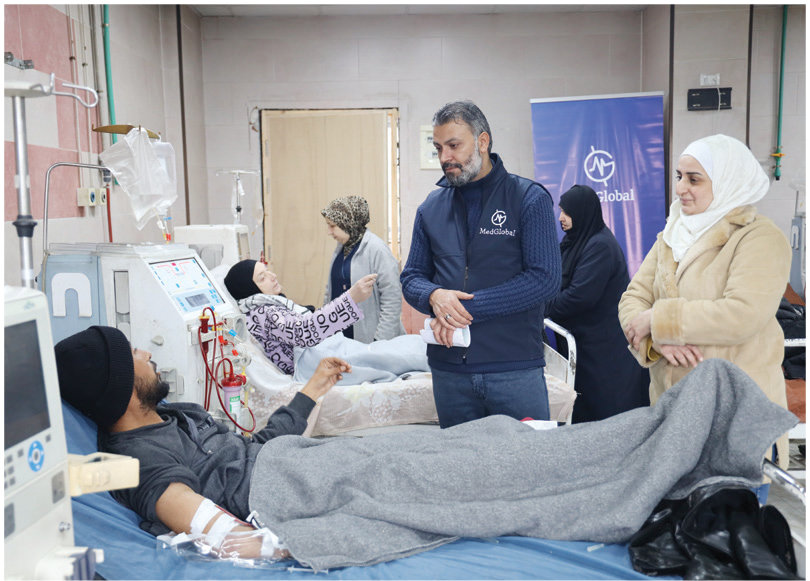
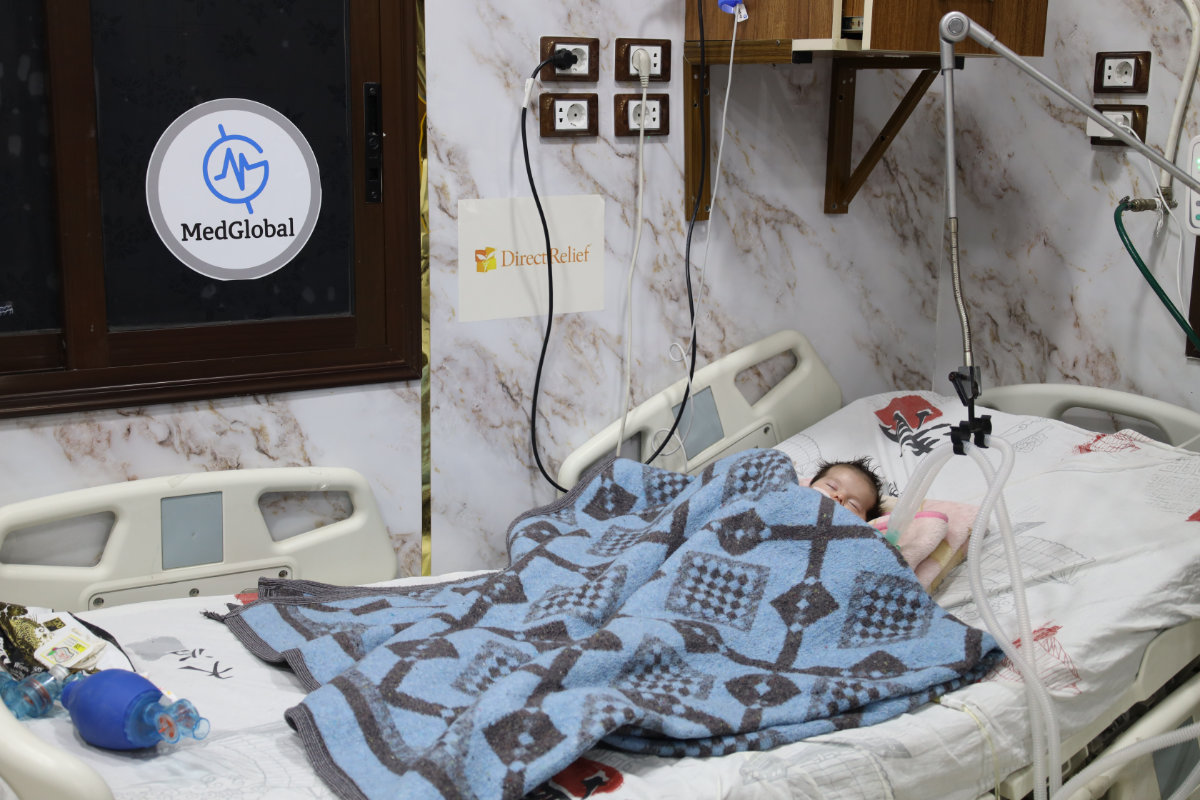
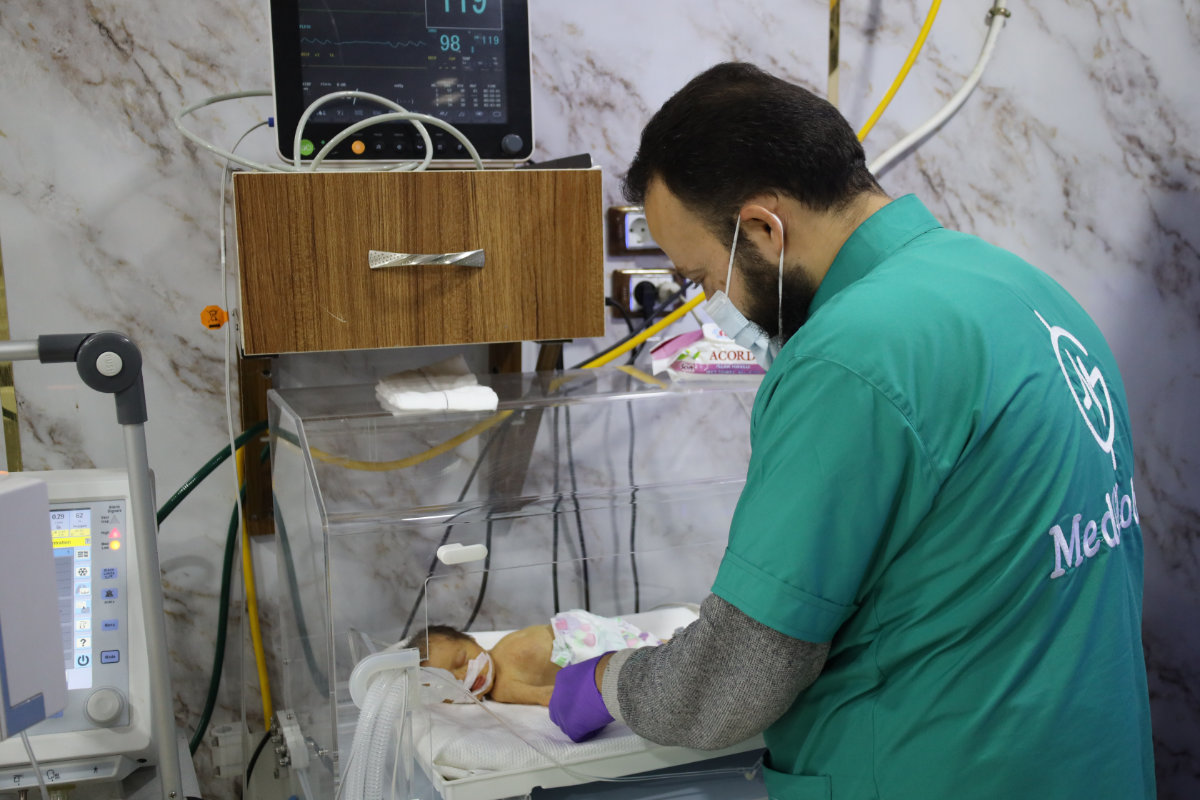
LONDON: Desperate to escape the violence raging across Sudan, thousands of people are setting off on the perilous journey to neighboring states. On the way, however, many are confronted by another hazard — deadly heat.
Dozens of people attempting to illegally cross the border into Egypt have died as the region reels from a severe summer heatwave. Earlier this month, temperatures in Egypt’s southern governorate of Aswan rose to a record 49.6 degrees Celsius in the shade.
The Refugee Platform, an independent Egyptian rights organization, said on June 17 that Aswan locals had found vehicles on remote desert roads filled with the bodies of migrants who had perished.

