WASHINGTON D.C.: Two years ago this week, the UAE and Bahrain formalized the peace deals they had reached with Israel the previous month by signing the Abraham Accords at the White House, in a ceremony overseen by then US President Donald Trump.
As Sheikh Abdullah bin Zayed and Abdullatif Al-Zayani, respectively the UAE and Bahrain’s foreign ministers, and former Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu put their signatures on the document on Sept. 15, 2020, the moment was hailed as the beginning of a new era of Middle East diplomacy.
As part of the agreement, Israel said it would suspend its plans to annex occupied Palestinian territories. Sheikh Abdullah said that the UAE remained committed to a two-state solution and that its support for the Palestinian cause was “unshakable.”
The prospect of immediate economic and diplomatic benefits prompted Sudan to normalize relations with Israel in October 2020. The North African country became a signatory to the Abraham Accords in January 2021, around the same time it was removed from the US State Sponsors of Terrorism list.
Morocco normalized its relations with Israel two months after Sudan did, with Israeli Defense Minister Benny Gantz signing a security agreement with his Moroccan counterpart in November 2021. Israel recognised Moroccan sovereignty over Western Sahara in exchange for establishing ties.
Two years on from the Abraham Accords signing ceremony on the White House lawn, it is now possible to assess some of the outcomes of the agreement, such as how it has affected bilateral ties and who stands to benefit most from them, in a logical and dispassionate manner.
Apart from diplomatic engagement and economic cooperation, Israel and the Abraham Accords signatories were expected to collaborate on a number of shared interests, including energy, agriculture, tourism, security and technological innovation.
Israeli and Bahraini government officials have been interacting with each other publicly since the signing of the accords. Israel began importing aluminum from Bahrain, and the two countries are planning to sign an agreement that allows the transshipment of goods arriving by sea in Bahrain onto planes heading to Israel.
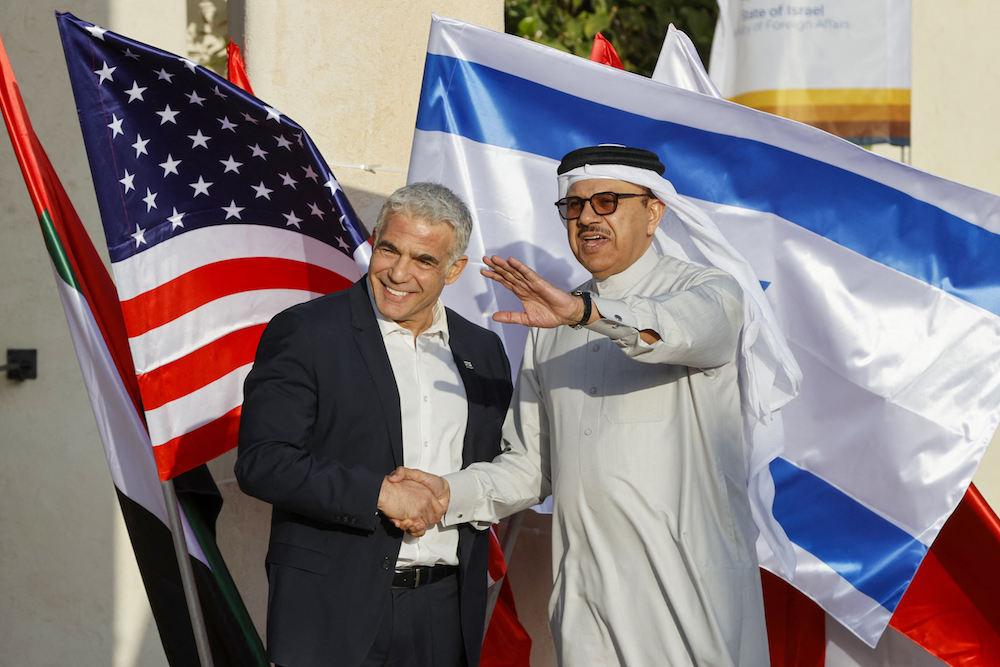

Israel’s Foreign Minister Yair Lapid (L) welcomes Bahrain's Minister of Foreign Affairs Abdullatif bin Rashid Al-Zayani upon his arrival for the Negev Summit, at Sde Boker in the southern Negev desert on March 27, 2022. (AFP/File Photo)
Last year Israel’s Prime Minister Yair Lapid, the foreign minister at the time, made the first ministerial visit to Bahrain, where he inaugurated the Embassy of Israel in Manama. In February this year, Gantz became the first Israeli defense minister to ever officially visit the Gulf country. He was accompanied by several top military and security officials, including the Israeli navy chief.
