IRBIL, Iraqi Kurdistan: Russia may be hoping it can replicate China’s success in brokering the re-establishment of diplomatic relations between Middle East heavyweights Saudi Arabia and Iran by overseeing a restoration of bilateral ties between Syria and Turkiye. But analysts caution that fundamental differences between the two normalization efforts militate against a quick breakthrough.
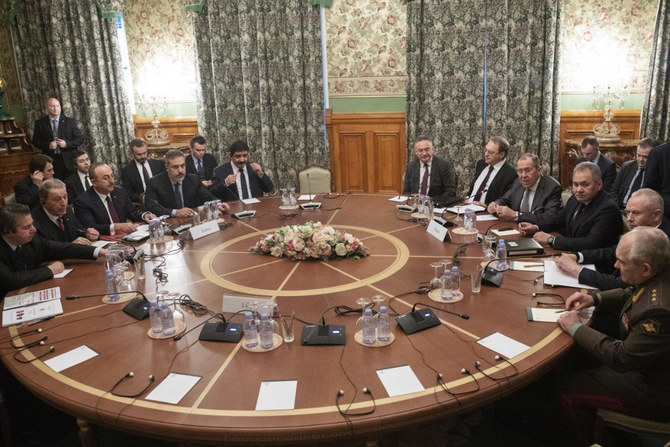
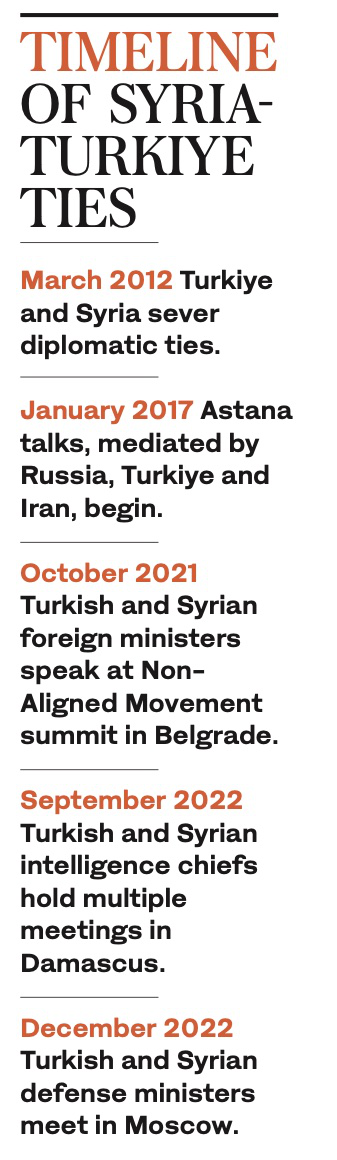
In December, Moscow hosted a meeting of Syrian and Turkish defense ministers for talks in what was seen as the beginning of a potential rapprochement between the two rivals. It was the highest-level meeting between Turkish and Syrian officials since the two countries severed ties in 2012 after the start of the Syrian civil war.