About 500,000 people from Sudan have fled to Egypt alone since the beginning of the conflict. (AFP)
It reported that 51 people died, presumably on their way to Egypt, as a result of dehydration, heat stroke or road accidents, compounded by lack of medical care. Survivors hospitalized in Aswan informed the Refugee Platform that the number of missing migrants exceeds those who have been found.
Many families have reported their loved ones missing. “My aunt lost contact with her 34-year-old son for two weeks earlier this month, only to later hear from a friend who had reached Egypt that he died of heat stroke before they crossed the border,” said Manal, a UK-based Sudanese nurse, whose name has been changed to protect her anonymity.
She told Arab News that her cousin, who was uprooted from his home in the capital Khartoum, had previously sent his mother, wife and their five-year-old son to Egypt when Sudanese women and minors were exempt from visa requirements.
The conflict between the Sudanese Armed Forces and the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces, which erupted on April 15 last year, has displaced 9.1 million people, with 2.1 million having fled abroad, according to UN figures.
According to the International Organization for Migration, about 500,000 people from Sudan have fled to Egypt alone since the beginning of the conflict.
This year's Global Peace Index, produced by the Sydney-headquartered Institute for Economics and Peace, classified Sudan as the second least peaceful country in the world, preceded only by Yemen.
Before its descent into horror, Sudan was Africa’s second-largest refugee host, accommodating over 1 million refugees from Syria, Ethiopia, South Sudan, Eritrea, the Central African Republic, Chad and Yemen.
Today, Sudanese refugees form the largest exile community in Egypt, with more than 300,000 registered with the UN Refugee Agency, UNHCR, in the neighboring country.