Gantz signed a memorandum of understanding with his Bahraini counterpart, formalizing a security relationship that his office claimed would “help advance intelligence cooperation, a framework for exercises, and cooperation between the countries’ defense industries.”
Gantz’ visit came as the US Navy’s 5th Fleet, based in Bahrain, launched its biennial International Maritime Exercise 2022. The Israeli Navy took part in the drill, for the first time publicly joining Arab and Muslim countries with which Israel does not have diplomatic relations.
With regard to Morocco and Israel, today the two countries cooperate in such areas as education, tourism, cross-border investment, renewable energy and security. Morocco has a strong Jewish tradition with many historic Jewish buildings, monuments and cemeteries, as well as the largest Jewish community in an Arab country. Israel, meanwhile, is home to one of the largest Moroccan expatriate communities.
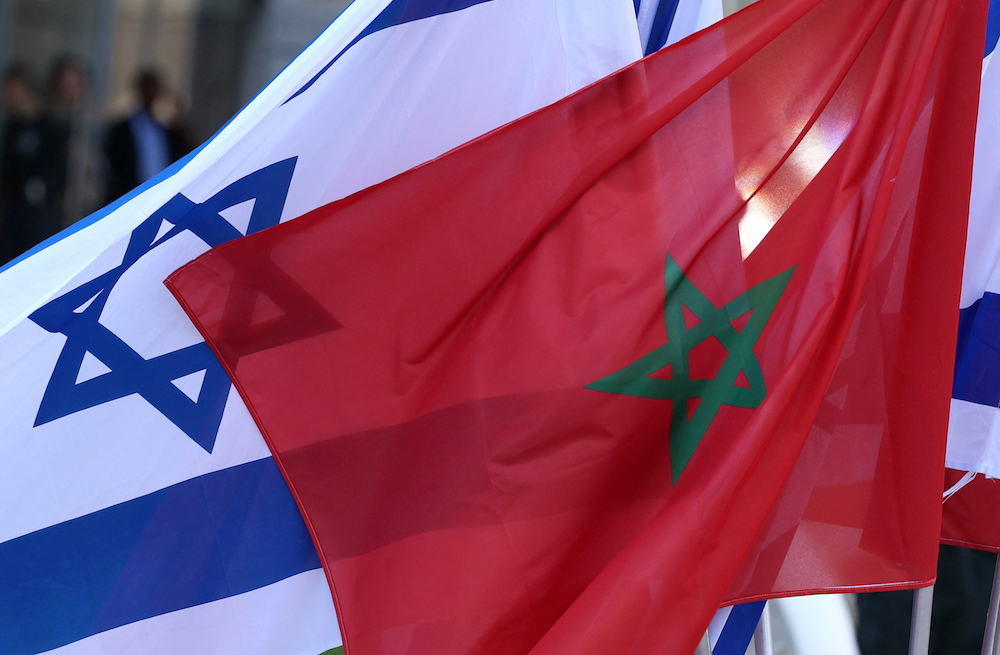

Israeli and Moroccan flags are pictured during an official ceremony in Israel's Mediterranean coastal city of Tel Aviv. (AFP)
An 84 percent year-on-year growth in Morocco’s trade with Israel to $41.6 million is viewed by the two countries as the beginning of a valuable new trading relationship. Israeli technical know-how combined with capital from the Abraham Accord partners, Bahrain and the UAE, could turbocharge Morocco’s moves to diversify away from fossil fuels .
By contrast, the full agreement between Israel and Sudan has yet to come to full fruition because of instability and the October 2021 coup. In May the Biden administration suspended development, trade and investment assistance to Sudan, including food aid related to its normalization deal with Israel, such as wheat shipments.
Predictably, trade and commerce between Israel and the UAE has flourished since the normalization of relations two years ago. In May this year, the two countries signed a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement that is expected to increase bilateral trade to more than $10 billion within five years, and add $1.9 billion to the UAE’s gross domestic product by 2030.
On June 27, Amir Hayek, Israel’s ambassador to the UAE, said in a message posted on Twitter that total trade volume between the two countries for the first five months of the year reached a value of $912.1 million, compared with $399.5 million during the same period last year.
