ROME: Italian voters rewarded Giorgia Meloni’s euroskeptic party with neo-fascist roots, propelling the country toward what likely would be its first far-right-led government since World War II, based on partial results Monday from the election for Parliament.
In a victory speech, far-right Italian leader Giorgia Meloni struck a moderate tone after projections based on votes counted from some two-thirds of polling stations showed her Brothers of Italy party ahead of other contenders in Sunday’s balloting.
“If we are called to govern this nation, we will do it for everyone, we will do it for all Italians and we will do it with the aim of uniting the people (of this country),” Meloni said at her party’s Rome headquarters.
“Italy chose us,” she said. “We will not betray (the country) as we never have.”
The formation of a ruling coalition, with the help of Meloni’s right-wing and center-right allies, could take weeks. If Meloni, 45, succeeds, she would be the first woman to hold the country’s premiership.
The mandate to try to form a government is given by Italy’s president after consultations with party leaders.
Meanwhile, former European Central Bank chief Mario Draghi, whose government collapsed two months ago, stays on in a caretaker role.
Differences among Meloni’s potential coalition partners could loom.
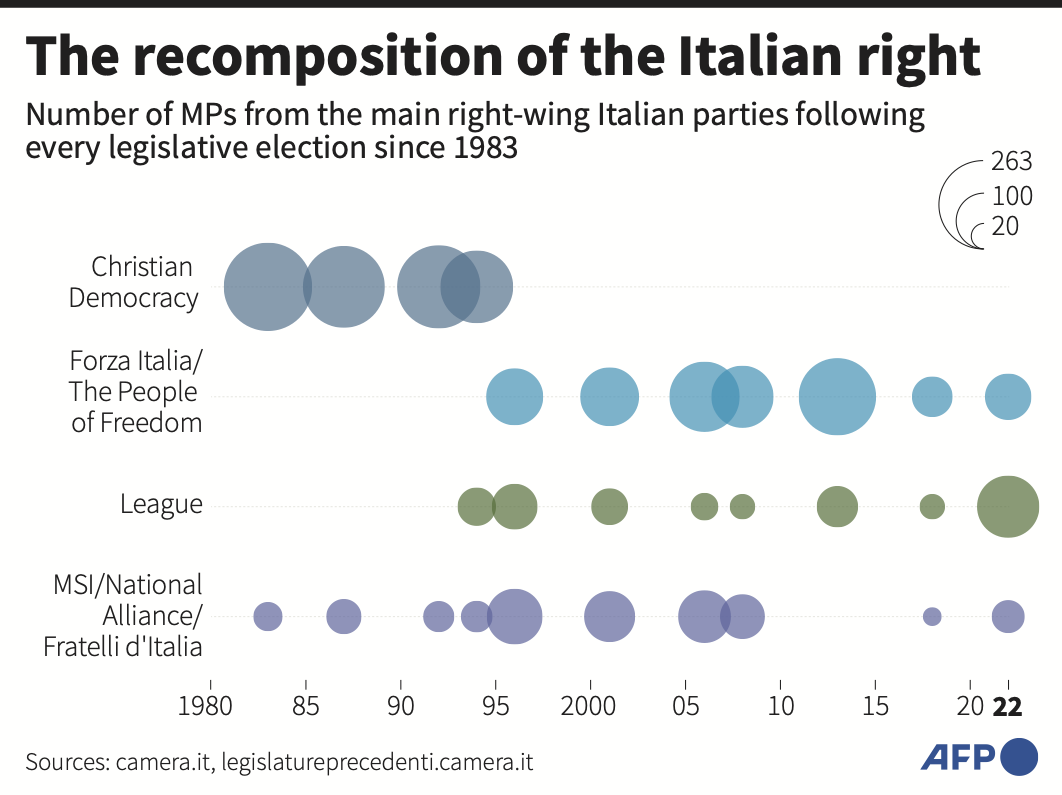
She has solidly backed the supplying of Ukraine with arms to defend itself against Russia’s invasion. In contrast, right-wing League leader Matteo Salvini, who before the war was a staunch admirer of Russian President Vladimir Putin, has voiced concern that Western sanctions could end up hurting Italy’s economic interests more that punishing Russia’s.
