DUBAI: In January, the drought which has stalked Iraq for the past three years caused water levels at Mosul dam in the north of the country to drop to their lowest levels since it was built in 1986. But, as the water receded, something unexpected emerged from beneath the surface.
To the amazement of onlookers, there stood the ruins of a 3,400-year-old city of the Mitanni Empire that had once occupied the banks of the Tigris River.
However, the settlement, located in present-day Iraqi Kurdistan, a semi-autonomous region, emerged for just two months before it sank into the waters once more. Archaeologists had to race against time to excavate as much of the site as possible while it stood exposed.
Working intensely for six weeks, the team uncovered more than 100 clay tablets etched with cuneiform script dating back to the early Assyrian period.
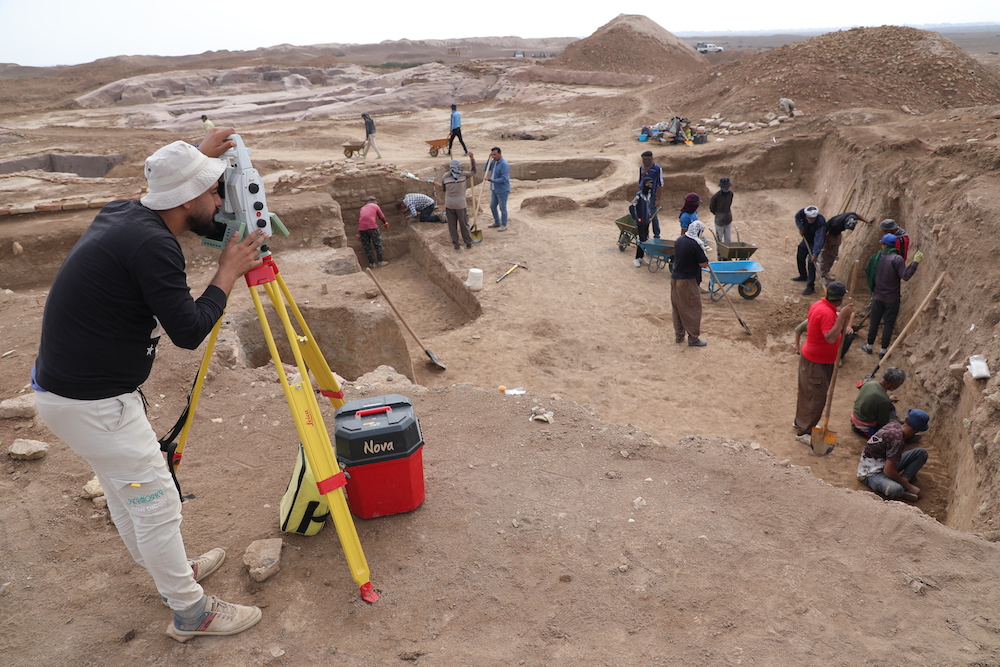

British Museum and Iraqi archaeologists carry out excavations in the ancient city of Girsu, the capital of the Kingdom of Lagash, in Dhi Qar, in Nov. 2021. (Getty Images)
A team of German and Kurdish archaeologists were able to date the site to the Bronze Age, around 1550 to 1350 BC. They believe the settlement could be the ancient city of Zakhiku, once a bustling political center.
Although undoubtedly an exciting discovery, the same extreme weather events that caused the water levels to drop are also damaging ancient sites in other parts of Iraq, frequently referred to as the “cradle of civilization.”
Scientists believe that the recent cases of extreme weather around the world, including flash floods in Europe and dust storms across the Middle East, are evidence of man-made climate change that will only become worse and more frequent unless carbon emissions are cut quickly and dramatically.
The precise impact these extreme weather events are having on the world’s heritage sites is still being studied. What is known for certain is that in some countries of the Middle East and North Africa, a fearsome mixture of desertification, drought and climate change is damaging artifacts and excavation sites and undermining conservation efforts.
In Yemen, for instance, intense rainfall is damaging the mud-brick highrises of the 16th-century walled-city of Shibam, a UNESCO World Heritage site nicknamed “Manhattan of the desert” by British explorer Freya Stark in the 1930s.
At the UNESCO World Heritage site of Bagerhat in southern Bangladesh, salt water from severe flooding caused by heavy rainfall is damaging the foundations of the city’s numerous Indo-Islamic mosques.
In Egypt, high temperatures, heavy rains and flooding are damaging the ancient stonework on monuments in Cairo, Luxor, Alexandria, and elsewhere.
Granite that was once rose-colored has faded to a pale pink or even light grey over the last 15 years, Abdelhakim Elbadry, a restoration expert who works at Karnak temple, told Reuters. “In every archaeological site here in Luxor, you can witness the changes.”
In central Iraq, meanwhile, strong winds have eroded many hilltop sites that are still difficult to reach for security-conscious archaeologists.
According to a study by UNESCO, the UN Environment Program and the Union of Concerned Scientists, climate change has become one of the most significant threats to historic sites and monuments.
The joint 2016 report, titled “World Heritage and Tourism in a Changing Climate,” examined the increasing climate vulnerability of these sites and its likely impact on global tourism. According to the UN, Iraq is the fifth most climate-vulnerable country in the world.
