further malnutrition, starvation, and an increase in preventable diseases.
INNUMBERS
* 3,900 people killed since violence began on April 15. (ACLED)
* 2.6m internally displaced persons, mostly from Khartoum. (IOM)
* 1/3 of population faced hunger before fighting began. (WFP)
The fighting has cut off access to essential resources and supply chains, making it almost impossible for humanitarian aid organizations to reach people in remote areas, particularly the troubled Darfur region.
Vulnerable populations, including pregnant and lactating women, infants and children, the sick and the elderly, are bearing the brunt of the catastrophe.
“I’ve met war widows and mothers with very young babies or infants who don’t have enough food to produce breast milk and feed their babies,” William Carter, head of the Sudan office for the Norwegian Refugee Council, told Arab News.
“In the near future, a malnutrition crisis is looming. The availability of locally produced food is likely to decrease. People have been forced to leave everything behind, and with limited access to resources or income, they are unable to meet even their basic needs.”
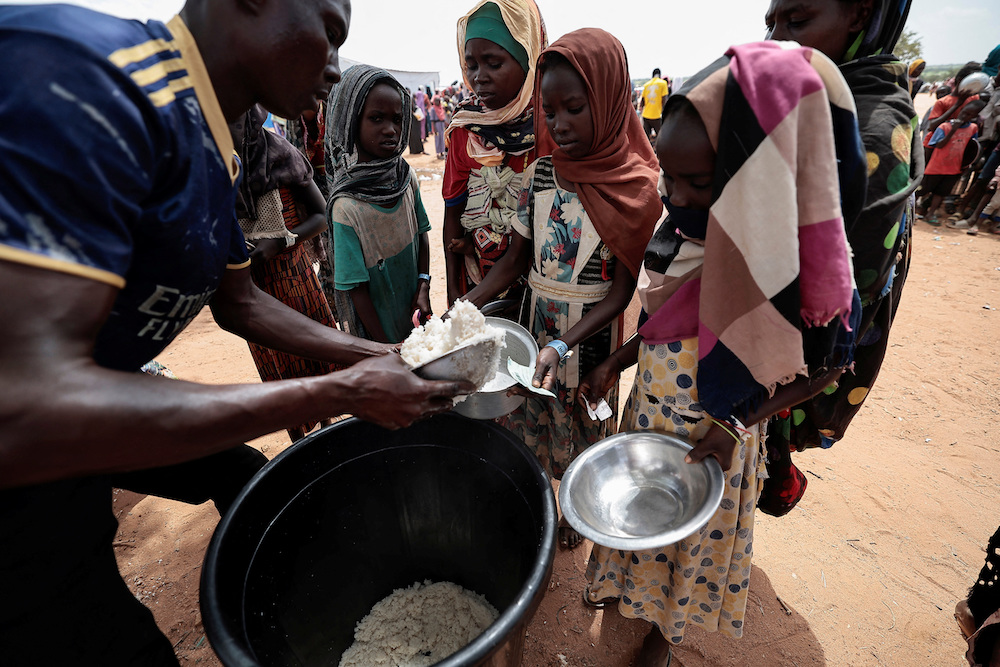

Sudanese girls who fled the conflict in Geneina in Sudan's Darfur region, receive rice portions from Red Cross volunteers in Ourang on the outskirts of Adre, Chad July 25, 2023. (Reuters)
Against this backdrop, international aid agencies, such as the UN Food and Agriculture Organization, have begun distributing seeds for staple crops such as sorghum, millet, groundnut, and sesame to bridge the impending gap in production.
“But more seeds are needed,” Salah Omar, executive director of the SPACES Organization based in Al-Jazirah state, southeast of Khartoum, told Arab News.
“Displaced people are very vulnerable. Their main work is farming. They could grow crops with local people here (in Al-Jazirah). It’s not too late to plant the seeds. We need more help for food production.”
The crisis not only poses a threat to livelihoods and public health. The collapse of Sudan’s food exports is also taking a toll on the country’s foreign currency reserves.
Cash crops like sesame and peanuts contributed significantly to export revenues, providing much-needed foreign currency for importing basic commodities.
Furthermore, regional networks have been impacted due to border controls and import difficulties, adding to the complexity of the situation.
Disruption to imports and exports is also having an impact on Sudan’s neighbors, straining international aid efforts and potentially destabilizing the wider region.
“NRC along with others is striving to address the issue by facilitating people’s access to local markets, for example through cash distribution,” said Carter.
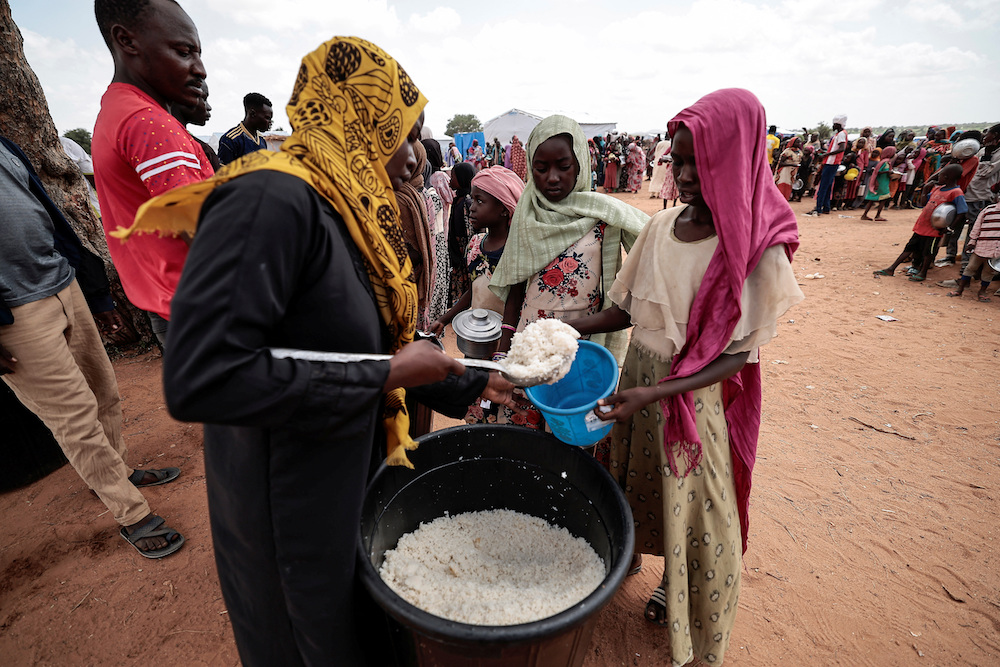

Pregnant women and mothers, children, the sick and elderly are particularly vulnerable to malnutrition. (Reuters)
In some instances, local groups have teamed up with international partners to meet the immediate needs of communities caught up in the fighting.
In central Bahri, a suburb north of Khartoum, a local group called the “Danakla Committee” — part of Sudan’s grassroots pro-democracy movement — has begun taking donations in order to meet the needs of local people trapped in their homes.
For those not receiving assistance, only an end to the fighting will alleviate their misery.
“If things continue as they are, we fear the humanitarian crisis will only escalate,” Khartoum resident Hassan told Arab News.
“Without food aid, we are left with nothing to eat. We urgently need an end to this war.”


























