LONDON: Domestic issues like the cost of living tend to dominate the minds of US voters ahead of election season. However, few can have ignored the gathering clouds of war in the Middle East and what this might mean for US allies in the region.
Indeed, events in Israel, Iran, and the Arab countries that have been dragged into their regional rivalry have already become a key feature of debate in November’s race for the White House, with the contenders setting out opposing positions.
Characteristically, Donald Trump, the Republican presidential nominee and former president, has said an escalating crisis in the Middle East could trigger a third world war — a catastrophe that only he could avert if he is returned to office.
During an interview on Aug. 12 with Elon Musk on the tech entrepreneur’s social media platform X, Trump said neither the war in Ukraine nor the conflict in Gaza would have happened had he occupied the White House instead of the incumbent Joe Biden.

Former US President Donald Trump. (AFP)
“If I were in office, the (Hamas-led) attack on Israel would never have happened, Russia would never have invaded Ukraine, we wouldn’t have inflation in our country, and the disaster in Afghanistan wouldn’t have occurred,” he said.
Promising he would contain the threats emanating from Tehran, he added: “All this stuff that you’re seeing now, all the horror that you look at. Israel, they’re all waiting for an attack from Iran. Iran would not be attacking, believe me.”
On the day Trump’s interview aired, the Israeli military said it was at “peak readiness” for a retaliatory attack for its killing of Hamas political leader Ismail Haniyeh in Tehran on Aug. 3 and senior Hezbollah commander Fuad Shukr in Beirut on July 30.
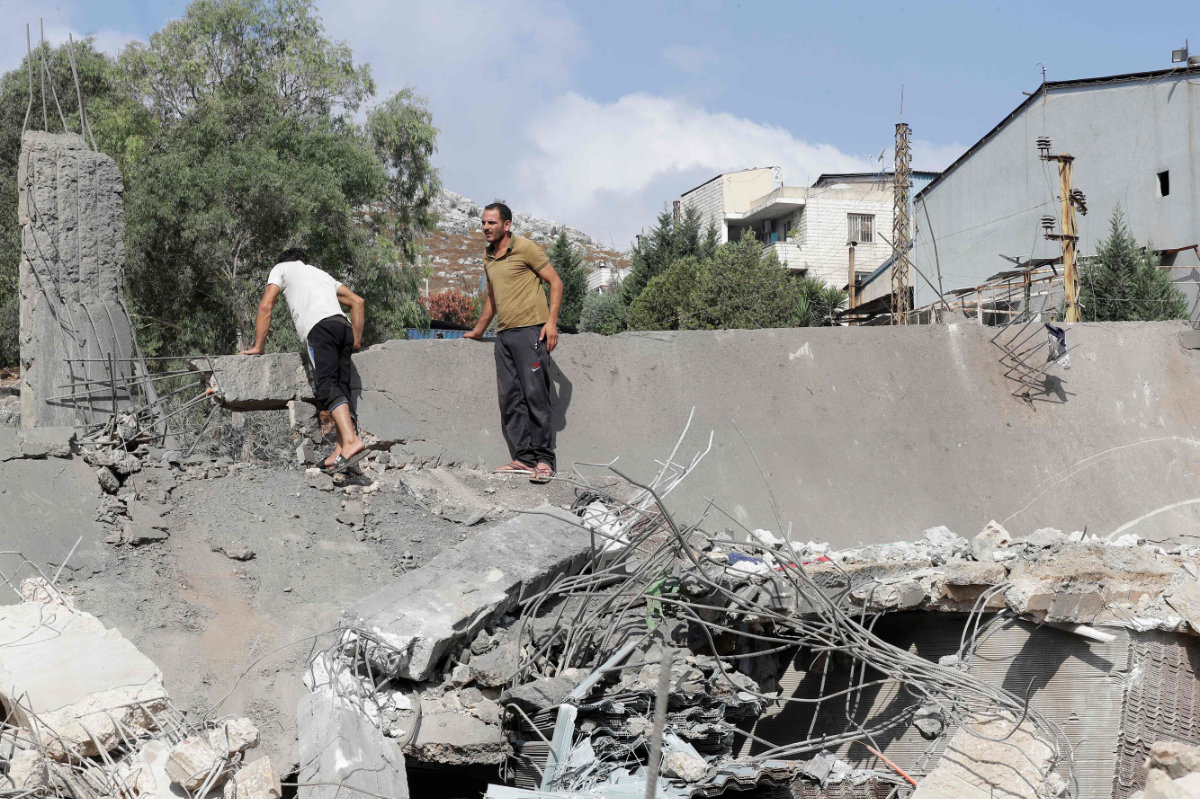

Lebanese residents inspect the damage to a building after an Israeli strike in the southern town of Kfour, in the Nabatiyeh district, on August 17, 2024, amid the ongoing cross-border clashes between Israeli troops and Hezbollah fighters. (AFP)
White House national security spokesperson John Kirby, meanwhile, said that while “it is difficult to ascertain at this particular time, if there is an attack by Iran and or its proxies, what that could look like,” Israel and the US had to be “prepared for what could be a significant set of attacks.”