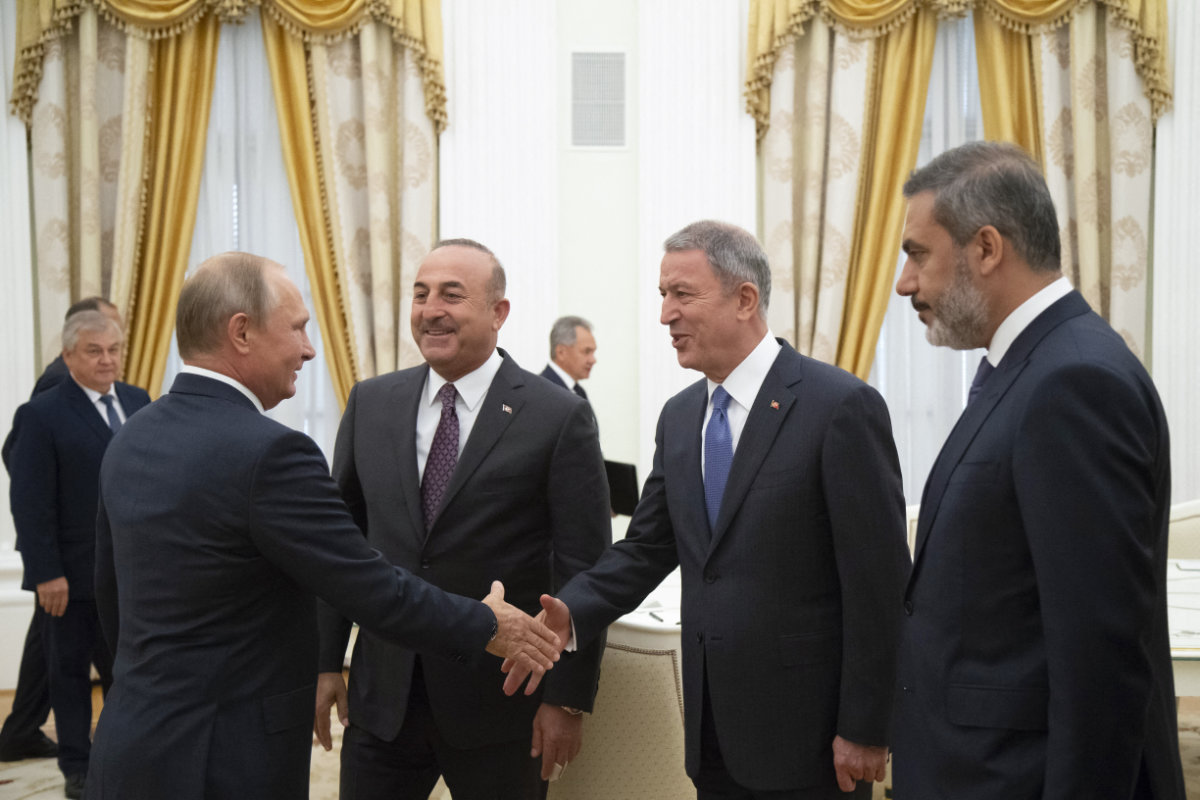

Russian President Vladimir Putin (L) welcomes Turkish FM Mevlut Cavusoglo, Turkish Defense Minister Hulusi Akar (2ndR) and Turkish Intelligence chief Hakan Fidan (R) prior to their meeting at the Kremlin in Moscow on August 24, 2018. (AFP)
Moscow will host another meeting between the deputy foreign ministers of Syria, Turkiye, Iran and Russia on April 3-4, where they will discuss the Syria situation. A senior Turkish official told Reuters that the meeting “is expected to be a continuation of the ministerial-level meetings that began during the normalization process” promoted by Russia.
“Russia has plenty of leverage with Syrian President Bashar Assad and good relations with Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan, which gives it authority and weight in the Turkiye-Syrian negotiations,” Joshua Landis, director of both the Center of Middle East Studies and the Farzaneh Family Center for Iranian and Arabian Gulf Studies at the University of Oklahoma, told Arab News.
“Syria and Turkiye also have a number of major stumbling blocks impeding an agreement — Turkiye occupies some 10 percent of Syrian soil and backs the rebel militias that opposed Assad’s rule,” he said.
