JEDDAH: Health systems the world over have been stretched to their absolute limits by successive waves of COVID-19, which have resulted in crowded hospitals, delayed medical procedures, and doctors and nurses becoming exhausted and overstretched.
A secondary consequence of the global health emergency has been the depletion of blood stocks required for life-saving transfusions, use during surgeries, and to treat medical conditions such as anemia, cancer and blood disorders.
Lockdown measures and strict controls on attending hospitals have prevented many people from donating blood. Even when restrictions have been lifted, COVID-19 infections and the fear of infection have kept a swathe of potential donors at home.
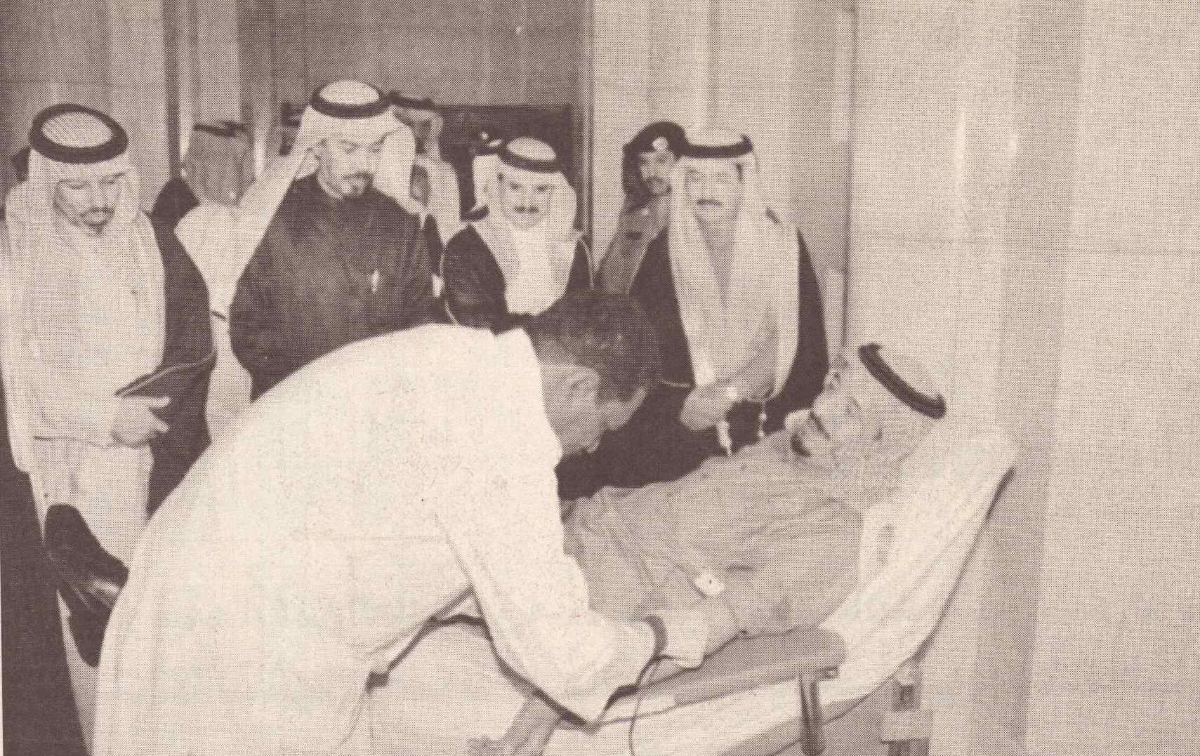
Prince Salman, as Governor of Riyadh, donates blood in the 1980s. (SPA)
Faced with the resulting shortages, health authorities in Saudi Arabia are keen to boost the Kingdom’s blood stock levels, which need to be constantly replenished to meet demand.
“There is an increased need for blood. (The situation has) worsened around the world due to the pandemic. The call is constant,” Dr. Maha Badawi, a hematology consultant and the director of blood transfusion services at King Abdulaziz University Hospital in Jeddah, told Arab News.
“COVID-19 negatively impacted blood supply globally and the problem was due to several factors. Although COVID-19 isn’t transmitted by blood, COVID-19-positive patients and individuals who were exposed to positive cases were required to isolate for periods of time to curb the spread of the infection.
“Another impact was the social-distancing measures. Mass campaigns and initiatives were suspended, restricting the number of donors in turn.”