President Biden has sought out the support of his counterparts in the UK, France, Germany and Italy to help de-escalate tensions in the region and also broker a ceasefire deal between Israel and the Palestinian militant group Hamas in Gaza.
The conflict in Gaza, which followed the Oct. 7 Hamas-led attack on southern Israel, has spilled over into neighboring countries, with Israeli rockets and drones striking targets across Syria and Lebanon, and the Iran-backed Hezbollah militia trading fire with Israel on the Lebanese border.

In a joint statement, the European leaders called on Iran to “stand down its ongoing threats of a military attack against Israel,” and highlighted “the serious consequences for regional security should such an attack take place.”
Trump’s pledge to prevent an Iranian counterattack is couched in his full-blooded support for Israel.
During his interview with Musk, Trump accused his opponent, the Democratic nominee Vice President Kamala Harris, of being “so anti-Israel” and having chosen “an anti-Israel radical left person” as her running mate, referring to Harris’s vice-presidential nominee Tim Walz.
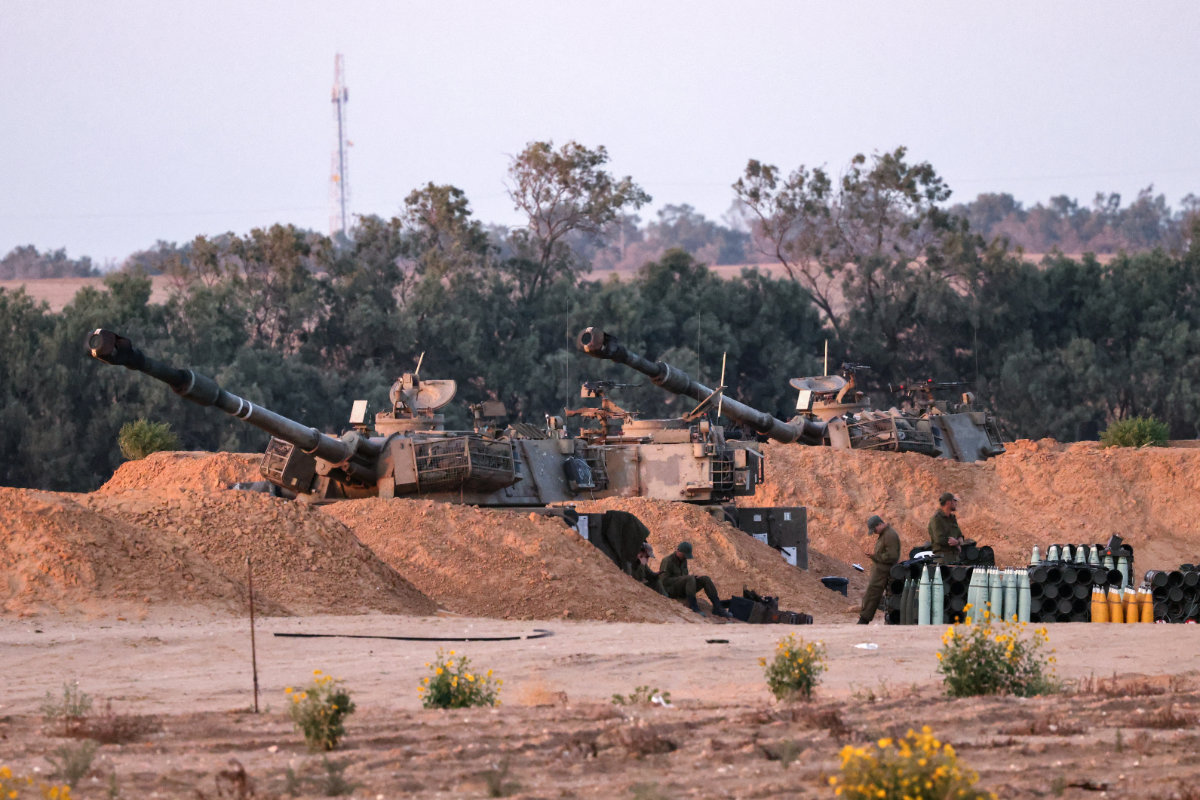

Israeli artillery units are positioned on the southern Israel border with the Gaza Strip, waiting to strike more targets. (AFP)
Trump’s support for Israel is widely recognized. In July, the leader of the Republican Jewish Coalition, Matt Brooks, said he believes Trump will give Israel a “blank check” to eliminate Hamas in Gaza should be return to office.