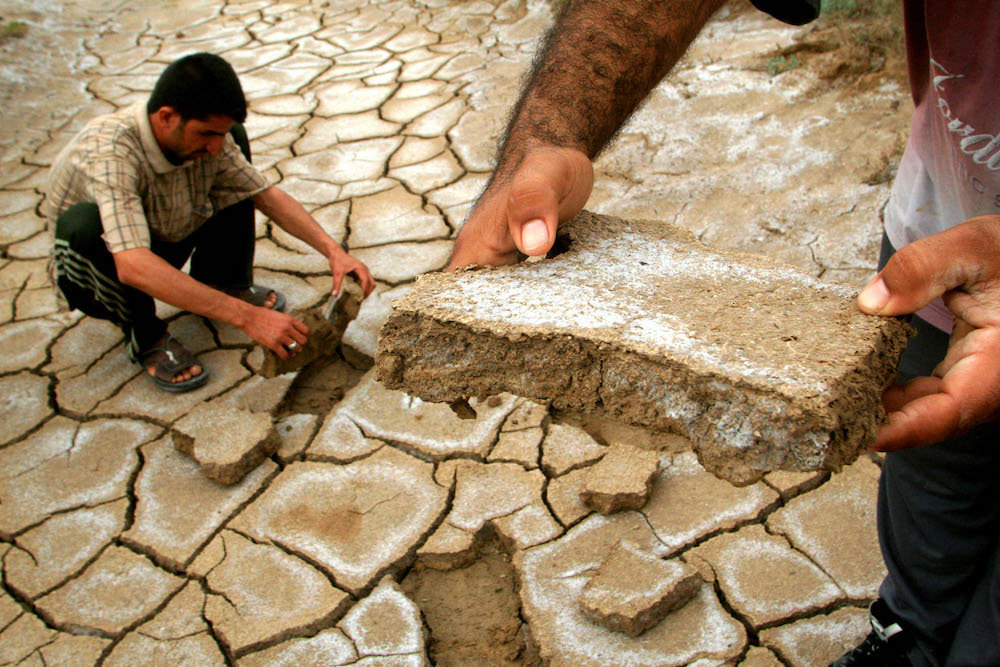

Iraqi men remove pieces of cracked earth from the marshes crossing the southern Iraqi town of Al-Azeir. The southern Iraqi wetlands have almost entirely disappeared. (AFP)
“We have three factors that affect cultural heritage in terms of climate change: Dust storms, rising temperatures and salinity — the salt in the soil,” Jaafar Jotheri, a geoarchaeologist at the University of Al-Qadisiyah in Iraq, told Arab News.
“Most of the sites are outside the cities in the desert, such as Ur. Dust storms don’t just affect people and other forms of life, but also heritage buildings. Dust gathers inside the site, affecting its structure, just as high winds create cracks and destroy surfaces.”
Additionally, extremely high temperatures during the day and cooler temperatures at night cause bricks in old structures to expand and retract, creating cracks.
Then there is the problem of increasing salinity. “People living in or outside cities, including farmers, are increasingly relying on ground water because there is no more fresh water in the rivers,” Jotheri said.
FASTFACTS
* Climate change is now a top threat to world heritage, says UNESCO.
* Marshlands of southern Iraq among the most vulnerable, the UN warns.
“The groundwater is more salty. We are taking the groundwater and using it for everyday life as well as irrigation, so we are increasingly exposing all kinds of surfaces to salt and saltwater.
“The more we use the salty groundwater, the more salty exposed surfaces will be. People use drains but then the salt also accumulates in the drain canals and reach the foundations of heritage buildings, creating cracks in the bricks and the walls.
It was not until recently that Iraq had to contend with what many regard as telltale signs of man-made climate change. “The temperature was mild, sandstorms were less harsh and less frequent, and we had fresh water, so we didn’t have to use groundwater,” Jotheri said.
Suspected climate change has also taken a toll on Iraq’s natural features. Entire lakes have disappeared, such as Sawa, known as “the pearl of the south,” located in the Muthanna governorate, which lies close to the Euphrates River.
The country’s once verdant wetlands in the south, which had been drained by Saddam Hussein and later reflooded after his fall, are disappearing once again — this time owing to changing weather patterns.
Bedouin communities who had lived in these areas for generations have been forced to leave as a result. “We are losing everything in Iraq, our natural landscape, our heritage and our traditions,” said Jotheri.
In Nov. 2021, the World Bank warned that Iraq could suffer a 20 percent drop in water resources by 2050 due to climate change.
In May, the Iraq News Agency reported that the number of dusty days had increased from 243 to 272 a year over the past two decades, and the country could experience up to 300 days of dust storms a year by 2050.
“Over the past two months I have personally witnessed over a dozen sandstorms in such a short period,” Lanah Haddad, regional director for Tarii, the Academic Research Institute in Iraq, told Arab News.
“The desertification and the increasing number of sandstorms is affecting the erosion of excavated sites or heritage buildings, which are already in ruins and have not been restored yet.”