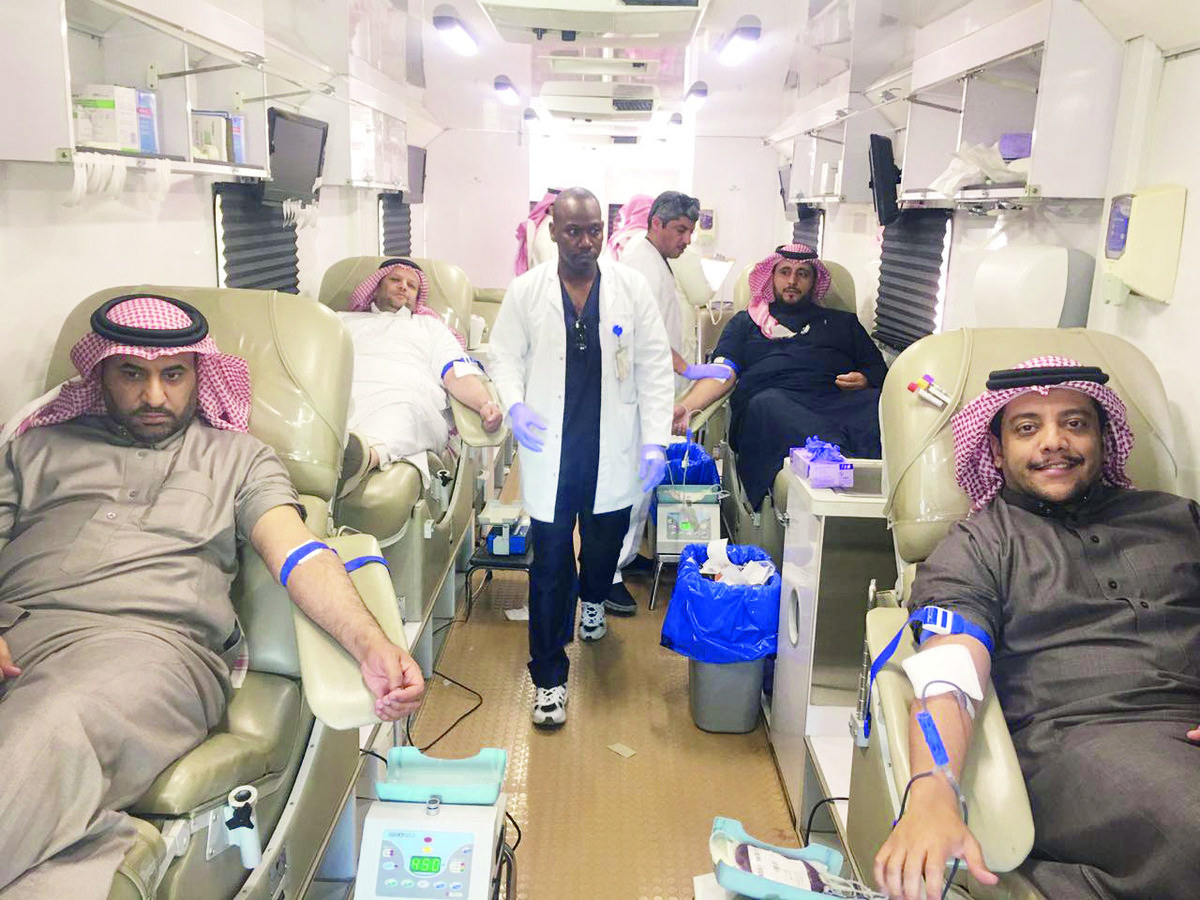
Raising public awareness and encouraging more donors to come forward is one of the many ways to keep the Kingdom’s blood banks adequately supplied. (SPA)
As a result, Saudi Arabia is now experiencing a shortage of type O in its stocks of red blood cells, and type AB in plasma stocks.
A retrospective study by King Abdullah Hospital in Bisha revealed a 39.5 percent decrease in donations to blood banks during the pandemic. Demand for blood also decreased during the same period, by 21.7 percent, probably as a result of the many surgeries that had to be canceled.
A study titled Awareness About Coronavirus and Challenges for Blood Services among Potential Blood Donors, published in 2021 in the medical journal Transfusion and Apheresis Science, used survey data drawn from a cross-section of the Saudi population to assess the factors that had prevented people from donating blood.
It found that social-distancing measures, misinformation about ways in which the disease can be transmitted, and a lack of knowledge among potential blood donors may have contributed to the prevalence of missed or postponed donations.
The majority of people surveyed said they were concerned about the virus being transmitted during the blood-donation process. Others were worried about coming into contact with fellow donors.
Maintaining ample blood stocks is an essential part of the preparations for responding to major incidents, such as natural disasters. (SPA)
The authors of the study advised health authorities to promote better donor education, encourage at-risk donors to defer donations, facilitate physical-distancing measures, and enforce the use of personal protective equipment to protect donors and medical staff.
In the face of these concerns, campaigns have been launched in the Kingdom to reassure the public and encourage them to donate blood.