During the first presidential debate with Biden in June when he was still the Democratic Party’s nominee, Trump had called the outgoing president “a very bad Palestinian” who does not want to help Israel “finish the job” against Hamas.
“He doesn’t want to do it. He’s become like a Palestinian — but they don’t like him because he’s a very bad Palestinian, he’s a weak one,” Trump said. This came despite Biden reiterating his strong support for Israel in its war against Hamas.
INNUMBERS
• $20 billion US weapons package sale to Israel approved on Aug. 13, including fighter jets and advanced air-to-air missiles.
• $674 million US contribution to humanitarian aid for Palestinians since Oct. 7, 2023.
Harris was chosen to replace Biden as the Democratic nominee after his poor performance in June’s debate raised concerns about his cognitive abilities. Although she is keen to reduce tensions in the Middle East, Harris has been critical of Israel’s conduct in Gaza.
While incessantly reaffirming her “unwavering commitment” to the existence and security of Israel, she stressed in her Arizona campaign speech on Aug. 9 that “now is the time” to secure a Gaza ceasefire and hostage release deal, adding that she and Biden are working “around the clock every day” to achieve this.
Harris also expressed her “serious concern about the scale of human suffering in Gaza, including the death of far too many innocent civilians” during a meeting with Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu on June 25.
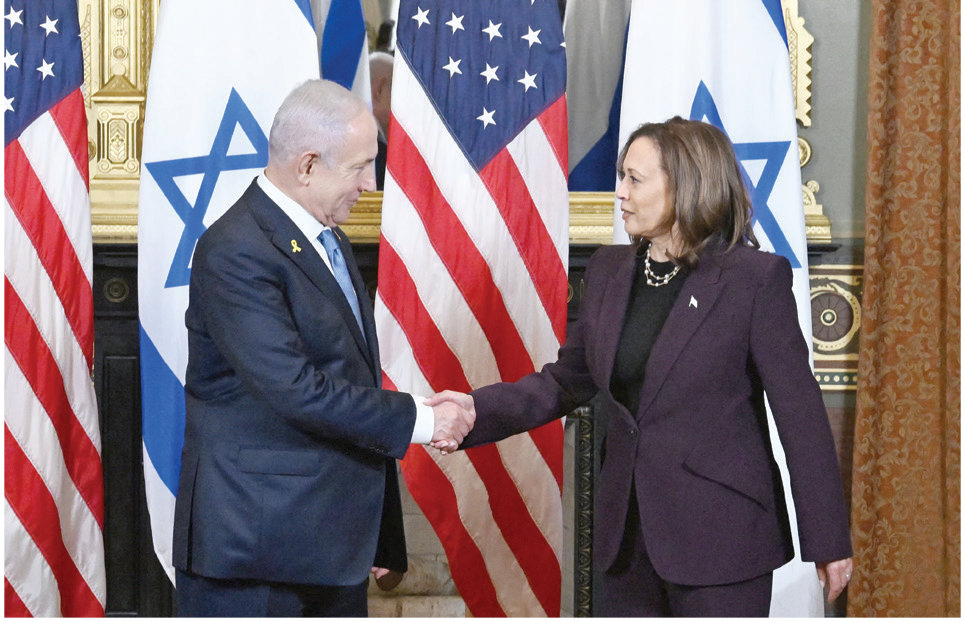

US Vice President Kamala Harris meeting with Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu in Washington last month. (AFP/File)
“I made clear my serious concern about the dire humanitarian situation there, with over 2 million people facing high levels of food insecurity and half a million people facing catastrophic levels of acute food insecurity,” she said following the meeting.
“What has happened in Gaza over the past nine months is devastating — the images of dead children and desperate, hungry people fleeing for safety, sometimes displaced for the second, third, or fourth time.