Former Premier Silvio Berlusconi, another long-time Putin admirer, has said that his inclusion in a center-right bloc’s coalition would guarantee that Italy stays firmly anchored in the European Union and one of its most reliable members.
With Italy’s households and businesses struggling with staggeringly high energy bills as winter approaches, Meloni has demurred from Salvini’s push to swell already-debt-laden Italy by tens of billions of euros for energy relief.
What kind of government the eurozone’s third-largest economy might be getting was being closely watched in Europe, given Meloni’s criticism of “Brussels bureaucrats” and her ties to other right-wing leaders. She recently defended Hungary’s Prime Minister Viktor Orban after the European Commission recommended suspending billions of euros in funding to Hungary over concerns about democratic backsliding and the possible mismanagement of EU money.
After opinion polls in the run-up to the vote indicated she would be headed to victory, Meloni started moderating her message of “God, homeland and family” in an apparent attempt to reassure the European Union and other international partners, worried about euro-skepticism.
“This is the time for being responsible,” Meloni said, appearing live on television and describing the situation for Italy and the European Union is “particularly complex.”
She promised more detailed comments later on Monday. In her campaign, she criticized European Union officials as being overly bureaucratic and vowing to protect Italy’s national interests if they clash with EU policies.
Projections based on votes counted from nearly two-thirds of the polling stations in Sunday’s balloting indicated Meloni’s Brothers of Italy party would win some 25.7 percent of the vote.
That compared to some 19.3 percent by the closest challenger, the center-left Democratic Party of former Premier Enrico Letta. Salvini’s League was projected to win 8.6 percent of the ballots, roughly half of what he garnered in the last 2018 election. Berlusconi’s Forza Italia party, appeared headed to win 8 percent.
Meloni’s meteoric rise in the European Union’s third-largest economy comes at a critical time, as much of the continent reels under soaring energy bills, a repercussion of the war in Ukraine, and the West’s resolve to stand united against Russian aggression is being tested. In the last election, in 2018, Meloni’s party took 4.4 percent.
Fellow euroskeptic politicians were among the first to celebrate. French politician Marine Le Pen’s party also hailed the result as a “lesson in humility” to the EU.
Santiago Abascal, the leader of Spain’s far-right Vox opposition party, tweeted that “millions of Europeans are placing their hopes in Italy.” Meloni “has shown the way for a proud and free Europe of sovereign nations that can cooperate on behalf of everybody’s security and prosperity.”
Nearly 64 percent of eligible voters deserted the balloting, according to the Interior Ministry. That is far lower than the previous record for low turnout, 73 percent in 2018.
Italy has had three coalition governments since the last election — each led by someone who hadn’t run for office, and that appeared to have alienated many voters, pollsters had said.
Meloni’s party was forged from the legacy of a neo-fascist party formed shortly after the war by nostalgists of Fascist dictator Benito Mussolini.
Italy’s complex electoral law rewards campaign alliance. Meloni was buoyed by joining campaign forces with Salvini and Berlusconi.
The Democrats went into the vote at a steep disadvantage since they failed to secure a similarly broad alliance with the left-leaning populists of the 5-Star-Movement, the largest party in the just-ended legislature.
Headed by former Premier Giuseppe Conte, the 5-Stars appeared headed to a third-place finish, with some 16 percent of the vote. Had they joined forces in a campaign agreement with the Democrats, their coalition would have roughly take the same percentage of Meloni’s alliance
The election Sunday came six months early after Draghi’s pandemic unity government, which enjoyed wide citizen popularity, collapsed in late July after the parties of Salvini, Berlusconi and Conte withheld support in a confidence vote.
Meloni kept her Brothers of Italy party in the opposition, refusing to join Draghi’s unity government or the two previous coalitions led by Conte.

