“The need is constant and each hospital blood bank requires a continuous flow to maintain its daily stock, depending on the hospital’s needs,” said Badawi.
“Because the longevity of donated blood components varies, so too does the availability of supply. Some components can be stored for a month or two, whereas others can be stored up to five days at a maximum, which means you constantly need donors.”
Red blood cells can normally be stored for up to 35 days but platelets can only be held for seven. Plasma can be stored for up to three years.
A number of conditions require patients to have regular blood transfusions, including sickle cell disease, a group of inherited red blood cell disorders. Healthy red blood cells are round and move smoothly through small blood vessels as they carry oxygen throughout the body. In a patient who has SCD, the red blood cells are hard and sticky and resemble a crescent or “sickle” shape.
These sickle cells die much quicker than regular red blood cells, which results in a constant shortage of red blood cells. In addition, as they travel through small blood vessels they can get stuck and block the blood flow, which can cause pain and serious medical problems.
Raising public awareness and encouraging more donors to come forward is one of the many ways to keep the Kingdom’s blood banks adequately supplied. (SPA)
In Saudi Arabia, about 4.2 percent of the population carries the gene for SCD and about 0.26 percent experiences symptoms.
“Blood transfusion is an effective treatment option for sickle cell patients as it lowers the amount of hemoglobin S in the red blood cells and increases the numbers of normal red blood cells, thus increasing the supply of oxygen to the body,” Dr. Qasim Dobie, an assistant professor of hematology at Jazan University, told Arab News.
“So frequent blood transfusions will lower the risk of stroke, especially in infants and children, and treat and prevent the severe complications of sickle cell disease.”
Maintaining ample blood stocks is also an essential part of the preparations for responding to major incidents, such as natural disasters or mass-casualty terrorist attacks, which might cause hospitals to be overwhelmed by demand for transfusions.
Currently, donors in the Kingdom must be at least 17 years old, weigh more than 50 kg and pass a brief medical examination. Saudi health authorities have made efforts to bolster the number of donation centers in a number of ways, including the introduction of a fleet of mobile clinics to make it easier for donors to attend.
FASTFACTS
56 - Ideal number of days between whole blood donations.
3 - Number of lives that can be saved with a single donation.
10 - Average adult’s blood volume in pints.
1 - Typical amount, in pints, of whole blood taken during donation.
(Source: Cedars-Sinai)
But medical practitioners say there is still room for improvement, particularly in terms of raising public awareness and encouraging more donors to come forward.
“Lack of awareness is one of the leading causes of the drop in blood donations,” said Badawi. “Blood is the best donation one can give to another human being. There are blood drives all year round.”
One of the Saudi initiatives is Wateen, an innovative smartphone app currently under the supervision of the Kingdom’s Ministry of Health.
Health authorities are seeking to encourage more people to give blood. (Supplied)
Wateen makes it easier for citizens and residents to manage blood donations by helping registered donors find the nearest clinic, keep track of when they are next due to give blood, and be aware of how many times they have donated in total.
“Since its initiation in 2018, Wateen has served as a means to unite donors and blood banks under one platform to help maintain adequate stocks,” Meshari Almalki, a spokesperson for Wateen, told Arab News.
“There’s a difference between a voluntary donation and a family/replacement donation. The latter is mainly done through direct messages from family members or acquaintances. The former is what we aim to empower and raise more awareness of.”
More than half a million registered users have made 1.1 million donations through the platform since it was launched. Year-round campaign attract many new donors but misunderstandings and misinformation can still cause potential donors to be apprehensive.
“There’s a fear that donors won’t be compatible, fear of needles or pain, fear of feeling faint or dizzy after donating, and fear of adverse reactions,” said Almalki.

Each hospital blood bank requires a continuous flow to maintain its daily stock, depending on the hospital’s needs.
(Supplied)
“These are all understandable. That’s why there are medical personnel to ensure the safety and health of donors and recipients. There are standard procedures that apply and that’s why, after conducting a survey, we launched our latest campaign to tackle these fears head on and hosted a therapist to answer all the questions.”
Resources such as the Wateen app are helping to narrow the gap between demand and supply of blood. But if the constant demand is to be met and blood stocks are to be replenished following the drain caused by the pandemic, more needs to be done to attract and reassure new donors.
“As far as health institutions go, all would benefit from more collaboration between the government authorities, the private sector, the education field and others for campaigns,” said Badawi.
“The campaigns don’t necessarily need to solely focus on blood-donation drives but could include lectures, talks and information sessions that highlight the importance of donating blood and refute falsehoods to activate a community of blood donors.
“Making it a habit to donate twice a year could make a significant impact. Take a friend or family member along — they’ll make it a habit, too.”





























