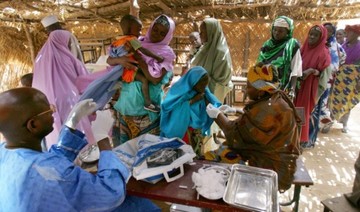
ABUJA: At least 26 people have died from a meningitis outbreak in Nigeria’s northwest Kebbi state, a local health official said on Tuesday.
Nigeria is one of the hotspots of the deadly disease in Africa where at least 1,700 cases were reported last year, with more than 150 deaths recorded in seven states.
Kebbi state Health Commissioner Musa Ismaila confirmed the outbreak, citing a surge in cases in three local government areas.
“We are saddled with the unfortunate situation of an outbreak with a rising number of cases,” Ismaila said in a statement, detailing symptoms that include fever, severe headaches, and neck stiffness.
A total of 248 suspected cases have been line-listed, with 11 samples sent to the National Reference Laboratory in the capital Abuja. Two samples returned negative, while nine are pending, he said.
Meningitis is the inflammation of tissue surrounding the brain and spinal cord which can be caused by viral or bacterial infections. It spreads mainly through kisses, sneezes, coughs and in close living quarters.
In response to the outbreak, the state government has distributed drugs to affected areas with isolation centers established with the support of Doctors Without Borders (MSF) in Gwandu, Jega, and Aliero, the three affected local government areas, Ismaila said.
Similarly, neighboring Sokoto state has issued a health warning following confirmation of an outbreak.
Last year, Nigeria became the first country in the world to roll out the “revolutionary” new Men5C vaccine against meningitis, according to the World Health Organization.
Meningitis outbreak kills 26 in northwest Nigeria, official says
https://arab.news/v5c4x
Meningitis outbreak kills 26 in northwest Nigeria, official says

- Kebbi state Health Commissioner Musa Ismaila confirmed the outbreak
- “We are saddled with the unfortunate situation of an outbreak with a rising number of cases”
France wildfire shuts down Marseille airport, halts trains

- The fire started in a vehicle in the area of Pennes-Mirabeau to the north of Marseille
MARSEILLE: A wildfire in southern France on Tuesday that forced Marseille airport to close and interrupted train traffic has not been fully contained, the country’s interior minister said.
Several forest fires have raged in recent days in southern France, fanning out at speed due to wind and parched vegetation after a heatwave, including Tuesday’s just north of France’s second largest city, Marseille.
Interior Minister Bruno Retailleau, during a Tuesday evening visit to firefighters in the region, said the fire could be contained overnight if winds weaken, as expected.
Scientists say human-induced climate change is increasing the intensity, length and frequency of extreme heat that fuels forest fires.
The fire started in a vehicle in the area of Pennes-Mirabeau to the north of Marseille, on the road to the airport, roaring across 700 hectares (1,730 acres) by the evening, firefighters said.
It sent plumes of acrid smoke billowing into the sky, causing the airport to close its runways shortly after midday (1000 GMT), a spokesman for the Marseille Provence airport said.
The spokesman later said that the airport would partially reopen at around 9:30 p.m. and that 54 flights had been canceled and another 14 redirected.
The website of the SNCF national rail operator showed more than a dozen train trips had been canceled in and out of the city.
It said rail travel to and from Marseille would remain “highly affected” on Wednesday.
Retailleau said 400 people have been evacuated and 63 houses damaged, with some dozen destroyed. He said about 100 people have suffered light injuries, including from emergency services.
“At the moment that I speak to you there are no deaths, which is remarkable given the extent of the fires,” he said. “But there are all the reasons to think we are headed toward a summer of high risk.”
Marseille Mayor Benoit Payan on X warned residents the fire was now “at the doors of Marseille,” urging inhabitants in the north of the city to refrain from taking to the roads to leave way for rescue services.
The mayor of Pennes-Mirabeau said two housing estates had been evacuated and firefighters had positioned themselves outside a retirement home to fight off approaching flames.
The Marseille Provence airport is the country’s fourth after Charles-de-Gaulle and Orly outside Paris, and Nice.
The fire near Marseille is just the latest to hit France in recent days.
To the west along the Mediterranean coast, near the city of Narbonne, more than 1,000 firefighters from around the country were seeking to contain another blaze.
It had crept across 2,000 hectares (4,900 acres) of trees since starting on the property of a winery on Monday afternoon, emergency services said.
In the village of Prat-de-Cest on Tuesday morning, trees were blackened or still on fire.
As she watched fire trucks drive to and fro, retiree Martine Bou recounted fleeing her home with her cats, tortoises and dog on Monday afternoon before returning.
But her husband, Frederic, stayed all night to hose down the great pines on the other side of the road so the fire would not engulf their home.