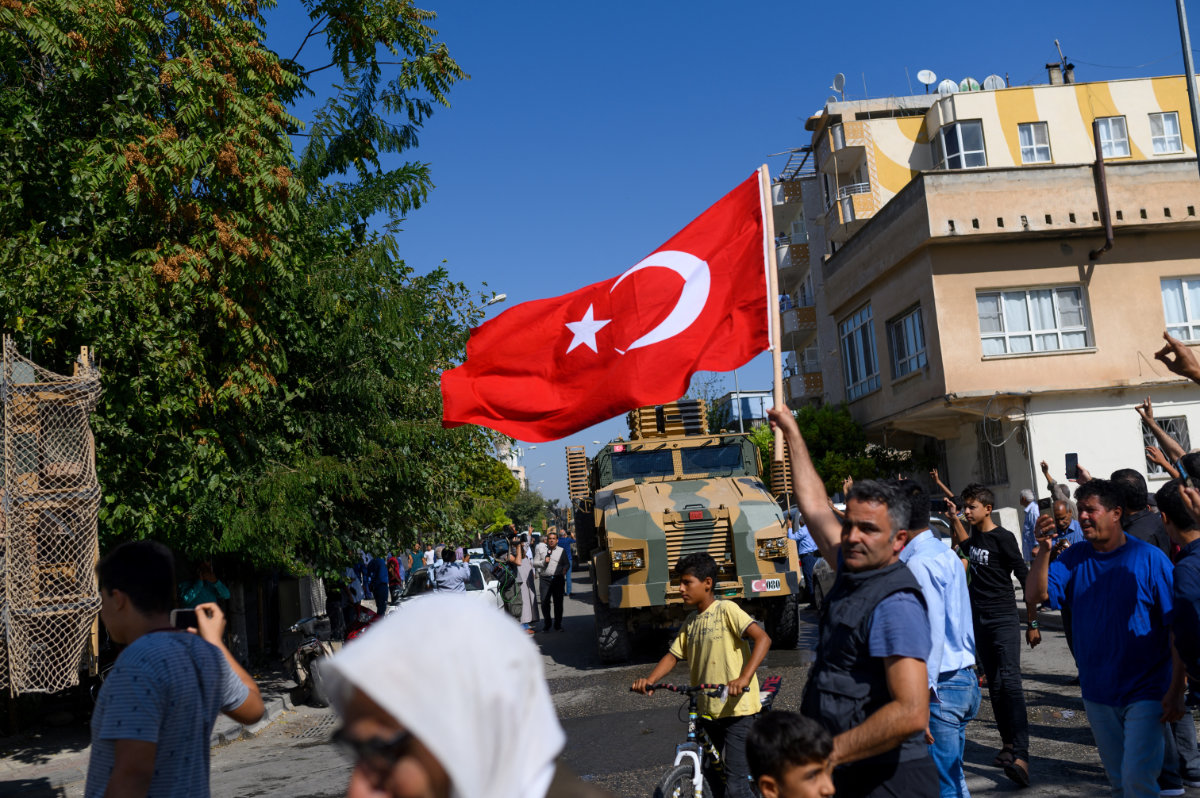

Turkish troops travel in vehicles toward Tal Abyad in Syria on October 10, 2019 as Ankara launched a broad assault on Kurdish-controlled areas in northeastern Syria. (AFP)
Though Beijing successfully served as a mediator between Riyadh and Tehran due to its cordial relations with both countries, the US has not had diplomatic relations with Iran for decades. Washington also opposes Assad and has discouraged allied nations from restoring relations with Damascus. Russia, on the other hand, maintains good ties with Turkiye and Syria.
There is one significant distinction between the nature of these relationships, however. China has much more balanced ties with Saudi Arabia and Iran than Russia does with Turkiye and Syria.
“Russia is deeply involved as a security guarantor for the Syrian government thanks to Moscow’s support for Damascus over the last decade of civil war,” Emily Hawthorne, a senior Middle East and North Africa analyst at the risk intelligence company RANE, told Arab News.
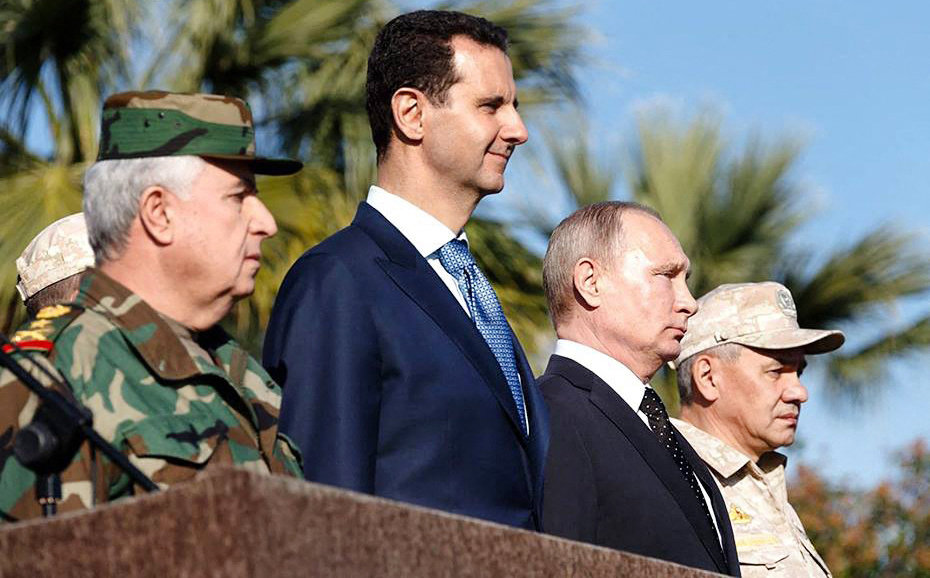

Syria’s Bashar Assad with Russia’s Vladimir Putin and Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu in Latakia, Syria. (AFP)
“This is very different from China’s more balanced relationship with both Saudi Arabia and Iran; China is not a security guarantor for either Tehran or Riyadh.