“We cannot look away in the face of these tragedies. We cannot allow ourselves to become numb to the suffering. And I will not be silent.”
In addition to killing more than 40,000 people in Gaza, at least 15,000 of them children, Israel’s bombing campaign in Gaza has brought health and sanitation services to their knees, wounded tens of thousands, and displaced some 1.9 million of the enclave’s 2.1 million population.
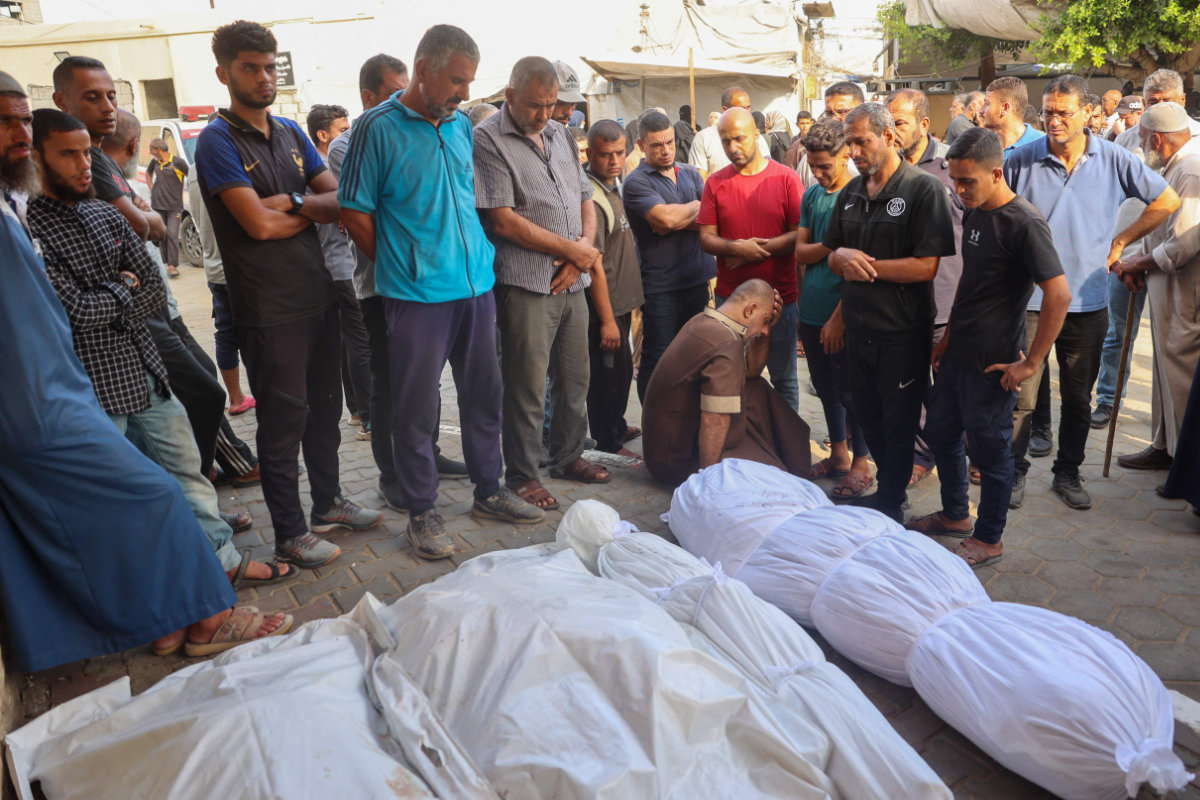

Palestinians mourn their relatives, killed in an Israeli strike, at the Al-Aqsa Martyrs hospital in Deir Al-Balah in the central Gaza Strip on August 17, 2024. (AFP)
Humanitarian aid agencies and human rights organizations have accused the Israeli government of committing war crimes against Palestinians, including the deliberate starvation of civilians in Gaza.
However, as far as the US election is concerned, debates and disagreements over the conflict appear somewhat superficial.
Ray Hanania, an award-winning former Chicago City Hall political reporter and columnist, believes “the two major party candidates are focused on addressing the politics of a potential widening regional war in the Middle East, but not in its causes.”
He told Arab News: “Both Harris and Trump are addressing the conflict in a limited way by expressing concerns for the unprecedented humanitarian crisis facing Gaza’s population, careful to only define that population in generic terms not as suffering civilians, women and children.
