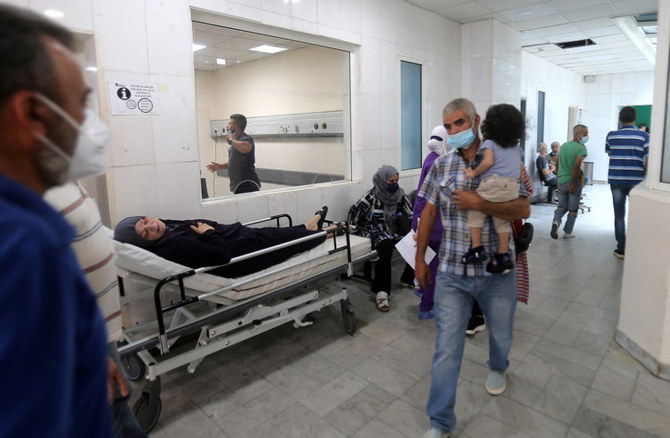
DUBAI: Last August, millions around the world watched in horror as footage of the devastating Beirut port blast looped on TV channels and social-media feeds for days. For residents of the Lebanese capital, that month was like no other in recent memory.
Within hours of the explosion on Aug. 4, people began to pour into the city’s hospitals with all kinds of trauma, disfiguring burns and wounds caused by flying glass and masonry. But then, Beirut’s public-health infrastructure itself was one of the biggest casualties.
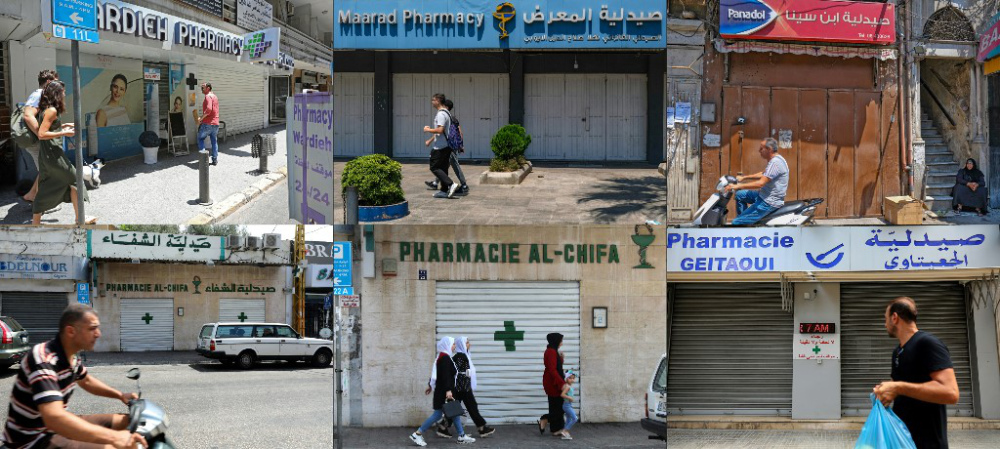
According to a World Health Organization assessment, four hospitals were heavily affected and 20 primary care facilities, serving approximately 160,000 patients, were either damaged or destroyed.
A year on, as Lebanon reels from the combined impact of economic chaos, medicine shortages, power cuts and repeated COVID-19 waves, the nation’s health system is on life support.
Furthermore, medical professionals report that they are not receiving sufficient protection while on duty as their workplaces lack the medical gear and the protocols necessary for dealing with the highly transmissible delta variant of COVID-19.
“The health situation in Lebanon is really dire,” Rabih Torbay, president and CEO of US-based humanitarian aid agency Project HOPE, told Arab News.

Lebanon reels from the combined impact of economic chaos, medicine shortages, power cuts and repeated COVID-19 waves. (AFP)
“It is a combination of the lack of electricity in hospitals, a lack of fuel for generators in hospitals and beyond, a lack of medicine for hospitals and clinics, the currency losing 90 percent of its value, doctors and nurses leaving and a rise in the number of COVID-19 infections.”
Lebanon took another jolt last week when the Central Bank announced that fuel subsidies had been halted. Already, according to CNN, many factories, including one that supplies the majority of Lebanon's intravenous lines to hospitals, have closed because of long power outages.