“Russia’s close relationship with the Syrian government certainly gives Russia power to mediate with Syria that few other countries have, but Russia lacks that same kind of relationship with Turkiye.”
Anton Mardasov, an independent Russian analyst and non-resident scholar of the Middle East Institute’s Syria program, doubts that Moscow can achieve what Beijing did since it is “a party to the conflict in Syria” even though it has tried to play the role of mediator.
 “The Kremlin finds itself in a difficult position: On the one hand, it would like to increase Damascus’ potential in order to absolve itself of responsibility for its survival,” Mardasov told Arab News. “In this sense, the restoration of Syrian-Turkish ties and deepening, for example, of economic cooperation, is Moscow’s goal.”
“The Kremlin finds itself in a difficult position: On the one hand, it would like to increase Damascus’ potential in order to absolve itself of responsibility for its survival,” Mardasov told Arab News. “In this sense, the restoration of Syrian-Turkish ties and deepening, for example, of economic cooperation, is Moscow’s goal.”
“Moreover, given the war in Ukraine and Turkiye’s importance as an economic partner, the Kremlin is interested in pushing Assad to get closer to Turkiye, as it is in Ankara’s interest, primarily given the refugee issue,” he said.
Strong disagreements between Ankara and Damascus over the future of northern Syria also complicate Moscow’s normalization efforts.
“The closest analogous territory between Saudi Arabia and Iran would be Yemen, but Yemen is its own sovereign country and the conflict dynamics are very different,” Hawthorne said.
“Among the challenges Russia would face trying to mediate restored Ankara-Damascus ties would be the challenging question of the future of northern Syria, and whether Damascus can promise to resolve Turkiye’s security concerns regarding Kurdish militants there.”

This aerial view shows a March 21, 2023, funeral procession for Kurdish men killed by Turkish-backed fighters in Jindayris, Aleppo. (AFP)
Mardasov said Assad is in a weak position and making unrealistic demands. He pointed out that Turkiye formally has no troops in northern Syria since allied opposition factions control those territories, although it has troops on the border and can swiftly intervene on behalf of these factions.
“The presence of Turkish troops in Idlib was formally approved not only by Russia but also by Iran within the framework of the Astana process,” he said, referring to the tripartite Russia-Iran-Turkiye Syria peace process launched in January 2017. “Therefore, to insist on their withdrawal is to insist on the breakdown of the agreements in Astana.”
On top of this, Turkiye controls Syrian territories that are home to millions of people, giving it significant leverage.
“This is actually quite a delicate situation since Russia, as Assad’s protector, is also in a dependent position on Turkiye, both in terms of projects against the background of the war in Ukraine and in terms of negotiations on the Syrian track,” Mardasov said. “Here, it is more about tactical steps so that Moscow does not worsen its position as, strategically, the situation is not too advantageous for the Kremlin.”
Landis anticipates negotiations will remain largely on hold until after Turkiye’s elections on May 14.