“I’ve never seen anything like it. I have never lived next to such an enormous fire,” he told AFP, reporting flames dozens of meters (more than a hundred feet) high.
The fire near Narbonne caused authorities to close the A9 motorway to Spain, but on Tuesday morning they said they were progressively reopening it to traffic.
Travelers no longer have to remove their shoes during security screenings at US airports

- All passengers between the ages of 12 and 75 were required to remove their shoes, which were scanned along with carry-on luggage
WASHINGTON: Travelers racing to catch a flight at US airports no longer are required to remove their shoes during security screenings, Homeland Security Secretary Kristi Noem said Tuesday.
Noem said the end of the ritual put in place almost 20 years ago was effective nationwide effective immediately. She said a pilot program showed the Transportation Security Administration had the equipment needed to keep airports and aircraft safe while allowing people to keep their shoes on.
“TSA will no longer require travelers to remove their shoes when they go through security checkpoints,” Noem said.
While shoe removal no longer is standard procedure, some travelers still may be asked to take off their footwear “if we think additional layers of screening are necessary,” she added.
Security screening sans shoes became a requirement in 2006, several years after “shoe bomber” Richard Reid’s failed attempt to take down a flight from Paris to Miami in late 2001.
All passengers between the ages of 12 and 75 were required to remove their shoes, which were scanned along with carry-on luggage.
The travel newsletter Gate Access was first to report that the security screening change would happen soon.
Travelers previously were able to skirt the requirement if they participated in the TSA PreCheck program, which costs around $80 for five years. The program allows airline passengers to get through the screening process without removing shoes, belts or light jackets, and without having to take their laptops and bagged toiletries out.
The TSA began in 2001 when President George W. Bush signed legislation for its creation two months after the 9/11 attacks. The agency included federal airport screeners that replaced the private companies airlines had used to handle security.
Over the years the TSA has continued to look for ways to enhance its security measures, including testing facial recognition technology and implementing Real ID requirements.
One of the most prominent friction points for travelers is the TSA at screening checkpoints. President Donald Trump’s Transportation Secretary Sean Duffy asked the public in an April social media post what would make travel more seamless.
The following day, Duffy posted on X that, “It’s clear that TSA is the #1 travel complaint. That falls under the Department of Homeland Security. I’ll discuss this with @Sec_Noem.”
Trump fired TSA Administrator David Pekoske in January in the middle of a second five-year term, though he was appointed by Trump during his first term in the White House. Pekoske was reappointed by President Joe Biden.
No reason was given for Pekoske’s departure. The administrator position remains vacant, according to the TSA website.
Trump’s previous tariff push terrified the world economy. He’s betting this time is different

- With Trump’s 90-day tariff negotiation period ending, he has so far sent letters to 14 countries that place taxes on imported goods ranging from 25 percent to 40 percent
WASHINGTON: When President Donald Trump last rolled out tariffs this high, financial markets quaked, consumer confidence crashed and his popularity plunged.
Only three months later, he’s betting this time is different.
In his new round of tariffs being announced this week, Trump is essentially tethering the entire world economy to his instinctual belief that import taxes will deliver factory jobs and stronger growth in the US, rather than the inflation and slowdown predicted by many economists.
On Tuesday, he told his Cabinet that past presidents who hadn’t aggressively deployed tariffs were “stupid.” Ever the salesman, Trump added that it was “too time-consuming” to try to negotiate trade deals with the rest of the world, so it was just easier to send them letters, as he’s doing this week, that list the tariff rates on their goods.
The letters marked a change from his self-proclaimed April 2 “Liberation Day” event at the White House, where he had posterboards with the rates displayed, a choice that led to a brief market meltdown and the 90-day negotiating period with baseline 10 percent tariffs that will end Wednesday. Trump, instead, chose to send form letters with random capitalizations and punctuation and other formatting issues.
“It’s a better way,” Trump said of his letters. “It’s a more powerful way. And we send them a letter. You read the letter. I think it was well crafted. And, mostly it’s just a little number in there: You’ll pay 25 percent, 35 percent. We have some of at 60, 70.”
When Trump said those words, he had yet to issue a letter with a tariff rate higher than 40 percent, which he levied Monday on Laos and Myanmar. He plans to put 25 percent tariffs on Japan and South Korea, two major trading partners and allies deemed crucial for curbing China’s economic influence. Leaders of the 14 countries tariffed so far hope to negotiate over the next three weeks before the higher rates are charged on imports.
“I would say that every case I’m treating them better than they treated us over the years,” Trump said.
Three possible outcomes
His approach is at odds with how major trade agreements have been produced over the last half-century, detailed sessions that could sometimes take years to solve complex differences between nations.