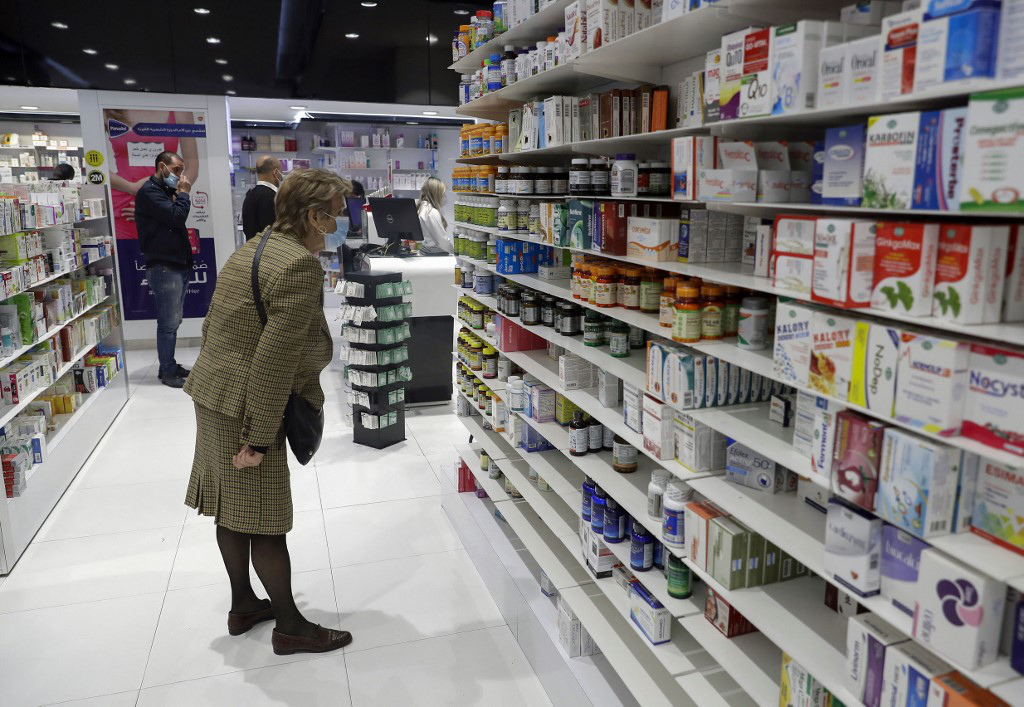
Nivine Bou Chakra, whose grandmother takes Nebilet for hypertension, said they have had to ration the stock of drugs they were able to buy last year. “You can’t find it now. And if you do, it’s expensive,” she told Arab News.
Bou Chakra’s father has run his own dental practice for more than 20 years. Many of his patients only visit if they have an emergency, “such as inflammation from an infected tooth,” she said.
“Since they can’t find antibiotics, they come to the dentist to take the tooth out. They do that because they can’t afford the alternative: Proper treatment.”
According to Ingrid Antonios, who is doing her residency at the anesthesiology and critical care department of the Hotel-Dieu de France hospital in Beirut, doctors and nurses are having to resort to cheaper, locally produced alternatives to imported drugs.
“A lot of products were, and still are, not available in the country for various reasons. From very basic stuff, such as painkillers and proton-pump inhibitors, to more specific medications for cancer, hypertension, diabetes and antibiotics,” she said.
Tony Noujaim, a master’s student, said it has become increasingly difficult to find diabetes and cholesterol medications for his father and aunt.
“We haven’t had the need to get them from across the border, at least not yet. But getting them involves a pharmacy treasure hunt in the north. Basically, we go from pharmacy to pharmacy until we eventually find what is a pretty basic and standard medicine,” Noujaim told Arab News.
And it is not just the people of Beirut who are struggling. About 19.5 percent of Lebanon’s population of 7 million are refugees from neighboring countries. Already living precariously in impoverished communities, few of them have the means or the connections to obtain vital medications at a time of scarcity.
It is hard to believe now that Lebanon’s health sector was in much better shape not so long ago, attracting patients from across the Middle East. But conditions began to deteriorate with the onset of the financial crisis in late 2019.
At the time, the New York-based Human Rights Watch warned that health professionals were struggling to meet the needs of their patients owing to the “government’s failure to reimburse private and public hospitals, including funds owed by the National Social Security Fund and military health funds, making it difficult to pay staff and purchase medical supplies.”
The steady depletion of foreign-currency reserves has made it difficult for Lebanese traders to import essential goods and “led banks to curtail credit lines” — a disaster for a nation that depends so heavily on imports.
“Lebanon imports 80 percent of its products — most of the country’s oil, medicine, meat, grain and other supplies come from abroad,” according to a report by Christian aid agency ACT Alliance.
“The pharmaceutical crisis has deepened in Lebanon as the central bank is unable to meet the cost of subsidized medicines.”

According to a World Health Organization assessment, four hospitals were heavily affected and 20 primary care facilities, serving approximately 160,000 patients, were either damaged or destroyed during the port explosion. (AFP)
The drastic devaluation of the currency has also made health insurance unaffordable for many Lebanese. “A challenge I faced at work was when a lady in her forties suffering from advanced cancer came to the emergency department in a critical condition following a severe infection,” Antonios, of the Hotel-Dieu de France hospital, told Arab News.
“She required admission to an intensive care unit, but she and her husband couldn’t afford to pay for admission. She had to be transferred to another hospital in a very unstable condition, which could have been life threatening.”
Amid Lebanon’s overlapping crises, electricity shortages have forced hospitals to rely on private generators to keep the lights on and their life-sustaining equipment functioning. But generators run on fuel, which is also now in short supply.
The American University of Beirut (AUB) Medical Center gave warning last week that its patients were in imminent danger owing to the fuel shortage.
“This means ventilators and other lifesaving medical devices will cease to operate. Forty adult patients and 15 children living on respirators will die immediately,” the AUB said in a statement.