“Both Harris and Trump are instead more focused on the politics of the potential conflict, blaming Iran, for example, and urging Arab states to refrain from engaging in the Gaza conflict.”
The two candidates, he said, “conspicuously avoid the cause of the conflict, which is Israel’s excessive and unbridled military violence in Gaza fueled by funding from the US government, including $20 billion given to Israel’s government by Congress this week.
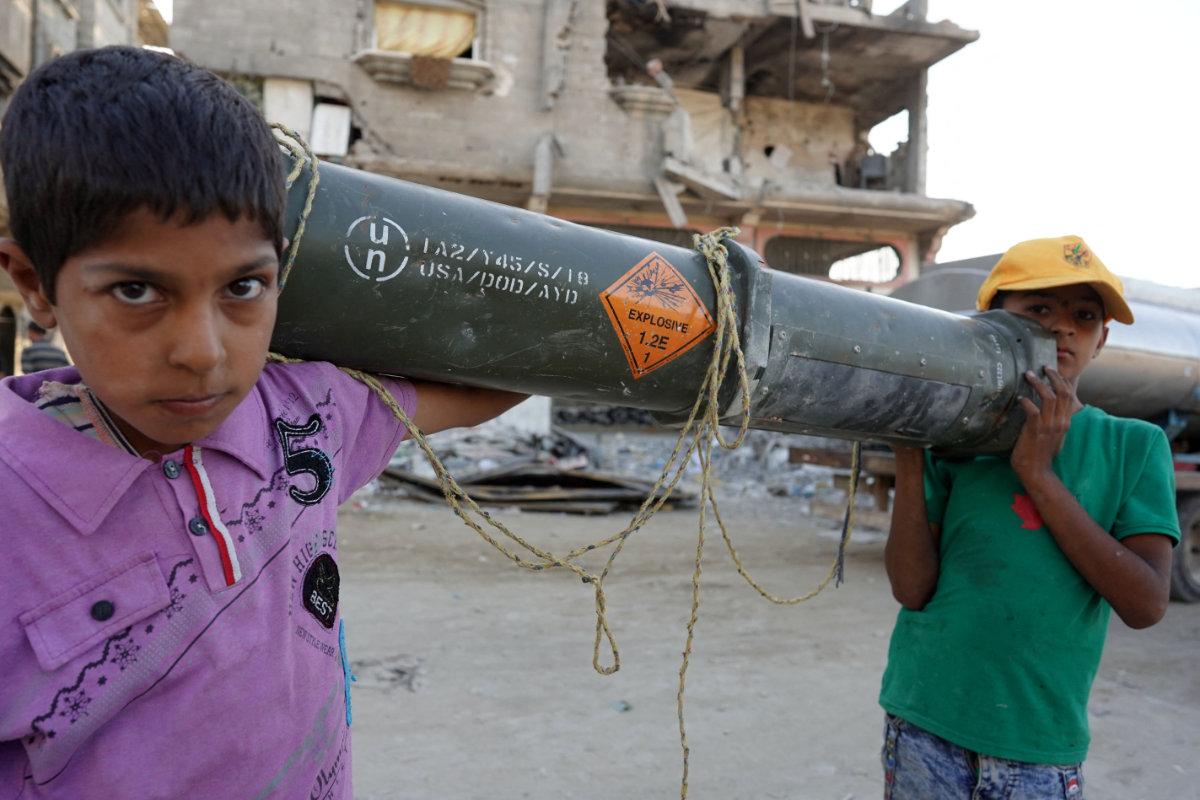

Palestinian children carry an empty US ammunition container in Khan Yunis in the southern Gaza Strip. US President Joe Biden has been unable to carry out his threats to withhold weapons of war from Israel despite the excessive and unbridled Israeli military violence in Gaza. (AFP)
“They don’t want to anger the political constituencies that support Israel, and then lose that vote in the upcoming presidential election, but they want to appear to be sympathetic to human suffering.”
He added: “This is all about politics, preserving their voter support — not about achieving real peace.”
Lebanese economist Nadim Shehadi also believes that “everything is now linked to the campaign circus and not about allies, interests, and there is certainly no strategy,” adding that it is unlikely “anyone in the region will listen to the US” until well after the election.
“This is too far ahead now,” he told Arab News. “Whoever wins the election in November will be inaugurated in January, and it will take around six months before they have a functioning administration — and who knows how much longer to have a policy strategy to implement.”