Mark Altaweel, a reader in Near East Archaeology at University College London’s Institute of Archaeology, is convinced that climate change poses a dire threat to world heritage.
“This includes more frequent sandstorms, weathering of sites, sometimes harsh and drastic rains, and other events that can damage or lead to degraded sites,” he told Arab News.
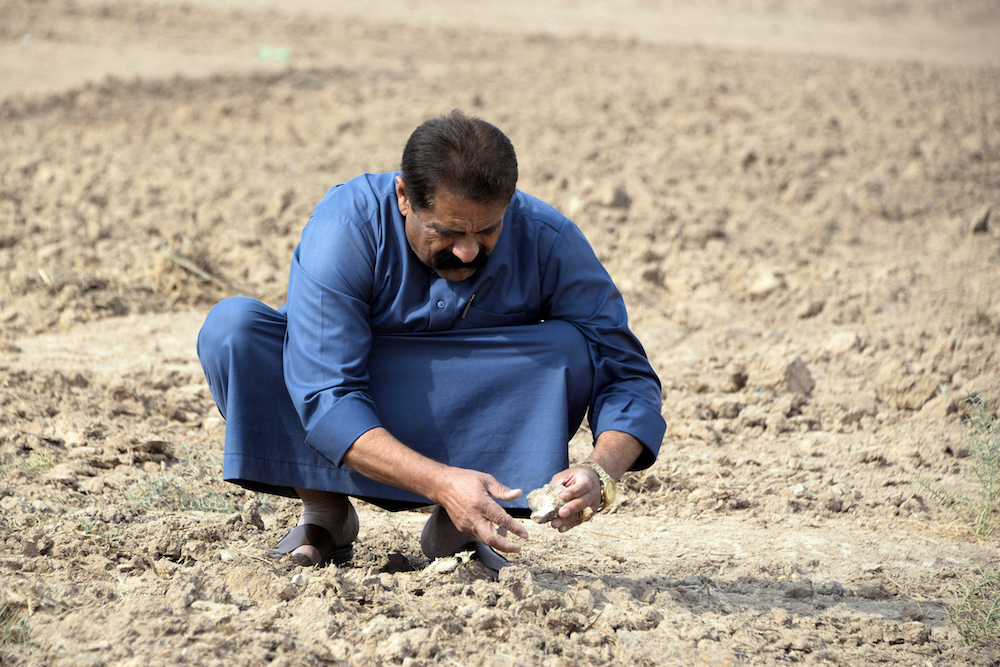

A farmer checks soil compacted by drought near Mosul, Iraq. (AFP)
For instance, Iraqi sites such as Taq Kisra, the remains of a Sasanian-era Persian monument, have weathered badly, and the structure has partially collapsed as a result.
“Mosques and old houses have collapsed in villages and different sites when you have sudden and violent rain events,” said Altaweel.
“The sandstorms disrupt our work, mostly affecting visibility and our equipment, but they can affect archaeological sites. For archaeologists, the main challenges are working in a place like Iraq with frequent sandstorms that also disrupt flights and work.”
To prevent further damage, Altaweel says the main thing that authorities can do is to tackle the immediate man-made causes, including overuse of groundwater and poorly managed surface water.
“There needs to be a re-greening effort, but it has to be done carefully to ensure plants survive, and plants can prevent sand from becoming airborne,” Altaweel said.
The international community also has a responsibility to protect heritage sites. Adam Markham, deputy director of the climate and energy program at the Union of Concerned Scientists, told TIME magazine in 2019 “that if the world wants to save these sites, countries will also need to share financial resources.”
Additionally, architects and archaeologists have discovered that adhering to traditional craftsmanship and knowledge is the best way to repair, restore and maintain the heritage of such sites. However, precious few individuals have such skills today.
In Cairo, at the Jameel School of Traditional Arts, the only school in Egypt dedicated to the study of traditional Islamic craftsmanship, students passionate about preserving centuries-old techniques are seen as essential for the restoration of Egypt’s multitude of ancient sites.

In Iraq, as in many other Arab countries, historic sites and monuments are potentially at risk from climate change. (AFP)
They are locked in a race against time as the suspected effects of climate change accelerate the destruction.
There are also prescient lessons for present-day societies as extreme climate events batter modern infrastructure, stretch resources and destroy livelihoods, creating the conditions for displacement and even conflict.
“If we look at locations of ancient sites situated in deserted areas, it shows clearly that climate change was an important factor for forced migrations, resulting in the abandonment of a settlement,” said Haddad.
“Societies always face challenges in providing water for agriculture and to their growing communities in urban spaces. We need to learn these lessons from the past to avoid conflict over water in the near future.”
Jotheri worries that the palpable effects of climate change, if not addressed urgently, could lead to further violence, particularly in societies such as Iraq.
“It will lead to tribal conflict, between the southern Iraqi tribes themselves and between other provinces in the country,” he said.
“We have a fragile state when what we need is a stable one to face the threat of climate change. If water, for example, is cut or reduced in the Tigris or Euphrates over the next few years, people will begin to fight over water.”


