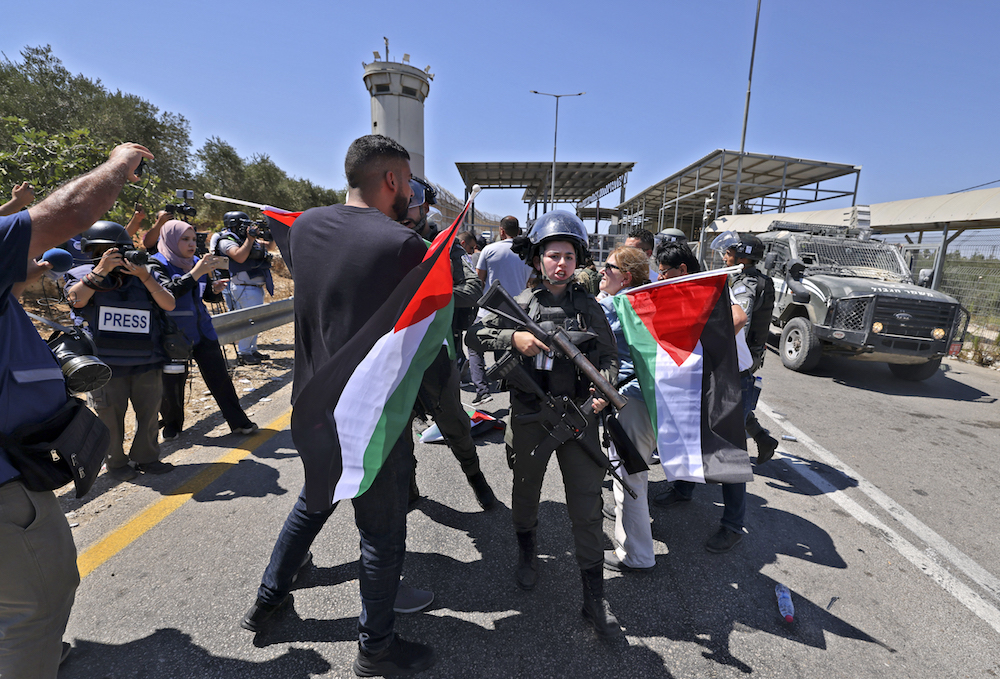

Palestinian and other activists raise national flags as they face Israeli security forces, during a demonstration against Jewish settlements. (AFP)
Israel and the UAE have also signed multi-billion-dollar deals in the fields of medicine, bilateral investment and space travel over the past two years.
In July, the US, Israel, the UAE and India announced the formation of a new bloc, I2U2, with the aim of enhancing technological collaboration in the region and tackling transnational challenges in six main areas: Water, energy, transportation, space, health and food security.
Tourism between the UAE and Israel has also expanded rapidly since 2020. Commercial flights between the two nations began in November 2020, with daily flights introduced the following year. Tourism websites aimed at attracting Arab visitors to Israel encourage them to visit Al-Aqsa Mosque and Jerusalem’s Muslim Quarter, in addition to the Museum of Islamic Art.
The flow of tourists in the opposite direction has been even more substantial. Between 2020 and 2021, about 230,000 Israelis visited the UAE, despite pandemic restrictions.