Water has also become a finite commodity because of prolonged mismanagement, infrastructure decay and the unmet energy needs of pumping stations and treatment plants.

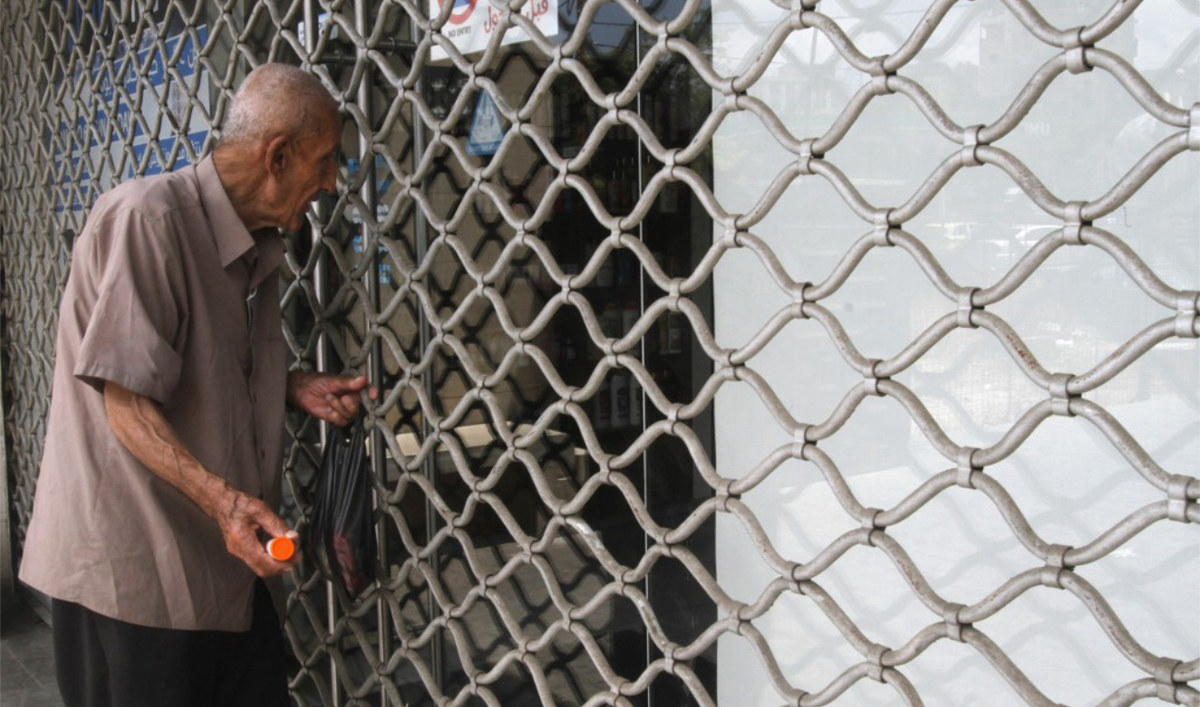
“The pharmaceutical crisis has deepened in Lebanon as the central bank is unable to meet the cost of subsidized medicines,” according to a report by Christian aid agency ACT Alliance. (AFP)
“A lot of the pumps are no longer in a position to supply water to homes, yet people can’t afford to buy bottled water,” said Torbay.
“It’s not just the lack of water. With lack of water comes infection outbreaks, diarrheal diseases and hygiene-related issues.”
Watching the health system beset by a lengthening list of problems, many medical professionals have made the difficult decision to leave the country. The trend started with the onset of the economic crisis and has only accelerated since the Beirut blast.
Amani Mereby, a Ph.D. candidate, said her physician now spends more time working in France, despite being in high demand in Lebanon.
“Because of the economic crisis, my physician, who was very successful in Lebanon, is having to divide his time between here and France,” she said. “The only reason he visits Lebanon once every two months is because he wants to help his patients.”

“A lot of products were, and still are, not available in the country for various reasons,” said Ingrid Antonios, who is doing her residency at the Hotel-Dieu de France hospital in Beirut. (AFP)
Among those who have been heading for the exits are colleagues of Antonios at the Hotel-Dieu de France hospital. “A large number of medical staff are leaving the country, from medical doctors to nurses, but also students,” he said. “It’s not just young people at the beginning of their careers. A lot of people in their thirties, forties and fifties are finding a way out where possible.”
For many, the reasons for departure are a mix of financial and emotional. “They can’t survive on the salaries they get paid,” said Torbay. “It’s also extremely difficult for a doctor or a nurse to take on a patient and not be able to heal them or give them the medicine they need.”
To many among the millions currently scraping by on their meager incomes, the remedy for Lebanon’s health system maladies lies either at the ballot box or the streets. They hold the same political elites blamed for the country’s deepening governance crisis, responsible for the unfolding health disaster.
“My friends call me delusional, but I have some hope,” Noujaim told Arab News. “After the Oct. 17, 2019, revolution, there was a huge political awakening in the country. My hope is confined to the next election.”


