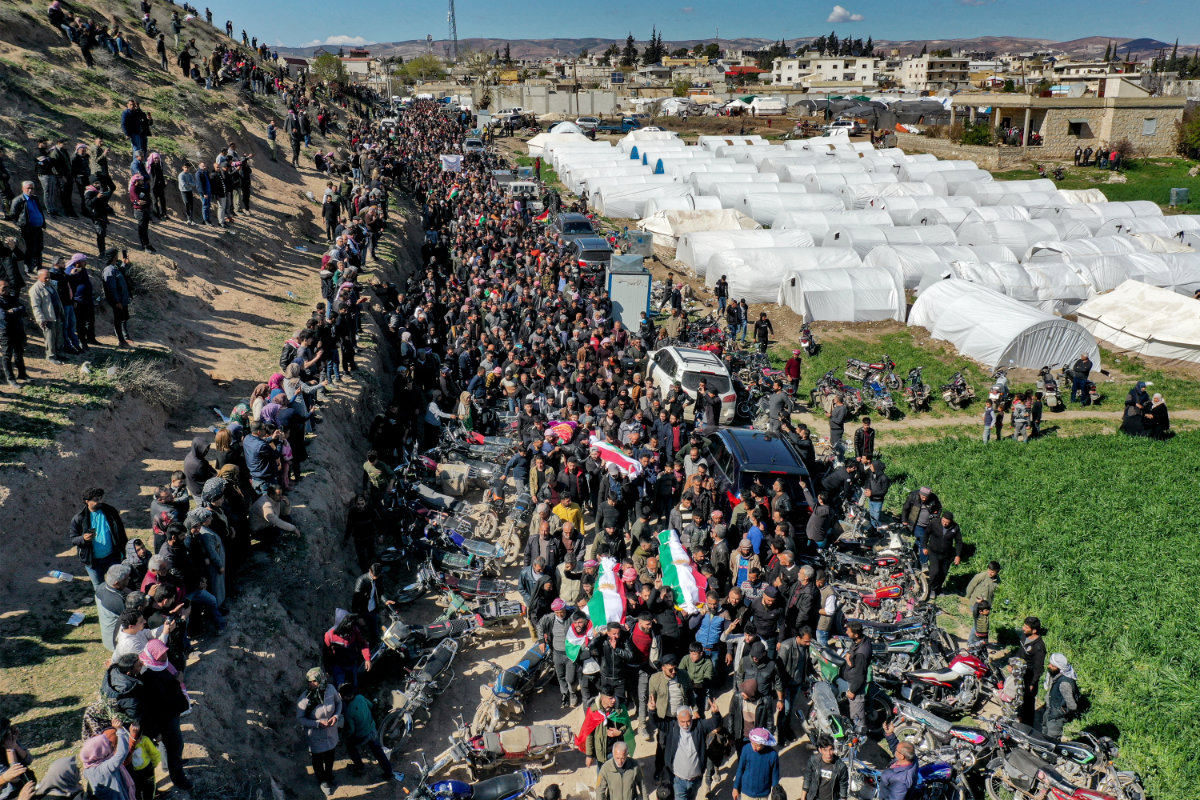
Syrian refugees passing through a Turkish border point. (AFP)
“The Turkish opposition has denounced Erdogan’s policies toward Syria and claims that it will move forward quickly with normalizing relations with Syria,” he said. “What is more, the Turkish opposition has little obligation to the Syrian rebel groups that Erdogan championed and has promised to protect.”
“If Kemal Kilicdaroglu wins in May, relations between Damascus and Ankara are likely to improve rapidly,” he added, “although the problem of dealing with the four million refugees and Islamist militiamen will not go away.”
Russia also has a self-interest in securing normalization.
“A more stable client state for Russia means a more stable foothold for Russia in the broader Middle East,” Hawthorne said.
Furthermore, the stakes are not too high for Russia if its efforts on this front stall.
“If Moscow fails in this endeavor, it is unlikely to markedly damage Russia’s standing in the Middle East, which relies more on Russia’s ability to maintain a Rolodex of vastly different bilateral relationships across the region,” Hawthorne said.
“Russian mediation could advance the conversation between Syria and Turkiye, but until Ankara and Damascus come to their own understanding on the future of northern Syria, it is unlikely Moscow will succeed.”