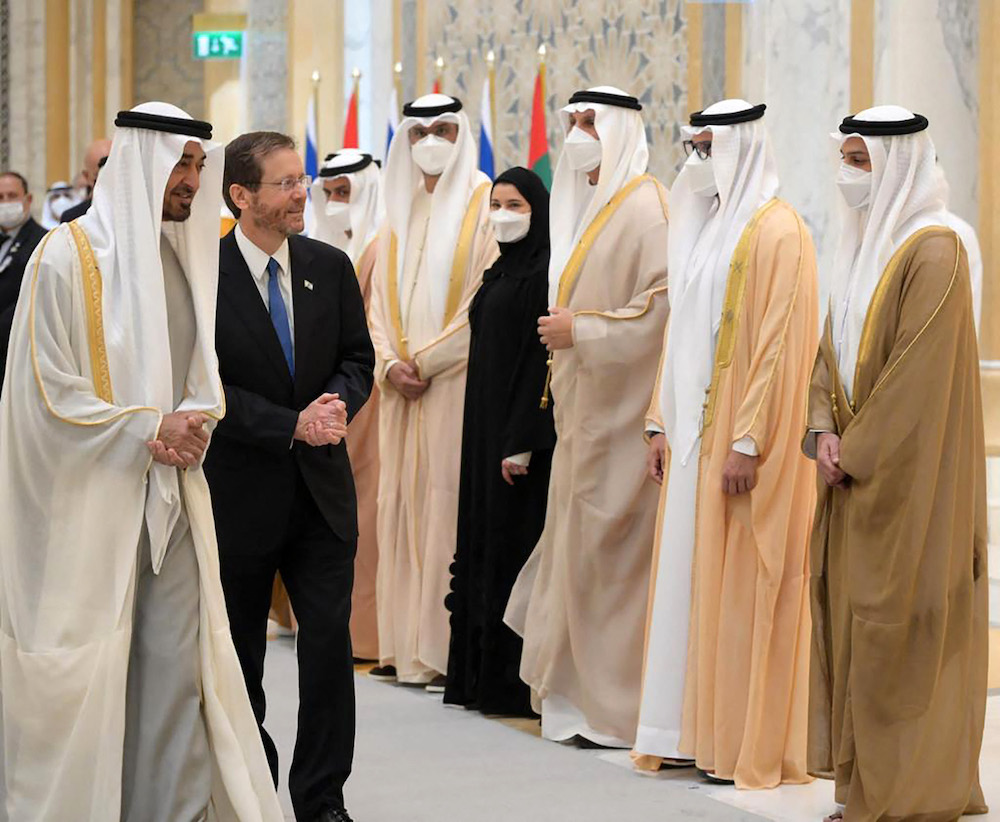

Then-Abu Dhabi Crown Prince Sheikh Mohammed bin Zayed Al-Nahyan (L) receiving Israel's President Isaac Herzog (2nd-L) in Abu Dhabi earlier this year. (AFP)
The increase in tourism between Israel and the UAE has, however, exposed the wide gulf that separates the two societies. In August many Arab and Israeli news outlets reported that Israeli police had briefly arrested two Emirati tourists after a shooting in Tel Aviv.
Though the pair were released and received an apology from the officers who arrested them, many social media users suggested that the Israeli police had racially profiled the tourists, mistaking them for Palestinians. One Twitter user said that “if you are Arab, Israel will always treat you like a suspect.”
The alleged arrest of the Emiratis is not the only reason Arabs worldwide have questioned whether normalization agreements will encourage the hardliners in positions of power in Israel to adopt a more reasonable stance toward Palestinians and the holy sites in Jerusalem.
Prince Turki Al-Faisal, Saudi Arabia’s former intelligence chief and a former ambassador to London and Washington, has expressed doubts that Arab normalization efforts with Israel will lead to improved rights for Palestinians.
“The Palestinian people are still occupied; they are still being imprisoned by the Israeli government. Attacks and assassinations of Palestinian individuals take place almost on a daily basis,” he told the Arab News talk show “Frankly Speaking” in May.
“The stealing of Palestinian land by Israel continues despite assurances that Israel gave to the signatories of the peace (accord) between the UAE and Israel. So, there is no sign whatsoever that appeasing Israel is going to change their attitude.”
In July, citing a poll carried out by the Washington Institute for Near East Policy, which asked residents of Arab countries about their views on Arab-Israeli normalization, UAE academic Abdulkhaleq Abdulla said Emiratis view the normalization process in a negative light. The 2022 poll found that only one in four Emiratis surveyed considered the improved ties to be a positive development.
In the lead-up to the signing of the Abraham Accords, Yousef Al-Otaiba, the UAE ambassador to the US, writing in the Israeli news website Ynetnews, said: “In the UAE and across much of the Arab world, we would like to believe Israel is an opportunity, not an enemy. We face too many common dangers and see the great potential of warmer ties. Israel’s decision on annexation will be an unmistakable signal of whether it sees it the same way.”