There are three possible outcomes to this political and economic wager, each of which could drastically reshape international affairs and Trump’s legacy.
Trump could prove most economic experts wrong and the tariffs could deliver growth as promised. Or he could retreat again on tariffs before their Aug. 1 start in a repeat of the “Trump Always Chickens Out” phenomenon, also known as TACO. Or he could damage the economy in ways that could boomerang against the communities that helped return him to the White House last year, as well as hurt countries that are put at a financial disadvantage by the tariffs.
Sen. Ron Wyden, D-Oregon, said Trump’s letters had “extended his tariff purgatory for another month,” essentially freezing in place the US economy as CEOs, foreign leaders and consumers are unclear of Trump’s actual strategy on foreign trade.
“The TACO negotiating tactic pioneered by Trump is making his threats less and less credible and reducing our trading partners’ willingness to even meet us halfway,” Wyden said. “There’s no sign that he’s any closer to striking durable trade deals that would actually help American workers and businesses.”
So far, the stock and bond markets are relatively calm, with the S&P 500 stock index essentially flat Tuesday after a Monday decline. Trump is coming off a legislative win with his multitrillion-dollar income tax cuts. And he’s confidently levying tariffs at levels that previously rocked global markets, buoyed by the fact that inflation has eased so far instead of accelerating as many economists and Democratic rivals had warned.
“By floating tariffs as high as 40 percent to even 100 percent, the administration has ‘normalized’ the 25 percent tariff hikes — yet this is still one of the most aggressive and disruptive tariff moves in modern history,” said Wendong Zhang, an economist at Cornell University. “This gradual unveiling, paradoxically, risks normalizing what would otherwise be considered exceptionally large tariff hikes.”
Others simply see Trump as a source of nonstop chaos, with the letters and their somewhat random tariff rates showing the absence of a genuine policy process inside his administration.
“It’s really just a validation that this policy is all over the place, that they’re running this by the seat of their pants, that there is no real strategy,” said Desmond Lachman, a senior fellow at the American Enterprise Institute, a right-leaning think tank.
Questions about how much money tariffs will generate
With Trump’s 90-day tariff negotiation period ending, he has so far sent letters to 14 countries that place taxes on imported goods ranging from 25 percent to 40 percent. He said he would sign an order Tuesday to place 50 percent tariffs on copper and said at the Cabinet meeting that at some point pharmaceutical drugs could face tariffs of as much as 200 percent. All of that is on top of his existing 50 percent tariffs on steel and aluminum, 25 percent tariffs on autos and his separate import taxes on Canada, Mexico and China.
“The obvious inference is that markets for now are somewhat skeptical that Trump will go through with it, or alternatively they think compromises will be reached,” said Ben May, a director of global economic research at the consultancy Oxford Economics. “That’s probably the key element.”
May said the tariffs are likely to reduce the growth in US household incomes, but not cause those incomes to shrink outright.
Trump has said his tariffs would close US trade imbalances, though it’s unclear why he would target nations such as Tunisia that do relatively little trade with America. Administration officials say trillions of dollars in tariff revenues over the next decade would help offset the revenue losses from the continuation and expansion of his 2017 tax cuts that were signed into law Friday.
The federal government has collected $98.2 billion in tariff revenues so far this year, more than double what it collected last year, according to the Bipartisan Policy Center.
At Tuesday’s Cabinet meeting, Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent said the tariff revenues could be “well over $300 billion by the end of the year.” Bessent added that “we don’t agree” with the Congressional Budget Office estimate that tariffs would bring in $2.8 trillion over 10 years, “which we think is probably low.”
The governments of Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, Myanmar, Thailand, Cambodia and South Africa have each said they hope for further negotiations on tariffs with Trump, though it’s unclear how that’s possible as Trump has said it would be too “complicated” to hold all those meetings.
Instead on Tuesday, Trump posted on social media that the tariffs would be charged as scheduled starting Aug. 1.
“There has been no change to this date, and there will be no change,” Trump said on Truth Social. “No extensions will be granted. Thank you for your attention to this matter!”
Supreme Court clears the way for Trump’s plans to downsize the federal workforce

- The high court action continued a remarkable winning streak for Trump, who the justices have allowed to move forward with significant parts of his plan to remake the federal government
WASHINGTON: The Supreme Court on Tuesday cleared the way for President Donald Trump’s plans to downsize the federal workforce despite warnings that critical government services will be lost and hundreds of thousands of federal employees will be out of their jobs.
The justices overrode lower court orders that temporarily froze the cuts, which have been led by the Department of Government Efficiency.
The court said in an unsigned order that no specific cuts were in front of the justices, only an executive order issued by Trump and an administration directive for agencies to undertake job reductions.
Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson was the only dissenting vote, accusing her colleagues of a “demonstrated enthusiasm for greenlighting this President’s legally dubious actions in an emergency posture.”
Jackson warned of enormous real-world consequences. “This executive action promises mass employee terminations, widespread cancelation of federal programs and services, and the dismantling of much of the Federal Government as Congress has created it,” she wrote.
The high court action continued a remarkable winning streak for Trump, who the justices have allowed to move forward with significant parts of his plan to remake the federal government. The Supreme Court’s intervention so far has been on the frequent emergency appeals the Justice Department has filed objecting to lower-court rulings as improperly intruding on presidential authority.
The Republican president has repeatedly said voters gave him a mandate for the work, and he tapped billionaire ally Elon Musk to lead the charge through DOGE. Musk recently left his role.
Tens of thousands of federal workers have been fired, have left their jobs via deferred resignation programs or have been placed on leave. There is no official figure for the job cuts, but at least 75,000 federal employees took deferred resignation and thousands of probationary workers have already been let go.
In May, US District Judge Susan Illston found that Trump’s administration needs congressional approval to make sizable reductions to the federal workforce. By a 2-1 vote, a panel of the US 9th Circuit Court of Appeals refused to block Illston’s order, finding that the downsizing could have broader effects, including on the nation’s food-safety system and health care for veterans.
Illston directed numerous federal agencies to halt acting on the president’s workforce executive order signed in February and a subsequent memo issued by DOGE and the Office of Personnel Management. Illston was nominated by former Democratic President Bill Clinton.
The labor unions and nonprofit groups that sued over the downsizing offered the justices several examples of what would happen if it were allowed to take effect, including cuts of 40 percent to 50 percent at several agencies. Baltimore, Chicago and San Francisco were among cities that also sued.
Among the agencies affected by the order are the departments of Agriculture, Energy, Labor, the Interior, State, the Treasury and Veterans Affairs. It also applies to the National Science Foundation, Small Business Association, Social Security Administration and Environmental Protection Agency.
The case now continues in Illston’s court.
France wildfire shuts down Marseille airport, halts trains

- Several forest fires have raged in recent days in southern France, fanning out at speed due to wind and parched vegetation after a heatwave
- The fire started in a vehicle in the area of Pennes-Mirabeau to the north of Marseille, on the road to the airport
MARSEILLE: A wildfire in southern France on Tuesday forced Marseille airport to close and interrupted train traffic as the blaze spread rapidly to the edges of the city.
Several forest fires have raged in recent days in southern France, fanning out at speed due to wind and parched vegetation after a heatwave.
Scientists say human-induced climate change is increasing the intensity, length and frequency of extreme heat that fuels forest fires.
The fire started in a vehicle in the area of Pennes-Mirabeau to the north of Marseille, on the road to the airport, roaring across 700 hectares (1,700 acres) by the evening, firefighters said.
It sent plumes of acrid smoke billowing into the sky, causing the airport to close its runways shortly after midday (1000 GMT), a spokesman for the Marseille Provence airport said.
The spokesman later said that the airport would partially reopen at around 9:30 p.m. and that 54 flights had been canceled and another 14 redirected.
The website of the SNCF national rail operator showed more than a dozen train trips had been canceled in and out of the city.
It said rail travel to and from Marseille would remain “highly affected” on Wednesday.
Marseille mayor Benoit Payan on X warned residents the fire was now “at the doors of Marseille,” urging inhabitants in the north of the city to refrain from taking to the roads to leave way for rescue services.
The mayor of Pennes-Mirabeau said two housing estates had been evacuated and firefighters had positioned themselves outside a retirement home to fight off approaching flames.
The Marseille Provence airport is the country’s fourth after Charles-de-Gaulle and Orly outside Paris, and Nice.
The fire near Marseille is just the latest to hit France in recent days.
To the west along the Mediterranean coast, near the city of Narbonne, more than 1,000 firefighters from around the country were seeking to contain another blaze.
It had crept across 2,000 hectares (4,900 acres) of trees since starting on the property of a winery on Monday afternoon, emergency services said.
In the village of Prat-de-Cest on Tuesday morning, trees were blackened or still on fire.
As she watched fire trucks drive to and fro, retiree Martine Bou recounted fleeing her home with her cats, tortoises and dog on Monday afternoon before returning.
But her husband, Frederic, stayed all night to hose down the great pines on the other side of the road so the fire would not engulf their home.
“I’ve never seen anything like it. I have never lived next to such an enormous fire,” he told AFP, reporting flames dozens of meters (more than a hundred feet) high.
The fire near Narbonne caused authorities to close the A9 motorway to Spain, but on Tuesday morning they said they were progressively reopening it to traffic.