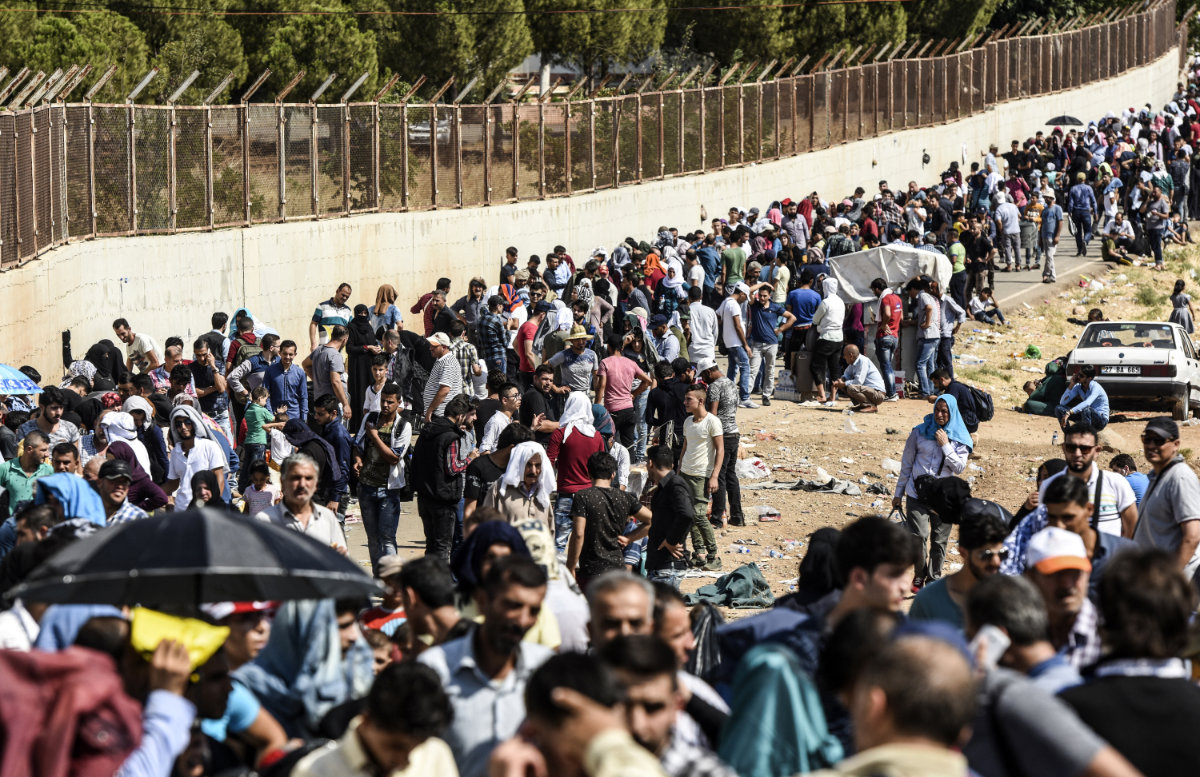
Syrian opposition supporters gather in the streets of al-Bab on the border with Turkiye on March 15, 2023, to mark the 12th anniversary of the start of the uprising against Syrian President Bashar Assad. (AFP)
Landis also pointed out that Russia has invested “a great deal” in Assad’s Syria and that Russian President Vladimir Putin’s “win” there has been a “great foreign policy success” for Russia.
However, Syria remains in “jeopardy” given the general boycott of Assad and the “devastating sanctions” imposed on Damascus.
“If Putin can undo Syria’s isolation and help revive regional diplomatic and trade agreements, he will have locked in his success,” Landis said.
Having said that, he is optimistic that Ankara and Damascus will eventually reach an agreement.
“I believe that Syria and Turkiye will normalize relations, even if the road is a bumpy one,” he said. “The two countries share a 764-km border. They have a common interest in getting American troops out of Syria, stopping the arming of the Kurds, and cracking down on ‘terrorism.’”
“Both have an interest in returning to the good relations that they shared before the war, which helped both countries to prosper and develop.”





