The flags of the UAE and Israel fly at the Expo 2020 Dubai. (AFP/File Photo)
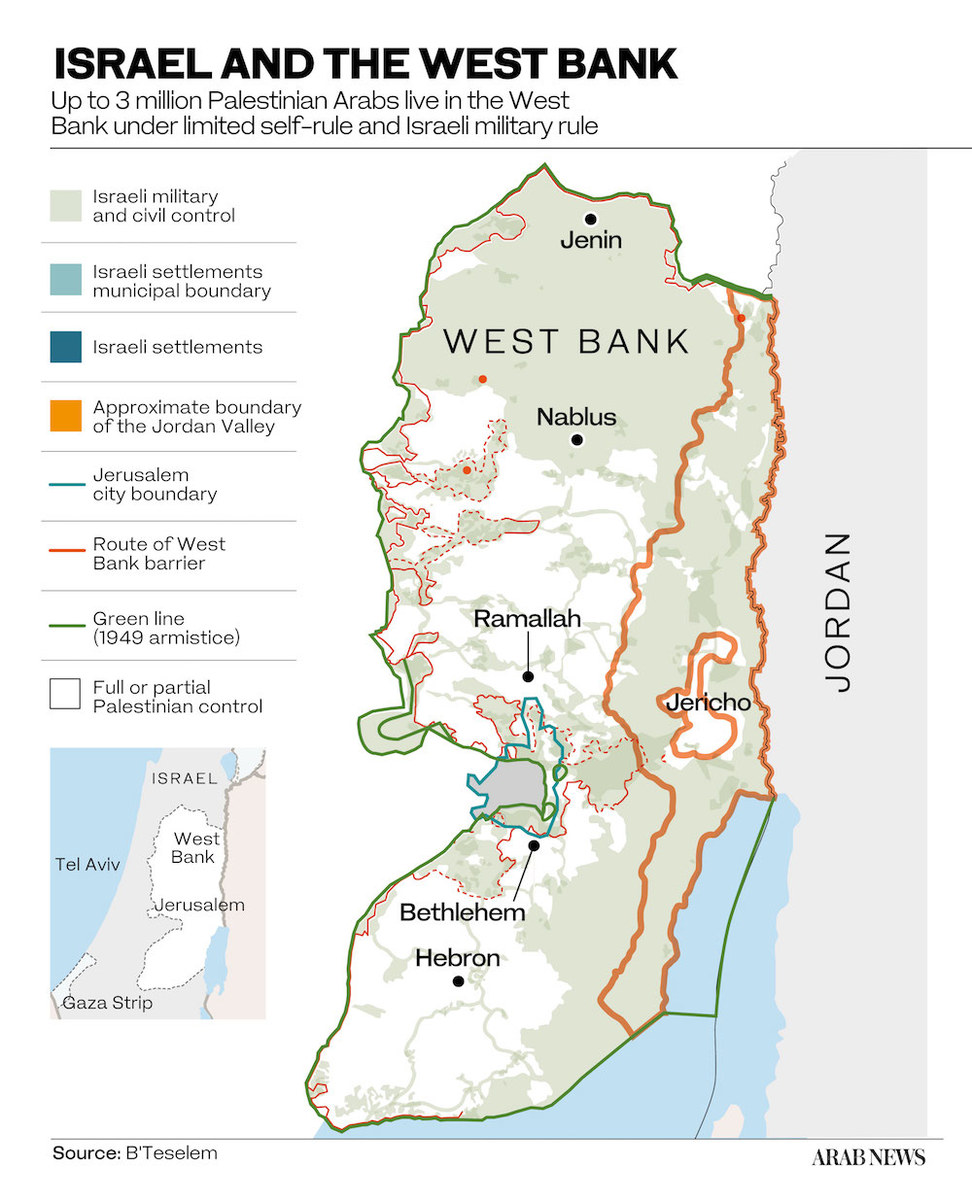
Two years on, following two military offensives against Gaza, few Arabs are probably under the illusion that the normalization initiatives under the Abraham Accords have changed Israel’s behavior, much less ended its policy on the annexation of Palestinian land.
Repeated calls by the Arab League for an end to Israeli violations of the sanctity of the holy sites in Jerusalem, a halt to the violence and the restoration of calm appear to have fallen on deaf ears.
Attacks by Israeli security forces on Muslim worshippers in Al-Aqsa Mosque and permission for Jewish prayers at the holy site are viewed by the Arab League as a flagrant provocation to Muslims everywhere.
Participating in a discussion on Sept. 8 organized by the Atlantic Council think tank to mark the two-year anniversary of the Abraham Accords, Al-Otaiba appealed for more to be done to advance a two-state solution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
“All the stuff that we’re talking about is great, but we can’t avoid talking about the two-state solution. We really can’t,” he said at the virtual event, during which he described the Palestinians as “the elephant in the room.”
Referring to the Abraham Accords, Al-Otaiba said: “I don’t think it was meant to solve — I think it was meant to buy space and time to create room for diplomacy to address the two-state solution. I still believe the two-state solution is the only game in town. I think we need to pursue it.”

