However, in a bid to stave off a full-fledged war in the Middle East, Shehadi expects that a victorious Harris administration would “engage with Iran” while a new Trump administration would more likely “engage with the Gulf countries.”
He said: “President Biden should have gone to the Gulf states in early October for help.”
Dania Koleilat Khatib, an expert in US-Arab relations and co-founder of the Lebanon-based Research Center for Cooperation and Peace Building, believes Arab and Muslim communities in the US are “becoming more vocal and active,” thereby gaining greater influence in elections and in public affairs. “Those two factors make it imperative for both Harris and Trump to tackle the issue,” she said.
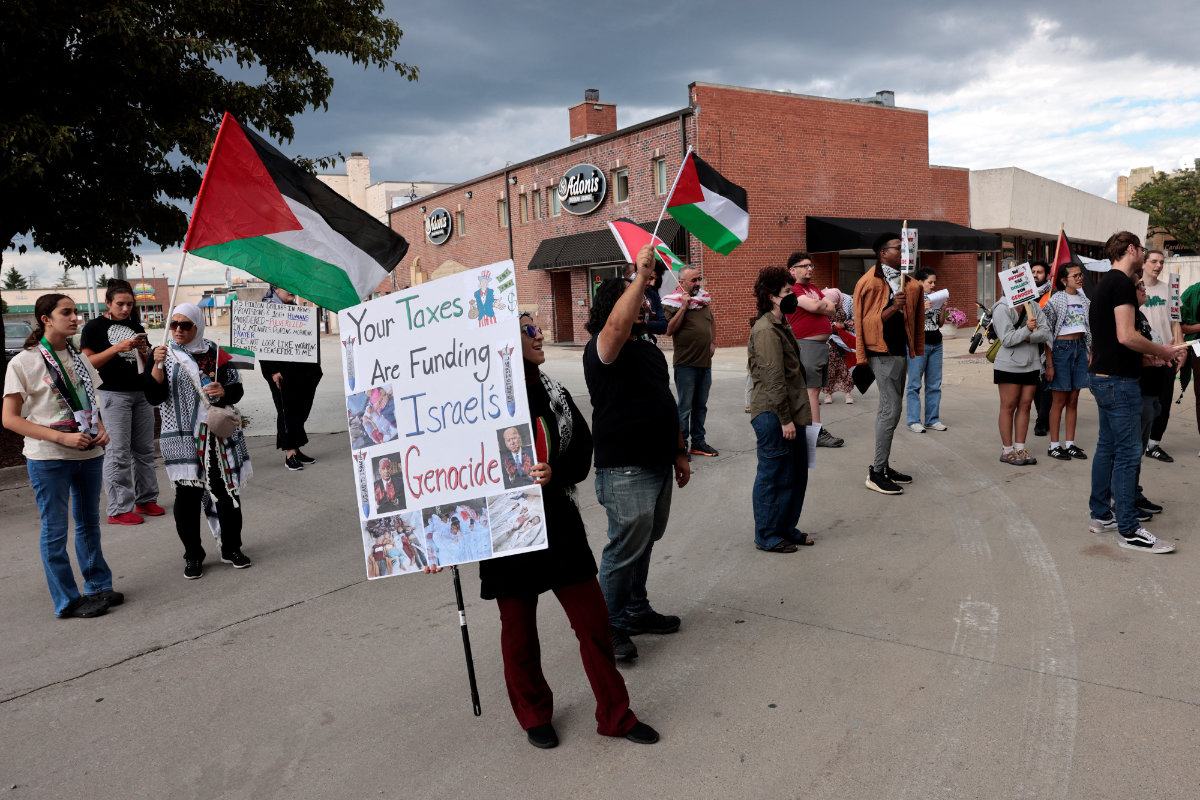

Demonstrators protest in support of the Palestinians who have died in Gaza outside of the Arab American National Museum in Dearborn, Michigan, on August 11, 2024. (AFP)
Addressing the Palestinian issue will require the next US president, regardless of who wins, to pressure Israel into reaching a fair solution, said Koleilat Khatib. To achieve this, they will have “no other choice” but to cooperate with regional allies like Saudi Arabia.
“First of all, the US should pressure Israel to accept a two-state solution — to accept at least an irreversible step,” she said. “So here, there will be a trade-off: regional recognition of Israel in return for a Palestinian state, which is not a new idea.
“This is what came in the Arab Peace Initiative. While this is not new, now I think the Americans will push for it and will take it more seriously — and, of course, they need to cooperate with Saudi Arabia.”