Many families have reported their loved ones missing. (AFP)
Nairobi-based World Food Program communications officer Alessandro Abbonizio described Sudan’s refugee crisis as “the world’s largest displacement crisis,” with hundreds of thousands of Sudanese people also fleeing to other neighboring countries, including Chad and South Sudan.
He said that while the WFP “has mobilized massive responses” in neighboring countries to support families fleeing Sudan, many of these nations already grapple with “high levels of food insecurity.”
“The arrival of Sudanese refugees in those countries is stretching WFP’s already underfunded refugee and humanitarian operations across the region,” he told Arab News. “In South Sudan, WFP has already had to reduce humanitarian assistance, and vulnerable families are only receiving half rations.”
An estimated 7.1 million people in South Sudan already face acute or worse food insecurity, as per UN figures, with the number of those facing starvation and death projected to almost double between April and July 2024, compared with the same period last year.
Abbonizio pointed out that thousands of people from Sudan continue to cross the border into South Sudan every week, adding that “families are arriving with stories of long journeys with little food or water and citing violence and lack of food as the main reasons that they left Sudan.”
South Sudan too has been experiencing extreme heat since March when authorities ordered schools to shut across the country. The country, which gained independence from Sudan in 2011, is highly exposed to climatic events such as droughts, floods and rising temperatures, which have led to further displacement, food insecurity and religious and ethnic unrest.
In Chad, “piecemeal funding has forced WFP to operate month-by-month, falling short of meeting the needs of refugees (including those from Sudan) and crisis-affected host communities,” Abbonizio said.
In the absence of preventive measures, worsening climatic conditions spell doom for the region, placing millions at greater risk of food insecurity and, consequently, malnutrition.

Long waiting times and lack of basic amenities at the Sudan-Egypt border are pushing increasing numbers of people in Sudan to take illegal routes into Egypt. (AFP)
A UN Food and Agriculture Organization report cautioned that extreme climatic events “could have major implications for several hotspots, including risk of floods in parts of South Sudan, Somalia, Ethiopia, Haiti, Chad, Mali and Nigeria, as well as Sudan.”
The Hunger Hotspots report, published on June 5, highlighted that “Mali, Palestine, South Sudan and Sudan remain at the highest alert level and require the most urgent attention.”
WFP’s Abbonizio warned that as the rainy season arrives in the coming weeks, access to parts of Eastern Chad will be cut off, potentially worsening the food insecurity crisis in the region.
Noting that 3.4 million people in Chad are projected to face acute food insecurity during the current lean season from June to August, he said: “This year is becoming a race against time as the rainy season is expected to begin in the coming weeks and could cut off access to parts of Eastern Chad.”
INNUMBERS
• 700,000+ Refugees and returnees who have fled from Sudan into South Sudan since April 2023.
• 900,000+ People projected to flee from Sudan into Chad by 2024 end.
• 300,000+ Sudanese refugees registered with UNHCR in Egypt.
Abbonizio called for urgent funding “to preposition food supplies for its refugee response ahead of the start of the rains,” adding that “WFP is also supporting hundreds of thousands of Sudanese refugees in Ethiopia, Uganda and Egypt with food, cash, and nutrition assistance.”
Meanwhile, long waiting times and lack of basic amenities at the Sudan-Egypt border are pushing increasing numbers of people in Sudan to take illegal routes into Egypt in hopes of finding sanctuary.

The conflict has displaced 9.1 million people, with 2.1 million having fled abroad. (AFP)
“Some of the bodies arrived with their skin peeled off and suffering from dehydration,” a medical source at a hospital in Aswan told the Mada Masr news outlet.
Survivors of the ordeal said that “dozens in the desert have no water,” and “entire families died because of the high temperatures and were left there.”
The precise number of people who have died in the process is difficult to ascertain. The Refugee Platform said that, between June 7 and June 9, 40 people, including children, women and entire families, lost their lives. The number is expected to rise as more bodies are uncovered.
In June last year, Cairo announced that all Sudanese people must hold valid visas prior to entering Egypt, scrapping a law that only required Sudanese men aged 16 to 50 to have a visa.
As Egypt has further tightened entry and residency requirements, at least 120,000 people, lacking travel documents, remain in limbo on the Sudan side of the border, according to an AFP news agency report.
Since September, Egyptian authorities have also carried out arrests of Sudanese refugees “based on their migration status.” The decision was made after authorities detected “unlawful activities,” including visa forgery, an Egyptian foreign ministry spokesperson told the Reuters news agency.

Cairo announced that all Sudanese people must hold valid visas prior to entering Egypt. (AFP)
In March, the Sudanese Dabanga Radio cited a thriving trade in forged Egyptian visas at the Argeen border crossing between the two countries.
In a condolence message to the families of those who have died trying to reach Egypt, Abdelgadir Abdallah, Sudan’s consul general in Aswan, warned of the dangers of using irregular means to enter Egypt. “Avoid using this method. Some areas in Sudan are safe; remain there,” he said.