The Arab Peace Initiative was proposed by Saudi Arabia’s late King Abdullah in 2002 to end the Arab–Israeli conflict. The Arab League endorsed the plan at the Beirut Summit that same year. It was re-endorsed at the 2007 and 2017 Arab League summits.
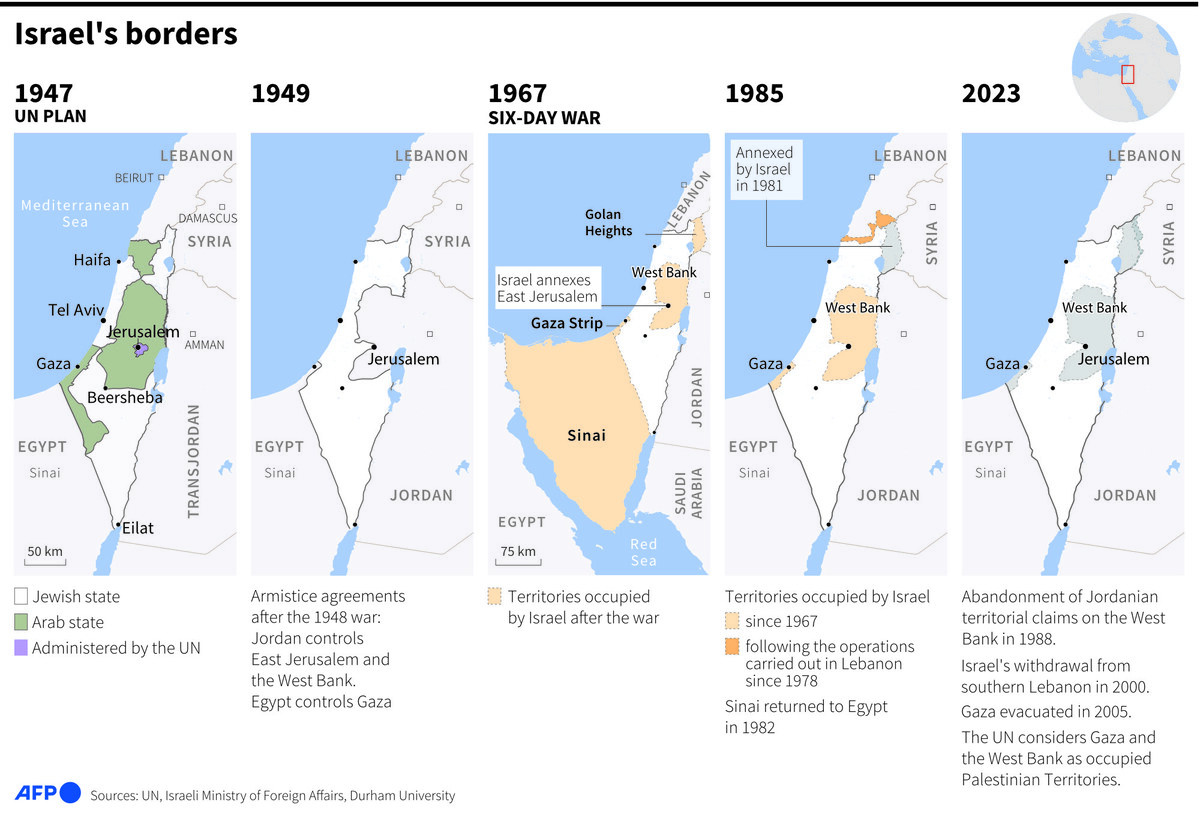
Maps showing the changes in Israel's borders since 1947. (AFP/ File)
The peace plan offers Israel normalization with all Arab states in return for its withdrawal from all territories occupied in 1967, the establishment of an independent and sovereign Palestinian state, and a just solution for Palestinian refugees.
Koleilat Khatib believes the US will also need to cooperate with regional allies like Saudi Arabia for the reconstruction of Gaza as well as peacekeeping.
“Israel has not yet agreed to make any concession because it enjoys unconditional support from the US,” she said. “The question is whether the US will be willing to pressure Israel. So far, the pressure has been minimal and mostly rhetorical, while in reality, arms transfers have continued smoothly, and Israel has been receiving the bombs it needs.
“As we head into the election season, the question is whether we’ll see members of Congress willing to stand against Israel.”

































